Density
advertisement

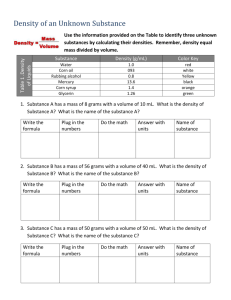
Density Study Guide Test Date: Tuesday, November 25th, 2014 BONUS! Make FLASH CARDS for this concept. Due Monday for 3 points. 1. What is the term for these descriptions? amount of matter in a given amount of space? mass per unit of volume? mass of 1 mL of a substance? mass of 1 cm3 of a substance? DENSITY 2. Explain, in your own words, and using any of the descriptions above, what density means. Use one or more examples to further explain your thoughts. Density is the amount of mass in a unit of volume of a substance. For example, if the mass of one cubic centimeter of a substance is less than the mass of another substance of the same volume, the more massive substance has more density. Density of a substance is a property that does not change unless the actual molecules change in some way. If either mass or volume change and the other stays the same, that means the molecules changed in some way, and that is how density can change. Cutting something in half does not decrease or increase density. 3. What are the two measurements needed to calculate density? Mass and volume 4. Which measurement should you always make first when finding the density of a solid object? Why? You should always measure mass first because if your method for measuring volume requires the object to become wet, it is possible for the mass of the water to be unnecessarily accounted for. This would cause an error to occur in the density calculation. More mass causes density to be larger. 5. Explain how to find the volume of these types of solid objects: a. A rectangular solid- When finding the volume of a solid object, you must measure its three dimensions (length, width, and height) to one estimated digit past a millimeter. Then, multiply the measurements together. Volume = Length x Width x Height. b. A cylindrical solid- When finding the volume of a cylinder, you must measure its height and radius. Radius can be found by measuring the longest side-side length of the top of the cylinder (diameter) and dividing by half. Then, multiply the height, the square of the radius (r2) and 𝝅(𝟑. 𝟏𝟒). V = h x r2 x 𝝅. c. A small object that can fit into a graduated cylinder - Small, solid objects’ volume can be measured using direct displacement. You must put water into a graduated cylinder about half way and record the initial water level to one estimated digit past a milliliter. When the object is placed carefully into the graduated cylinder, the water rises. The amount of water rise is called “displacement”. Displacement can be found by subtracting the initial water level from the final water level. (displacement = final – initial). Each mL of displaced water is equal to 1 cm2 of volume. d. A large object, not small enough for a graduated cylinder- The process for finding the volume of a large object comes from the idea of direct displacement, but instead, the displaced water flows out of the container. The amount water that escapes from the container that the object is placed into represents the volume of the object. In this class, we used an overflow cup with a spout and filled it with water just to the point where nothing drips out of the spout. Then, we placed a beaker under the spout and submerged the entire object into the water. The water that overflowed into the beaker was measured. Each mL of water represents 1 cm3 of volume of the object. 6. What is the label/unit for density of a solid substance? g/cm3 (This is derived from the units that measure mass and volume. Since density is calculated by dividing mass/volume, the unit is the label for mass/the label for volume) 7. Explain how to find the volume of a liquid substance: The volume of a liquid substance is found using a graduated cylinder. Volume is measured in mL. 8. What is the label/unit for density of a liquid substance? Density of a liquid substance is labeled using g/mL, since volume is measured in milliliters. Since density is calculated by dividing mass/volume, the unit is the label for mass/the label for volume) 9. Which of the following are necessary for density to change? (select any/all that are true) Cutting an object into smaller pieces WILL NOT CHANGE THE DENSITY BECAUSE IT DOES NOT AFFECT THE ARRANGEMENT, SIZE, MASS, OR TYPE OF MOLECULE THAT MAKE UP THE SUBSTANCE. Changing the number of molecules in a substance Changing the type of molecules that make up the substance FILL IN THE BLANK Word Bank: mass, density, wood, layers, holes, mix, smaller, fresh, volume(2), more, less 10. In order to determine the density of liquids relative to other liquids, you can see if they form layers. However, if the densities are very close, it is possible for the liquids to mix. 11. Salt water is more dense than fresh water because there is more mass per unit of volume in salt water. 12. Whenever density is being calculated, you must divide mass by volume 13. Many types of wood float on water because there are less molecules in a given amount of space. Even if a solid object that floats is cut into smaller pieces, its density is not affected. Putting holes into an object that floats will not have an effect on its density either. 14. What are three reasons for why some substances are more dense than others? 1. The atoms that make up the more dense substances have more mass 2. Atoms that make up a more dense substance are smaller.(and more can fit in a specific volume) 3. Atoms might be arranged differently so more can fit into the same volume. Be prepared to explain these rules about density, using complete sentences Attach separate sheets if necessary. Floating and Sinking Explain, using complete sentences, why some substances float in water and why some sink. Here you should include: Substances less dense than water float BECAUSE they have less mass per unit of volume when compared to water. Substances more dense than water sink BECAUSE they have more mass per unit of volume when compared to water. Some substances float, but become fully submerged (sinking just below the surface of the water). This is because the density of the substance is equal to that of water. The density of water is 1g/cm3. Density and Temperature WE EAT CHOCOLATE CAKE WARM-EXPAND; COOL-CONTRACT Explain, using complete sentences, what happens to density when a substance is cooled and when it is warmed. Use an example that further validates your claim. Be sure to explain what happens to volume and mass and how that affects density. Temperature affects density because it directly affects the volume of objects, without changing the mass. When temperature is increased, the volume increases because molecules expand, which causes density to decrease. When temperature is decreased, the volume decreases because molecules contract, which causes density to increase. This rule about density was proven by observing that cold water sank below room-temperature water, and hot water rose to the top. Liquid forms layers with the least dense at the top and most dense at the bottom. Students— You can remember the relationship between temperature, volume and density by using math! Start with the density of room temperature water. The density is 1 g/cm3. -Knowing that COOL-CONTRACTS, decrease the volume. Calculate Density with the smaller volume. -Then, knowing that WARM-EXPANDS, increase the volume in the equation. Calculate density with a larger volume.