Cell Model You are to produce a model of a Plant Cell OR an Animal
advertisement

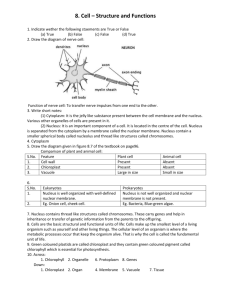
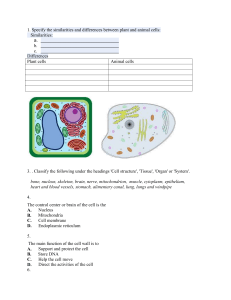
Cell Model You are to produce a model of a Plant Cell OR an Animal Cell. Your model can be 2D or 3D and can be created in any way you choose. An example may be to use a plastic bottle as your cell, with a table tennis ball as the nucleus and shredded paper as the cytoplasm etc… You are limited only by your imagination. Task 1: ____Model includes all assigned parts ____Presentation of Cell Includes: Colorful Size of parts according to scale Labels for each cell part - All parts must be typed and clearly labeled. Creativity Task 2: Your task is to describe the function of each of the following parts, the type of cell it’s found in and an additional fact of each cell part. The definitions must be typed and in sentence form. Some of the information is in your text book but you will need to do some research for this task. Cell organelles Cell membrane Cytoplasm Vacuole Mitochondria Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Chromosomes Golgi bodies If a plant cell you will also need to include Cell Wall Chloroplast Cell Model Task 2 – Definitions Cell Wall: The plant cell wall provides the most significant difference between plants cells and other cells. It is up to many micrometers in thickness and, due to its rigid shape, it also gives plant cells a defined shape. The cell wall is the reason for the difference between plant and animal cell functions. Because of its rigid structure, plant cells do not have the opportunity to develop nervous systems, immune systems and mobility. This cell does not have an outer membrane but is stronger than any other. Cell walls are found on all cells. Chloroplast: The chloroplast is the part of the cell responsible for photosynthesis. It has a permeable outer membrane, a less permeable inner membrane, an inter-membrane space, and an inner section called the stoma. This type of cell is found in a plant cell. Cytoplasm: Cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that fills the cell. It is eighty percent water and is usually clear in color. It is more of a thick substance than a watery one and is found inside the cell membrane. Cytoplasm is found in all cells. Mitochondria: The mitochondria are the power centers of the cell, and come in a variety of shapes, being about the size of bacteria. They are membrane-bound organelles, and like the nucleus, have a double membrane. Vacuole: The vacuole is responsible for maintaining the shape and structure of the cell. Plants do not grow by increasing the size of the cytoplasm; they increase the size of their vacuoles. It is a large vesicle which is also used to store nutrients, metabolites and waste products. It is only found in plant cells. Chromosomes: Chromosomes are only found in animal cells, and are found in the nucleus (see definition for nucleus below) of each cell, where the DNA molecule is packaged into thread-like structures... chromosomes! Each chromosome is made up of DNA tightly wrapped many times around proteins called histones, which support its structure. Chromosomes are not visible in the cell’s nucleus when the cell is not dividing, not even under a microscope, but the DNA that makes up chromosomes becomes more tightly packed during cell division and is then visible through a microscope. Nucleus: The nucleus is a bit like the brain of a cell, helping control eating, movement and reproduction. It is not always in the center of the cell, it will be a big dark spot somewhere in the middle of all of the cytoplasm. However, it probably will not be found near the edge of the cell, because that might be a dangerous place for it to be. It can be found in most plant and animal cells. Cell Membrane: All cells have membranes, the difference between them being that plant cells have rigid cell walls while animal cell membranes are flexible. It can automatically fix itself when torn, making it a very handy membrane to use. The truly special part of the cell membrane is the presence of different proteins on the surface that are used for many things, such as cell receptors, enzymes, surface antigens, and transporters.