Evolution and Ecology Lecture Outline
advertisement

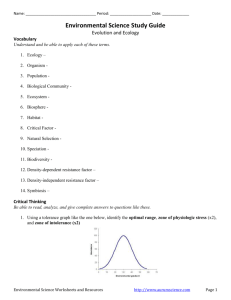
Environmental Science Notes Outline Unit 3: Evolution and Ecology Evolution and Ecology 1. Define ecology - 2. Ecologists organize life into these categories. Define each one. a. Organism – b. Population – c. Biological Community – d. Ecosystem – e. Biosphere – 3. Define habitat – a. Give two examples of factors that can define a habitat. 4. What is a niche? 5. Describe the difference between a generalist species and a specialist species. 6. Describe the difference between a native and non-native species. a. Are all exotic species villainous? aurumscience.com/environmental/3_interactions/lecture.html 1 Environmental Science Notes Outline Unit 3: Evolution and Ecology 7. What is an indicator species (and give examples)? 8. What is a keystone species (give examples)? 9. What is a foundation species (give an example)? 10. Define critical factor – 11. Label the optimal range, zones of physiologic stress (x2), and zones of intolerance (x2) in the figure below. Evolution 12. There are three types of adaptations seen in living organisms. Define each: a. Physical adaptations – b. Behavioral adaptations – c. Physiologic adaptations – aurumscience.com/environmental/3_interactions/lecture.html 2 Environmental Science Notes Outline Unit 3: Evolution and Ecology 13. Define evolution - 14. Define natural selection - 15. What is the primary source of the genetic variety behind natural selection and evolution? 16. Describe the three forms of evidence of evolution: a. Physical similarities – b. Comparing DNA – c. Vestigial Structures – 17. How is Sickle-cell anemia an example of natural selection in the human race? What advantage does it provide? a. What geographic areas tend to have more people with the disease? 18. How long has life existed on Earth? 19. Define divergent speciation – a. Describe an example: 20. Describe the four factors that will favor natural selection and speciation: a. aurumscience.com/environmental/3_interactions/lecture.html 3 Environmental Science Notes Outline Unit 3: Evolution and Ecology b. c. d. 21. Define convergent speciation – a. Describe an example: 22. Define artificial selection – a. Describe an example: 23. Define biodiversity - 24. Within the biodiversity of the Earth, how many species are actually discovered? How many are hypothesized to exist? a. The majority of known species are ________________. 25. Why is biodiversity important? 26. Define species diversity – 27. Define species richness – aurumscience.com/environmental/3_interactions/lecture.html 4 Environmental Science Notes Outline Unit 3: Evolution and Ecology 28. Define species evenness – a. Give an example of species richness and species evenness: 29. Define habitat fragmentation – 30. What does the theory of island biogeography state? 31. What is the purpose of corridors? Classification 32. List the taxon that humans belong in for each of the different levels of classification. Give at least one reason why they are placed in each taxon. Taxon Reason Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family 33. The final two taxa are used to determine scientific name. What is the scientific name of the modern human? (Use the correct format) 34. Two animals with many classification levels in common are considered to be ___________ aurumscience.com/environmental/3_interactions/lecture.html 5 Environmental Science Notes Outline Unit 3: Evolution and Ecology _____________________. Population Growth Patterns 35. What shape does a logistic growth pattern take? Draw it on the graph to the right. 36. What causes the population growth to slow down? Density-Dependent Factors – Density-Independent Factors – 37. At what point do logistic growth curves eventually stabilize? aurumscience.com/environmental/3_interactions/lecture.html 6 Environmental Science Notes Outline Unit 3: Evolution and Ecology 38. What shape does an exponential growth pattern take? Draw it on the graph to the right. a. What is missing that allows the population to grow so rapidly? 39. Define and label overshoot. 40. Define and label dieback. 41. What is irruptive growth? Community Interactions 42. Describe and give an example of each of the following types of community interactions: a. Predator-Prey b. Intraspecific competition c. Interspecific competition 43. How do plants and animals avoid competing with their own species? Give an example. 44. Define and give an example of each of the following types of symbiosis: a. Mutualism – b. Commensalism – c. Parasitism – aurumscience.com/environmental/3_interactions/lecture.html 7 Environmental Science Notes Outline Unit 3: Evolution and Ecology d. Parasitoidism - aurumscience.com/environmental/3_interactions/lecture.html 8