Chapter 5 Review Answers
advertisement

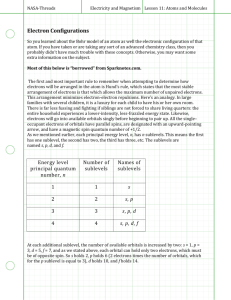
Honors Chemistry - Chapter 5 Review Name: __________ KEY _________________ Section 5.1: Models of the Atom 1. How many sublevels are in the following principal energy levels? Which sublevels? a. n = 1 One - s e. n = 5 Four – s, p, d, f b. n = 2 Two – s, p f. n = 6 Three – s, p, d c. n = 3 Three – s, p, d g. n = 7 Two – s, p d. n = 4 Four – s, p, d, f 2. How many orbitals are in the following sublevels? a. 1s sublevel One d. 4f sublevel Seven b. 2p sublevel Three e. 5s sublevel One c. 3d sublevel Five f. 6p sublevel Three 3. How many electrons can each of the following sublevels hold (maximum)? a. s Two c. d Ten b. p Six d. f Fourteen 4. What is the shape of an s sublevel orbital? Sphere 5. What is the shape of a p sublevel orbital? Dumbbell 6. What was the problem with Rutherford’s planetary model of the atom? It could not explain chemical properties 7. Bohr proposed that electrons were found in specific circular paths called orbits 8. What happens to the distance between energy levels as you increase in energy? It decreases. 9. What does “electron cloud” mean? A region of space with the highest probability, or likelihood, of finding an electron. Not an exact path. 10. How do electrons move from energy level to energy level? Gain or lose energy Section 5.2: Electron Arrangement in Atoms 1. Electrons arrange themselves around the nucleus in order to make the most stable arrangement. 2. What are the three rules for writing electron configurations? Give the definition of each. a. Aufbau’s Principle – electrons occupy the lowest energy levels first b. Pauli Exclusion Principle – electrons in the same orbital have opposite spin c. Hund’s Rule – electrons enter orbitals individually before pairing up Honors Chemistry - Chapter 5 Review Name: __________ KEY _________________ 3. Write the complete electron configuration for each of the following elements: a. Hydrogen 1s1 b. Vanadium 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d3 c. Magnesium 1s22s22p63s2 d. Cesium 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d105p66s1 e. Arsenic 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p3 4. Write the abbreviated electron configuration for each of the following elements: a. Cesium [Xe] 6s1 b. Lithium [He] 2s1 c. Aluminum [Ne] 3s23p1 d. Silver [Kr] 5s24d9 e. Gallium [Ar] 4s23d104p1 5. Identify the elements below based on their electron configurations: a. 1s22s22p63s23p5 Chlorine b. 1s22s22p5 Fluorine c. 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d105p5 Iodine 6. Which elements are exceptions to the Aufbau Principle (Name 2): Copper (Cu) and Chromium (Cr) 7. Explain why the actual electron configurations for some elements differ from those assigned using the Aufbau principle. They try to achieve stability through a half filled sublevel 8. True or False: The configuration 4s23d4 is more stable than the configuration 4s13d5. False. Full sublevels are the most stable, but half-filled sublevels are the next best. In 4s23d4, the s sublevel is full, but the p sublevel is neither full, nor half full. In 4s13d5, both s and p sublevels are half full. This goes against Aufbau’s principle. Honors Chemistry - Chapter 5 Review Name: __________ KEY _________________ Section 5.3: Physics and the Quantum Mechanical Model 1. What is the frequency of radiation with a wavelength of 5.00 x 1015 m? Use the equation: C = λν to find that ν = 5.996 x 10-8 Hz 2. What is the energy of a photon with a frequency of 2.22 x 1014? Use the equation: E = hν to find that E = 1.471 x 10-19 J 3. Suppose your favorite radio station broadcasts at a frequency of 1600 Hz. What is the wavelength of the radiation? Use the equation: C = λν to find that λ = 1.874 x 105 m 4. Arrange the following types of electromagnetic radiation in order of increasing frequency based on the chart below: a. Infrared d. Radio waves b. Gamma rays e. Microwaves c. Visible light f. Ultraviolet Radio < Microwave < Infrared < Visible < Ultraviolet < Gamma or D < E < A < C < F < B Radio waves have the lowest frequency and the longest wavelength. Gamma rays have the highest frequency and the shortest wavelength. 5. Label the parts of the wave (4 parts): Crest Wavelength Amplitude Trough Honors Chemistry - Chapter 5 Review Name: __________ KEY _________________ 6. What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency? What does this mean? Inversely proportional. As one increases, the other will decrease. If you increase wavelength, frequency decreases. If you decrease wavelength, frequency increases. 7. Einstein proposed that light is composed of particle-like quanta of energy known as photons 8. True or False: Heisenburg stated that the position and velocity of subatomic particles can be determined with certainty. False Don’t forget to know about the BALMER series of light.