goal sheet - nucleus and DNA
advertisement

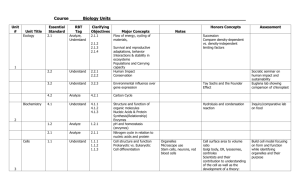
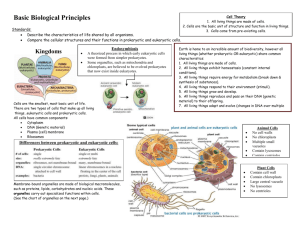
Nucleus, prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic, DNA and replication Name: Know Understand Do Nucleus Eukaryotic Prokaryotic The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells. The nucleus is not found in prokaryotic cells. Summarize the structure and function of the nucleus. Identify the nucleus in plant and animal cells. Plasma membrane Plasma membrane is found in all cells. ribosomes Ribosomes are found in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. DNA RNA Nuclear membrane, complex DNA and RNA are found in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. DNA is not enclosed in a nuclear membrane. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Infer that prokaryotic cells are less simple, less complex cells than more advanced, eukaryotic cells. Explain that with few exceptions, all cells of an organism have the same DNA. Linear chromosomes There are no membrane-bound organelles in prokaryotic cells. There are circular DNA strands in prokaryotic cells. There are linear chromosomes in eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells. Double-stranded complementary Double-helix Alternating Phosphate-sugar groups Rungs Nitrogenous base pairs Adenine, Thymine Guanine, cytosine Weak hydrogen bonds Compare genetic material in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Explain the double-stranded, complementary nature of DNA as related to its function in the cell. Identify the nucleotide subunits in DNA. DNA is a double helix or “twisted ladder” structure. The sides of DNA are composed of alternating phosphate-sugar groups. The “rungs” of the DNA ladder are composed of complementary nitrogenous base pairs. (adenine,A bonds to thymine,T and guanine, G bonds to cytosine, C) Nitrogenous base pairs are joined by weak hydrogen bonds. DNA replication Daughter cells Parental DNA Mutations spontaneous radiation DNA replication allows daughter cells to have an exact copy of parental DNA. Deletions Additions substitutions Mutations can be deletions, additions, or substitutions. Mutations are changes in DNA coding. Mutations can be random and spontaneous. Relate the structure of DNA to the function of replication. Explain how mutations in DNA result from interactions with the environment (radiation and chemicals). I can 1. Are ribosomes found in plant cells, animal cells or both? 2. What is the circular form of DNA called? 3. What type of cells contains plasmids? 4. Which cell is smaller, eukaryotic or prokaryotic? 5. What is the subunit of DNA? 6. What are the sides of DNA composed of? 7. What are the “rungs” of the DNA ladder composed of? 8. What does A bond to? 9. What does G bond to? 10. What are nitrogenous base pairs joined by? 11. What allows daughter cells to have an exact copy of parental DNA? 12. What are changes in DNA coding called? 13. What are the three types of mutations?