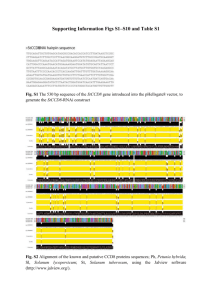
Online Resource 1 Animals and tissue samples Muscle samples
advertisement

Online Resource 1 Animals and tissue samples Muscle samples were collected at an abattoir from adult pigs of the Pietrain and Czech Large White breeds (m. biceps femoris, m.b.f.) and from 44-day-old fetuses (hind limb). Also, muscle (m.b.f. and m. longissimus lumborum et thoracis, m.l.l.t.) and other tissue samples (heart, tongue, diaphragm, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, ovary, adipose tissue, lymph node and brain) were collected from an adult crossbred (Pietrain x Czech Large White x Czech Landrace) for transcription profiling. Samples of m.l.l.t., m.b.f., heart, lung, kidney, brain and liver tissues from Czech Landrace and commercial crosses with Czech Landrace in different age categories (one-, seven- and 14-day-old piglets and adult animals) were collected to isolate mRNA for real-time RT-PCR. Samples were collected within 30 min after slaughter, immersed in RNAlater (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany) and stored at -20 °C until used. All pigs were slaughtered according to protocols for certified national slaughterhouses under the supervision of an independent veterinarian. Principles of ethical standards were adhered to during all sample collections. For linkage mapping of EEF1A1 and EEF1A2 the Hohenheim three-generation pedigrees Meishan x Pietrain (MxP), Wild Boar x Pietrain (WxP) and Wild Boar x Meishan (WxM) [Geldermann et al., 2003] were used. Allele frequencies were estimated in eight pig breeds (Czech Large White, Czech Landrace, Pietrain, Black Pied Prestice, Czech Meat Pig, Hampshire, Duroc and Meishan). Reference Geldermann H, Müller E, Moser G, Reiner G, Bartenschlager H, Cepica S, Stratil A, Kuryl J, Moran C, Davoli R, Brunsch C (2003) Genome-wide linkage and QTL mapping in porcine F2 families generated from Pietrain, Meishan and Wild Boar crosses. J Anim Breed Genet 120:363-393. doi: 10.1046/j.0931-2668.2003.00408.x Online Resource 2 Strategy of sequencing of EEF1A1 cDNA and genomic DNA of EEF1A1 and EEF1A2 EEF1A1: cDNA sequence encompassing the whole coding sequence of EEF1A1 (1389 bp) was obtained from clones of a subtracted fetal hind limb muscle cDNA library [Bílek et al., 2008; Stratil et al., 2008] and the sequence was deposited in the EMBL/GenBank database under accession number FM995600 (submitted Feb. 9, 2009). By alignment with the human EEF1A1 genomic sequence (ENSG00000156508, transcript EEF1A1-009; Ensembl, http://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Info/Index), individual exon sequences were identified. The study of the porcine genomic sequence of EEF1A1 was initiated when the genomic sequence was not available. On the basis of the cDNA sequence PCR primers EEF1A1-2Aak, -2Bak; -Cf, -Br were designed (see Online Resource 3) and used to determine the partial genomic sequence (from exon 2 to exon 8; Pietrain). For sequencing of the 5´ end of the gene and the 5´ upstream and 3´ downstream sequences, BAC clones from the porcine genomic BAC library were used [Rogel-Gaillard et al., 1999]. By using PCR primers EEF1A1-D and -E (Online Resource 3), two positive BAC clones were identified (PigI153C5 and PigI-345G10). The clone PigI-345G10 was