File
advertisement

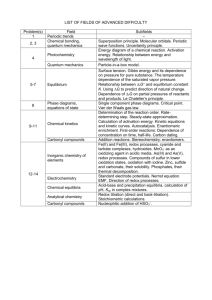
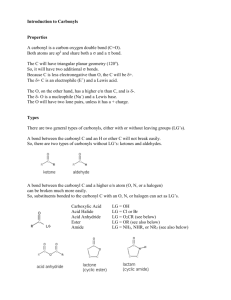
Organic Chemistry Richards Introduction Retrosynthetic Analysis Control Absolute / Relative Weinreb Amide Latent Polarity Oxidation Level Functional Group Interconversion (alkyle methyl ketone (HgO / H2SO4) Synthesis of Rings Reduction Carbonyl to alcohol (NaBH4 LiAlH4) Carboxylic acid to alcohol (BH3) Amide to amine (BH3) Reductive amination (Na(CN)BH3) Partial Reduction of ester to aldehyde (DIBAL or LiAlH4 then partial oxidation using PCC or TPAP/NMO) Nitrile to aldehyde (DIBAL) Oxidation Alcohol to Aldehyde (PCC or TPAP/NMO) Alcohol to Carbonyl (Dess-Martin Periodinane DM) Alcohol to ketone (Na2Cr2O7) Alcohol to carboxylic acid (KMnO4) Dihydroxylation (OsO4 / NMO) Epoxidation (m-CPBA) Ozonolysis (O3 then Me2S (aldehyde), H2O2 (carboxylic acid), NaBH4 (alcohol)) Protecting Groups Introduction Aldehydes / Ketones (Acetal – (HO(CH2)2OH) on , acid off) Diol (Acetal – aldehyde on, acid off) Carbonyl (dithane HS(CH2)3SH on, BuLi / Hg2+ off) Diels Alder reaction 1,6-dicarbonyls from cyclohexenes (ozonolysis) Hetero-Diels Alder and 5 membered rings Stereo specificity and Stereo selectivity Endo / Exo Baldwin Rules Carbonyl Chemistry Alkene Oxidations Alcohol (trialkylsilylchloride / imidazole on, TBAF off) Phenol (NaH / MeI on, HBr off) Nitrogen (amide – harsh conditions) Nitrogen (BOC on, TFA off) Deprotection by hydrogenation (cleavage of R-OH or R-NH bond with hydrogen – only practical for benzyl group) (H2 / Pd / C) Deprotection by hydrogenation of carboxybenzyl group CBz Basic Addition to carbonyl group containing adjacent stereo genic centre (felkin anh model) Curtin Hammett principle Chelation control Stereoselective aldol reactions Ways to control enolate geometry o Cyclic enolate precursor o Boron enolates Alkenes Reduction of alkyne gives CIS alkenes Wittig reaction Destabilised ylids CIS Stabilised ylids TRANS Horner-Wadsworth Emmons Metathesis Asymmetric Synthesis Types of chirality Catin-Ingolg-Prelog rules Simple calculations o Number of stereoisomers = 2n o Enantiomeric excess o Specific rotation o Optical purity Chiral Pool Resolution Resolving agents Auxiliaries Chiral auxiliaries Dave Evans Auxiliaries o Diels Alder o Aldol Asymmetric Catalysis Chiral catalysts vs auxillaries Addition of XY to prochiral ketone Oxazaborolidene Asymmetric oxidation (OsO4) Page Organosulfur Bew Click Chemistry Advantages Resonance of N3 Copper Ruthenium Mechanism Tetrapeptide analogs Multicomponent Reactions Advantages Strecker Synthesis Free radical mediated Organoboron Resonance of isocyanide Passerini Ugi Stevenson Heck Stille (tin) Suzuki (boron) Sonogashira (copper) Negishi-Kumada (grinyard) Buchwald-Hartig Formation of Pd(0) Introduction Sulfide formation o Harpps’ reagent Sulfide reactions o Stevens & sommelet rearrangements Sulfoxide formation o Allylic sulfoxide – sulfenic ester rearrangement Sulfoxide reactions o Pummerer rearrangement o Intramolecular pummerer o Syn-elimination of sulfenic acid Use as reagents o Kornblum oxidation o Swern oxidation Sulfone reactions o Julia reaction Heteroaryl sulfones Alkyl halides o Ramberg-Backlund reaction o Cheloptropic elimination of SO2 Sulfur Ylids o Simple o Oxosulfonium o Epoxides from carbonyl groups o Reactions with enones o Trost reagents Thioketones o Corey-Winter Organosilicon o o o o Introduction Chemistry Sila-pummerer Peterson Vinyl silanes Electrophilic substitution o o o Allyl silanes Reactions with electrophiles Silyl enol ethers Ireland-Claisen Ozonolysis Epoxidation Oxidation to enone Hydroboration Alkylation Conjugate addition Mukaiymama Orthoesters OrganoSelenium Introducton of Se Selenoxide elimination Selinium ion cyclization Selenium dioxide# Organophosphorus Mitsunobu Corey-Fuchs Seyferth Gilbert Bestmann modification