Answers
advertisement

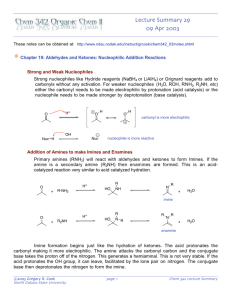
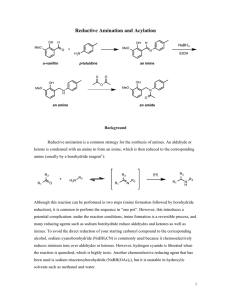
Imine Formation Major concepts The imine is a functional group in which Carbon and Nitrogen are double bonded Aldehydes and ketones react with primary amines under acid catalyzed conditions to form imines The Aldol condensation and imine formation are mechanistically similar, so they can be recognized to give structurally similar results. Vocabulary Imine Condensation Students should be able to: Identify the nucleophile and electrophile in imine formation. Predict the product of imine formation Use retrosynthesis to determine the structures of the carbonyl and amine that formed the imine Daily Problems 1. Which of these molecules can serve as an electrophile in imine formation? Explain. O O O HO O O O O Cl H H2N The electrophile for imine formation must be an aldehyde or ketone. 2. Which of these molecules can serve as the nucleophile in imine formation? Must have a primary amine or NH3 3. Draw the imine products that form when acetaldehyde is condensed with each of these amines with catalytic acid. 4. Draw the imine products that form when methylamine is condensed with each of these aldehydes/ketones and catalytic acid. 5. Give the structure of the amine and the carbonyl compound necessary to make these imines under acidic conditions. NH3 Cumulative Problems: 6. Predict the products of these imine formations and aldol condensations. How are they similar to each other. (Hint: Use the example strategy of identifying the nucleophile and electrophile and drawing the condensed product.) Extension problem: 7. Draw a product for the condensation of two alcohols and a carbonyl. Remove water, just as before, but notice that oxygen can’t make three bonds in a stable manner.