used to determine upstream and downstream sequences of EEF1A1 by primer walking. From the obtained sequence, PCR primers were designed to amplify fragments of genomic DNA and to sequence a Pietrain pig (for the primers, see Online Resource 3; the primers for sequencing by primer walking are not shown). The fragments with indels or repetitions (heterozygotes) were cloned in plasmids using the QIAGEN PCR Cloningplus Kit (Qiagen). The sequence of the porcine EEF1A1, including the 5´ UTR, 3´ UTR, 5´ upstream and 3´ downstream sequences, was deposited in the EMBL/GenBank database under accession number FM995601 (submitted Feb. 9, 2009). EEF1A2: Porcine sequence TC348097 (http://compbio.dfci.harvard.edu/tgi/; an updated sequence is currently listed under TC603294 and it does not differ in the region of interest), which was highly identical (93% of 1155 nt) with the human EEF1A2 coding sequence (Ensembl, ENST00000217182), was used to design four pairs of PCR primers (EEF1A2-1A, -1B; -2A, -2B; -3A, -3B; -4A, -4B) to sequence the porcine EEF1A2 gene, from exon 4 to exon 8 in genomic DNA. Information on the primers is presented in Online Resource 3. A complete genomic sequence of the porcine EEF1A2 was obtained by sequencing the PCR fragments amplified on a PAC clone with EEF1A2 using the above-mentioned primers, as well as other primer pairs (see Online Resource 3) and primers for primer walking (designed on the basis of the obtained sequences; data not shown). The PAC clone (TAIGP714G09049Q) was identified by screening PAC library (PAC-TAIGP714; breed German Landrace) [Al-Bayati et al., 1999] with PCR primers 9A and 9B (Online Resource 3). Exon/intron organization of EEF1A2 was determined on the basis of comparison with human EEF1A2 (Ensembl, release 52; ENSG00000101210; transcript EEF1A2-201). The obtained sequence has been deposited in EMBL/GenBank database under accession number FM992107. References Bílek K, Knoll A, Stratil A, Svobodová K, Horák P, Bechyňová R, Van Poucke M, Peelman LJ (2008) Analysis of mRNA expression of CNN3, DCN, FBN2, POSTN, SPARC and YWHAQ genes in porcine foetal and adult skeletal muscles. Czech J Anim Sci 53:181-186. Stratil A, Knoll A, Horák P, Bílek K, Bechyňová R, Bartenschlager H, Van Poucke M, Peelman LJ, Svobodová K, Geldermann H (2008). Mapping of the porcine FBN2, YWHAQ, CNN3, DCN, POSTN, SPARC, RBM39 and GNAS genes, expressed in foetal skeletal muscles. Anim Genet 39:204-205. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.2007.01678.x Rogel-Gaillard C, Bourgeaux N, Billault A, Vaiman M, Chardon P (1999) Construction of a swine BAC library: application to the characterization and mapping of porcine type C endoviral elements. Cytogenet Cell Genet 85:205-211. doi: 10.1159/000015294 Al-Bayati HK., Duscher S, Kollers S, Rettenberger G, Fries R, Brenig B (1999) Construction and characterization of a porcine P1-derived artificial chromosome (PAC) library covering 3.2 genome equivalents and cytogenetical assignment of six type I and type II loci. Mamm Genome 10:569-572. doi: 10.1007/s003359901046 Online Resource 3 PCR primers for sequencing, SNP analysis, SCH and RH mapping, and amplification conditions of EEF1A1 and EEF1A2 Gene Accession no. Primer name Primer sequences (5´-3´) EEF1A1-Zf EEF1A1-Zr EEF1A1-U