Series & Parallel Circuits Lab: Combination Circuits Analysis
advertisement

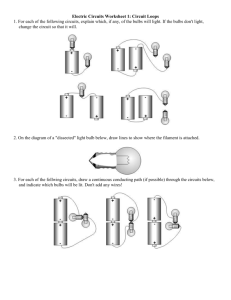
Elaborate Series and Parallel Circuits Begin discussion by introducing the concept that in the real world few circuits are pure series or pure parallel. Most circuits are a combination of real and series circuits. Have students discuss how combination circuits can be analyzed. They need to understand that circuits can be broken into parts and analyzed part by part and then recombined to understand the complete circuit. The discussion is complete with a video that explains how to break the circuit apart for analysis www.youtube.com/watch?v=0MKcxCHkT1c Provide students with some combination circuits ranging from simple to difficult and allow them to work and calculate the voltage and current at each device as well as total current and resistance for the entire circuit. Examples: http://www.myteacherpages.com/webpages/MrMauser/files/circuits%20worksheet_1_.pdf Combined Series and Parallel Lab Instructions: Construct each of the circuits below using the PhET Circuit Simulation. Each light bulb/resistor is 10 Ω by default. The battery has a potential difference of 9 V by default. Complete the RVIP charts mathematically and check your answers with the “Non-Contact Ammeter” and “Voltmeter.” Then answer the questions following each diagram. A. Series Circuit in a Parallel Circuit R V I R1 P S1 1 2 3 R2 R3 S2 S3 23 battery 1. On a separate sheet of paper, draw a schematic version of this circuit ( then draw simplified versions to solve. 2. 3. 4. 5. and ) and Explain which part of the circuit is in series. Explain which part of the circuit is in parallel. Compare the current in the top branch to the current in the middle branch. Explain why. Rank the light bulbs in order of brightness. In terms of current flow and resistance, explain why. If bulb R2 were removed (right-click to remove), explain what happens to the other two bulbs and why. 6. Determine which bulbs are affected by each of the switches (S1, S2, S3). Explain why. B. Parallel Circuit in a Series Circuit R V I R1 P 1 R2 2 3 12 R3 battery 7. On a separate sheet of paper, draw a schematic version of this circuit ( then draw simplified versions to solve. and ) and 8. Explain which part of the circuit is in series. Explain which part of the circuit is in parallel. 9. Rank the light bulbs in order of brightness. In terms of current flow and resistance, explain why. 10. Compare the potential difference across R3 to the potential difference across the other two bulbs. Explain why. 11. If R3 were removed (right-click to remove), explain what happens to the other two bulbs and why. 12. If R2 were removed, what kind of circuit does this become? 13. After R2 is removed, determine what happens to the brightness of each bulb and explain why. (Hint: Complete the chart if you get stuck. R 1 3 battery V I P C. Series Circuit in a Parallel Circuit in a Series Circuit (Bonus) R V I R1 P 1 2 R2 3 4 R3 R4 23 123 battery 14. On a separate sheet of paper, draw a schematic version of this circuit ( then draw simplified versions to solve. and ) and 15. Explain which parts of the circuit are in series. Explain which part of the circuit is in parallel. 16. Rank the light bulbs in order of brightness. In terms of current flow and resistance, explain why.