Urinary system student notes
advertisement
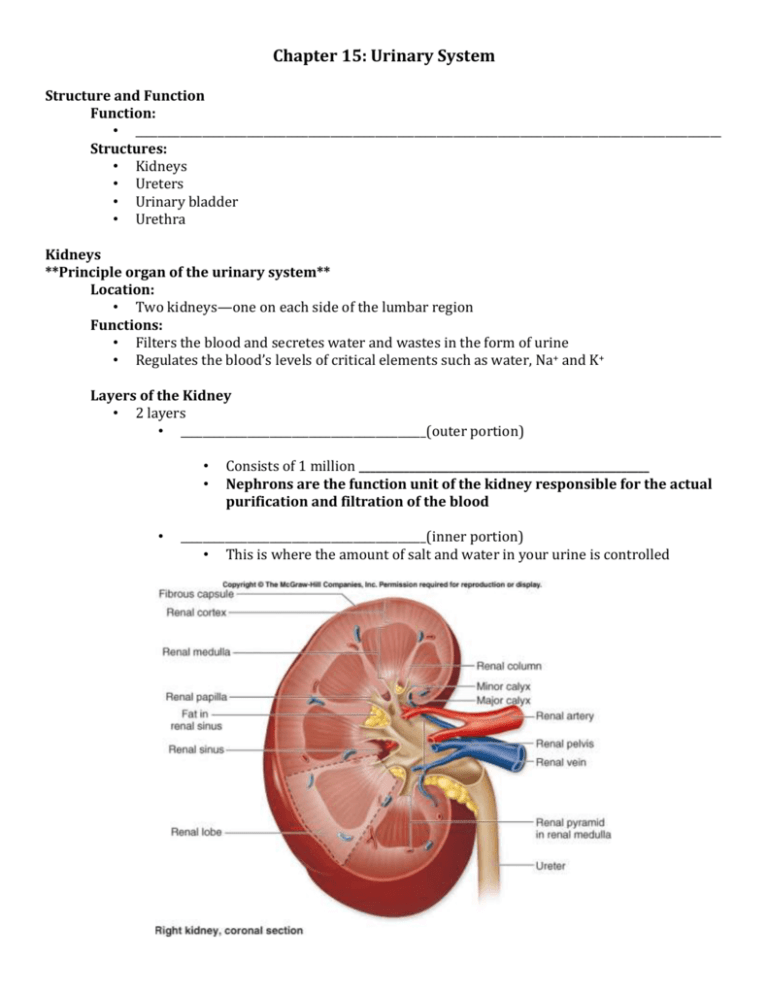
Chapter 15: Urinary System Structure and Function Function: • _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Structures: • Kidneys • Ureters • Urinary bladder • Urethra Kidneys **Principle organ of the urinary system** Location: • Two kidneys—one on each side of the lumbar region Functions: • Filters the blood and secretes water and wastes in the form of urine • Regulates the blood’s levels of critical elements such as water, Na+ and K+ Layers of the Kidney • 2 layers • ____________________________________________(outer portion) • • • Consists of 1 million ____________________________________________________ Nephrons are the function unit of the kidney responsible for the actual purification and filtration of the blood ____________________________________________(inner portion) • This is where the amount of salt and water in your urine is controlled Nephrons: • Functional unit of kidney • Consists of: _______________________________________________________—ball shaped cluster of capillaries ___________________________________________________________________– encloses the nephron ____________________________________________________________– tube like portion of nephron Urinary Bladder Location: • Sac above the urethra Function: • Hold urine until it is expelled through the urethra Urethra Location: • Single canal located under the urinary bladder Function: • Carries urine from the bladder to outside of the body ___________________________________________________________________ *Opening in the urethra to the outside of the body Diagnoses associate with the urinary system ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ • Involuntary discharge of urine at the time of cough, sneeze, or strained exercise ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ • Inherited condition of multiple cysts that gradually form in the kidney, causing destruction of normal tissue that leads to renal failure. • Diagnosed in adults presenting with hypertension, kidney enlargement, and recurrent urinary tract infections ______________________________________________________________________________________________ • Occurs when bacteria enter urinary tract, especially the urethra and bladder • Symptoms include dysuria and increase urinary frequency _______________________________________________________ • Classified depending on where they stone is found • Nephrolithiasis _________________________________ • Ureterolithiasis _________________________________ • Cystolithiasis ____________________________________ Caused by a build up of calcium and other chemical compound Procedures associated with the urinary system ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ • Breaks a kidney stone into small pieces that can more easily travel through the urinary tract and pass through the body Radiography _________________________________________________________________________________________ • X-rays of urinary tract after contrast is injected into blood stream and passes through the kidney. Contrast reveals blockages and possible trauma ____________________________________________________________________________________________ • X-ray of the kidney, ureter and bladder ____________________________________________________________________________________________ • X-ray of upper urinary tract to detect the presence of stones or obstructions _____________________________________________________________________________________________ • X-ray of bladder and urethra taken during urination Lab tests associated with the urinary system ___________________________________________________________ • Physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine Tests for: ____________________________________________________________ • A protein typically found in blood • Indicates something could be wrong with glomerulus ____________________________________________________________ • Measures concentration of urine pH • Measures acidity of urine Glucose • Measures amount of sugar in uring • Can indicate a variety of clinical conditions