EEF1A1-V EEF1A1-Q ccgcgttgctgtggctct ttggttggcaatcaggcagatat catatgcttcggagccactcttag cgcgtcctccatcttgagac ctgggaaagtggtgtcgtgtg Location in genomic sequence 5´ upstream 5´ upstream 5´ upstream intron 1 5´ upstream EEF1A1-R ccgatgacgacgatgttgat exon 2 EEF1A1-2Aak EEF1A1-2Bak EEF1A1-Cf EEF1A1-Br EEF1A1-3f EEF1A1-3r acgtcgattcgggcaagtc ccagaaattggcacaaatgcta ttggctacaaccctgatacag cgttcttccaccactgattaag ggtggaagaacggtctcagaact ccctttttgagccattttcagat exon 2 exon 4 exon 4 exon 8; 3´ UTR exon 8; 3´ UTR 3´ downstream PWa on BAC PigI-345G10 PWa on BAC PigI-345G10 FM995601 EEF1A1-X EEF1A1-Y EEF1A1-Y1 EEF1A1-Y2 EEF1A1-D EEF1A1-E aaagaagcattttgaggaactatg tggcacttcctaaaatttgtagta tctggaccaagagggagatagat gctgctacatcaaacctcgtact aattatgctgtgctgtgaatac gcatttagcacattttagacat 3´ downstream 3´ downstream 3´ downstream 3´ downstream intron 5 intron 6 CR904955 EEF1A1-5F EEF1A1-5R ggccttgctcagtgggttag cccctcattcagcaatcaca BAC end of PigI-345G10 EEF1A1 PWa on BAC PigI-345G10 PWa on BAC PigI-345G10 PWa on BAC PigI-345G10 FM995600 FM995600 FM995600 FM995600 PWa on BAC PigI-345G10 Amplicon MgCl2 Size (bp) (mM) ~600 HotStarb Ta (°C) Comments 1810 1.0 50 882 1.0 60 857 2.25 60 1258 1.5 57 925 1.0 57 1480 2.0 52 379 2.0 55 356 2.5 57 394 1.0 55 62 HotStarTaq polymeraseb; sequencing HotStarTaq polymerase; sequencing LA DNA polymeraseb; sequencing; SNP analysis (FM995601:g.2111A>G) RsaI PCR-RFLP: allele G: 754 + 128 bp allele A: 581 + 173 + 128 bp LA DNA polymerase; sequencing LA DNA polymerase; sequencing LA DNA polymerase; cloning; sequencing LA DNA polymerase; sequencing LA DNA polymerase; sequencing LA DNA polymerase; BAC screening; SNP analysis (FM995601:g.3535C>T) HpaII PCR-RFLP: allele T: 356 bp allele C: 295 + 61 bp LA DNA polymerase; SCH mapping Online Resource 3 PCR primers for sequencing, SNP analysis, SCH and RH mapping, and amplification conditions of EEF1A1 and EEF1A2 (continued) EEF1A2 TC348097 FM992107 EEF1A2-1A EEF1A2-1B EEF1A2-2A EEF1A2-2B EEF1A2-3A EEF1A2-3B EEF1A2-4A EEF1A2-4B EEF1A2-27A EEF1A2-16B EEF1A2-22A EEF1A2-15B EEF1A2-9A EEF1A2-9B cgacaacatgctggagccct gagcctccagcagggacacg ggttcaagggctggaaagtgga ggcctcgctcagagcctcg accttcgcgcccgtgaaca gggccgtgtggcagtcaatg gcagatcagcgccggctact gccgctcttcttctccacgttc gtgggcaccgcacagacatt agaaaggggaggtcagccagtg attttgcagacagtgggggtgc gggacaccctgacctcaaccaa tgagcaagtatgaggcccagga ctggtctccctggcggtgac exon 4 exon 5 exon 5 exon 6 exon 6 exon 7 exon 7 exon 8 intron 1 intron 2 intron 2 intron 2 intron 5 intron 5 EEF1A2-5A EEF1A2-2B EEF1A2-11A EEF1A2-11B acgcaggcattggcactgtg see above ctgaggtgaagtcggtggagatg cgctgcctgggaagacgg intron 5/exon 6 exon 6 exon 6 intron 6 745 1.5 65 1224 2.0 62 1447 2.0 62 878 2.0 62 969 HotStarb 60 646 HotStar 60 169 2.25 60 140 2.0 60 LA DNA polymerase; sequencing LA DNA polymerase; sequencing LA DNA polymerase; sequencing LA DNA polymerase; sequencing HotStarTaq polymerase; comparative sequencing HotStarTaq polymerase; comparative sequencing LA DNA polymerase, without DMSO; PAC screening; RH mapping LA DNA polymerase; comparative sequencing 212 HotStar 58 HotStarTaq polymerase; SNP analysis (FM992107:g.6609C>G) Hin6I PCR-RFLP allele G: 212 bp allele C: 173 + 39 bp a Primers were designed on the sequence that was obtained by sequencing (primer walking, PW) of BAC clone PigI-345G10 (Jouy-en-Josas, France). b HotStarTaq Master Mix Kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA, USA); LA DNA Polymerases Mix (Top-Bio, Prague, Czech Republic). Online Resource 4 PCR primers for transcription profiling and analysis of expression of EEF1A1 and EEF1A2 in various tissues, and for housekeeping genes GAPDH and HPRT1 Gene Accession no. EEF1A1 FM995600 Primer name EEF1A1_11A EEF1A1_11B EEF1A2 FM992107 EEF1A2_7A EEF1A2_7B GAPDH AF141959 GAPDH_3A GAPDH_3B HPRT1 NM_001032376.2 HPRT_1AF HPRT_1BR Primer sequences (5´- 3´) Location ttgcattctaccaccaactcgt aacattgactggagcaaaggtg aacgtgtcagtcaaggacatcc cgggtggttcagaatgatga aaaggccatcaccatcttcc gccccacccttcaagtgagcc aaggacccctcgaagtgttg cacaaacatgattcaagtccctg exon 5 exon 6 exon 6 exon 7 exon 4 exons 5-6 exon 7 exon 8 Amplicon size (bp) 157 111 135 122 Online Resource 5 Allele frequencies at SNPs FM995601:g.2111A>G and FM995601:g.3535C>T (EEF1A1), and FM992107:g.6609C>G (EEF1A2) in eight pig breeds Czech Large White FM995601:g.2111A>Ga (EEF1A1) n G A 14 0.68 0.32 FM992107:g.6609C>G (EEF1A2) n G C 14 0.14 0.86 Czech Landrace 22 0.77 0.23 25 0.00 1.00 Czech Meat Pig 15 0.93 0.07 15 0.30 0.70 Pietrain 26 0.54 0.46 23 0.04 0.96 Black Pied Prestice 7 0.21 0.79 7 0.29 0.71 Hampshire 6 0.92 0.08 6 0.83 0.17 Duroc 11 1.00 0.00 12 0.54 0.46 Meishan 22 0.80 0.20 8 1.00 0.00 Breed a The same animals were tested for SNP FM995601:g.3535C>T; all pigs were homozygotes CC, except two Meishan and one Czech Meat Pig, who were heterozygotes CT. Online resource 6 Potential pseudogenes and pseudogene fragments of porcine EEF1A1 in the pig genome sequence (Sscrofa10.2)a Scrofa10.2 sequence (GCA_000003025.4) was blasted with the EEF1A1 cDNA sequence derived from FM995601.1. The sequences were adjusted manually for maximum alignment lengths and analysed by ClustalW2. Chromosome Position Strand Identities Gaps SSC1 119675490 - 119677217 Minus 1493/1751 (85%) 32/1751 (2%) Processed pseudogene (from exon 1 to exon 8) 139609140 - 139610422 Plus 1005/1329 (76%) 51/1329 (4%) Processed pseudogene (from exon 1 to exon 7) 11959737 - 11961058 Plus 1104/1348 (82%) 27/1348 (2%) Processed pseudogene (from exon 3 to exon 8) 133456562 - 133458318 Minus 723/916 (79%) 225/292 (77%) (without 601-nt insertion) 44/916 (5%) 9/292 (77%) Processed pseudogene (from exon 1 to exon 7; insertion is in exon 3) 98804674 - 98805016 91658469 - 91659113 Plus Plus 270/344 (78%) 541/673 (80%) 20/344 (6%) 29/673 (4%) Fragment homologous to exon 8 Processed pseudogene (from exon 5 to exon 8) 97802672 - 97804350 Plus 1505/1721 (87%) 52/1721 (3%) Processed pseudogene (from exon 1 to exon 8) 119617258 - 119619084 Minus 1135/1376 (82%) (without 2 insertions of 204 and 278 nt) 78/1376 (6%) Fragmented and truncated processed Within pseudogene (3 fragments from exon 3 to exon 8 LOC100156563 are within the sequence) 75507884 - 75517394 145475919 - 145476277 Minus cds 1050/1391 (75%) Plus 302/360 (84%) cds 7/1391 (1%) 1/360 (0%) 13578954 - 13579494 Minus 450/554 (81%) 19/554 (3%) SSC2 SSC3 SSC4 SSC6 SSC7 Comments Exon-intron structure (exons 2 – 8). Closed reading frame (potential pseudogene)b Fragment of processed pseudogene (from exon 1 to exon 3) Fragment of processed pseudogene (from exon 7 to exon 8) NCBI gene LOC100517693 (partial) Within LOC100157010 