Phase Diagram 1
advertisement

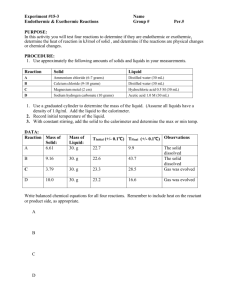
ANSWERS: Energy, Solids, and Liquids Worksheet 1. A 15.75-g piece of iron absorbs 1086.75 joules of heat energy, and its temperature changes from 25°C to 175°C. Calculate the specific heat capacity of iron. Q=mc∆T 1086.75 J = (15.75)(c)(150) c = 0.460 J/goC 2. How many joules of heat are needed to raise the temperature of 10.0 g of aluminum from 22°C to 55°C, if the specific heat of aluminum is 0.90 J/g°C? Q=mc∆T Q = (10.0g)(0.90)(33) Q = 297J 3. To what temperature will a 50.0 g piece of glass raise if it absorbs 5275 joules of heat and its specific heat capacity is 0.50 J/g°C? The initial temperature of the glass is 20.0°C. Q=mc∆T 5275 J = (50.0)(0.50)(∆T) ∆T = 211oC Final Temp = 211 + 20.0 = 231oC 4. 100.0 mL of 4.0°C water is heated until its temperature is 37°C. If the specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g°C, calculate the amount of heat energy needed to cause this rise in temperature. 100.0 mL = 100.0g Q=mc∆T Q = (100.0)(4.184)(33) Q=14,000 J 5. What is the specific heat capacity of silver metal in J/goC if 55.00 g of the metal absorbs 47.3 calories of heat and the temperature rises 15.0°C? Q=mc∆T 47.4 cal = (55.00)(c)(15) c = 0.05745 cal/goC c = 0.24 J/goC 6. A 2.70 gram piece of metal is heated to 98.7 C. It is then added to a beaker containing 150 mL of water at 23.5 C. The final temperature of the water and metal is 25.2 C. What is the specific heat of this metal? Heat Lost = Heat Gained - mc∆T metal = mc∆T water -(2.70)(c)(-73.5) = (150)(4.184)(1.7) c = 5.4J/goC ___________________________________________________________ 7. In an exothermic reaction, is the chemical potential energy of the products less or greater than that of the reactants? Products have less potential energy. Energy is released in an exothermic reaction so the products end up with less potential energy. 8. In an endothermic reaction, is the chemical potential energy of the products less or greater than that of the reactants? Products have more potential energy. Energy is adsorbed in an endothermic reaction so products end up with more energy stored in them. 9. Classify the following as exothermic or endothermic reactions: a. 550 KJ is released - EXOTHERMIC b. the metabolism of glucose in the body provides energy - EXOTHERMIC c. The synthesis of proteins requires energy - ENDOTHERMIC d. 125 KJ is absorbed - ENDOTHERMIC 12. Classify the follow as exothermic or endothermic and provide ∆H for each reaction: a. CH4 + 2 O2 ---> CO2 + 2 H2O + 890 kJ EXO ∆H = -890 kJ b. Ca(OH)2 + 65.3 KJ --> CaO + H2O ENDO ∆H = +65.3 kJ c. 2 S + 3O2 ---> 2 SO3 + 790 KJ d. N2 + O2 + 90.2 KJ --> 2 NO EXO ∆H = - 790 kJ ENDO ∆H = +90.2kJ 13. Old "hot packs" are based on the crystallization of sodium acetate from a highly concentrated solution. What is the sign of ∆H for this crystallization? Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? ∆H is negative Reaction Is exothermic 14. Define the molar heat of fusion of a substance? Molar heat of fusion is the heat/energy required to melt a mole of a substance. 15. How much energy would it take to melt 36 g of ice at 0oC if the molar heat of fusion of water is 6.02 KJ/mole 36g = 2.0 mole Energy = 2.0 mole x 6.02 kJ/mole = 12 kJ 16. Define the molar heat of vaporization of a substance? Molar heat of vaporization is the heat/energy required to convery 1 mole of a substance from the liquid to gaseous phase. 17. Rank the following intermolecular forces from the strongest (1) to the weakest (3): _1__ Hydrogen Bonding 18. _3_ London Dispersion Forces __2_ Dipole-Dipole Interactions Use your best judgment to rank the following on boiling points from lowest (1) to highest (4): _1_ CH4 _4_ H2O _2__ CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 19. Define the normal boiling point of a substance? Normal boiling point is the boiling point at 1 atm of pressure _3_ CH2Br2 Phase Diagram 1 For each of the questions on this worksheet, refer to the phase diagram for mysterious compound X. 20. If you have a sample of this compound at 70 atm and 200oC and you raise the temperature to 500oC, what will happen (keeping the pressure the same)? _solid will turn to liquid_ 21. If you were to have a bottle containing compound X in your closet, what phase would it most likely be in? _GAS_ 22. At what temperature and pressure will all three phases coexist? ____around 50 atm and 350oC__ 23. If I have a bottle of compound X at a pressure of 45 atm and temperature of 1000 C, what will happen if I raise the temperature to 4000 C? _____sublimate (go from solid to gas)_________ 24. Why can’t compound X be boiled at a temperature of 2000C ____never exists as a liquid at 200oC 25. If you wanted to, could you drink compound X? NO: it is only a liquid at really high temps and pressures__________ Around 100oC 26. 27. Around 400oC 28. N/A 29. Liquid to gas 30. Around 800oC 31. Solid to liquid around 100oC and then liquid to gas around 200oC 32. What is happening to the average kinetic energy of the molecules in the sample during section 1? The average kinetic energy is increasing 33. What is the name of the process happening during section (4)? Boiling or Vaporization 34. What would be the name of the process happening during section (4) if time were going the other way? Condensing 35. What is the melting point of this substance? 0oC 36. At what temperature would this sample boil? 100oC 37. When this substance is melting, the temperature of the ice-water mixture remains constant because: a. Heat is not being absorbed b. The ice is colder that the water c. Heat energy is being converted to potential energy d. Heat energy is being converted to kinetic energy 38. When a given quantity of water is heated at a constant rate, the phase change from liquid to gas takes longer than the phase change from solid to liquid because a. The heat of vaporization is greater than the heat of fusion b. The heat of fusion is greater than the heat of vaporization c. The average kinetic energy of the molecules is greater in steam than in water d. Ice absorbs energy more rapidly than water does 39. The temperature at which a substance in the liquid state freezes is the same as the temperature at which the substance a. Melts b. Sublimes c. Boils d. Condenses Read the vapor pressure diagram above. 40. What is the boiling point of ethanol at normal atmospheric pressure (1 atm). Remember, 1 atm = 101.3 kPa Around 80oC 41. What is the boiling point of chloroform at 1 atm? Around 60oC 42. In a closed container, what is the approximate vapor pressure of water at 80oC? 50 kPa