Within LOC102160176 Within LOC100512950 Within LOC102165177 LOC100511506 LOC100620900 - Online resource 6 Potential pseudogenes and pseudogene fragments of porcine EEF1A1 in the pig genome sequence (Sscrofa10.2)a (continued) SSC7 81509056 -81510833 Minus 425/503 (84%) 148/176 (84%) 333/395 (84%) 17/503 (3%) 3/176 (2%) 1/395 (0%) Fragmented and truncated processed Within pseudogene (3 fragments from exon 4 to exon 8 LOC102160893 are within the sequence; two insertions are SINE (PRE-1)) SSC8 SSC9 28631144 - 28632821 28754240 - 28756842 Plus Minus LOC100521383 LOC100514912 Plus Exon-intron structure (exons 2 – 8)b. ORF LOC100737797 29641242 -29642530 Plus 99/1760 (6%) cds 3/1389 (0%) cds 3/1389 (0%) 0/180 (0%) 1/258 (0%) 4/218 (2%) 3/95 (3%) Processed pseudogene, complete (exons 1 – 8) Exon-intron structure (exons 2 – 8)b. ORF 28922157 - 28924779 1336/1760 (76%) cds 1075/1389 (77%) cds 1078/1389 (78%) 152/180 (84%) 197/258 (76%) 164/218 (75%) 67/95 (71%) Fragmented and truncated pseudogeneb (4 fragments, exons 3, 6, 7 and 8 are within the sequence); exon – intron structure LOC100512298 7533723 -7535904 Minus 1459/1756 (83%) (two insertions excluded) 80/1756 (5%) Processed pseudogene, complete (exons 1 – 8). LOC100524033 Insertion (235 nt incl. one direct repeat) in exon (partial) 6, and SINE (PRE-1) (258 nt incl. one direct repeat) in exon 8 SSC10 29315076 - 29315786 Plus 698/713 (98%) 2/713 (0%) SSC11 SSC12 58620529 - 58620889 48458853 - 48460381 Plus Minus 336/403(83%) 1283/1563 (82%) SSC13 804499 – 805617 Minus 923/1193 (77%) 11467914 – 11469648 Minus 26413088 - 26413397 Minus 1371/1749 (78%) (without 53-nt insertion) 260/323 (80%) Fragment of processed pseudogene (from exon 6 to exon 8) 43/403 (11%) Fragment homologous to exon 8 36/1563 (2%) Processed pseudogene (from exon 1 to exon 8) 80/1193 (7%) Fragment of processed pseudogene (from exon 3 to exon 8)b 72/1749 (4%) Processed pseudogene, complete (exons 1 – 8) 13/323 (4%) Fragment of processed pseudogene (from exon 5 to exon 7)b LOC100516935 (partial) LOC100153897 LOC100152300 - Online resource 6 Potential pseudogenes and pseudogene fragments of porcine EEF1A1 in the pig genome sequence (Sscrofa10.2)a (continued) SSC14 95159960- 95160956 Minus SSC15 28341082 - 28342983 Minus SSC16 75371586 - 75372415 Plus 708/851 (83%) (without 162-nt insertion) 1474/1682 (88%) (without 226-nt insertion, PRE-1) 779/838 (93%) SSC17 2488137 - 2488560 Minus 372/468 SSCX 67392142 - 67393219 Plus 10301240 - 103013277 Plus 177/209 (85%) 519/608 (85%) (284-nt insertion and 40-nt deletion excluded) 748/881 (85%) a 31/851 (4%) Fragment of processed pseudogene (from exon 6 to exon 8) - 26/1682 (2%) Processed pseudogene (exons 1– 8) LOC100738918 (partial) 10/838 (1%) Fragment of processed pseudogene (from exon 6 to exon 8) 45/468 (10%) Fragment of processed pseudogene (exons 7 – 8) 3/209 (1%) Fragmented and truncated processed 26/608 (4%) pseudogene (two fragments; from exon 5 to exon 8) - 16/881 (2%) Within LOC102162801 Fragment of processed pseudogene (from exon 5 to exon 8) - The specificity of the EEF1A1 pseudogene status was ascertained on the basis of homologies of 5´ UTR and/or 3´ UTR of EEF1A1 gene and the query sequences. b It could not be unequivocally proved whether this is EEF1A1 or EEF1A2 pseudogene.