heat/energy
advertisement

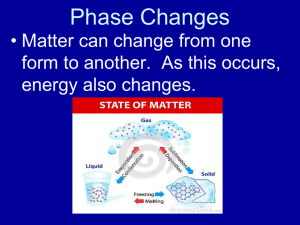
To cause the state of matter to change…. Heat/Energy needs to be….. added or removed Heat that is removed is…. Exothermic surroundings system heat Heat that is added is…. Endothermic surroundings system heat Endothermic versus Exothermic Example WS Scenario Endo or Exo? Explain 1 Your car burns gasoline as you drive from home to school Exothermic – “burning “ releases energy 2 Jerry is baking homemade bread in the oven. Endothermic – “baking” absorbs energy 3 The ice melts in your glass of water. Endothermic – “melting” absorbs energy 4 Sodium and chlorine combine in an explosive reaction to form table salt. Exothermic – “explosive” shows releasing energy 5 Barry Balloon lights his candles to get his hot air balloon to fly. Exothermic – “lighting” candles releases energy 6. Water freezes on the pavement and the roads become icy. Exothermic – “freezing” releases energy Endothermic versus Exothermic Example WS Scenario Endo or Exo? Explain 7. Mom puts a pot of water on the stove and the water begins to boil Endothermic – “boiling” absorbs energy 8. Water condenses on the side of your glass of cold lemonade. Exothermic - “condensation” releases energy 9. A glass of water left out overnight evaporates. Endothermic – “evaporation” absorbs energy 10. A plant carries out photosynthesis. Endothermic“photosynthesis” absorbs energy 11. A tree grows. Endothermic – “growing” absorbs energy 12. Sally gets really sweaty as she runs. Then she stops running and the sweat evaporates. (Hint: A 2-part question) Exothermic- “sweat” giving off energy Endothermic – “evaporation” absorbs energy Changes in State Liquid gas : Vaporization To cause this change…. heat/energy needs to be added Hvap surroundings system heat Heat of vaporization Gas liquid : Condensation To cause this change…. heat/energy needs to be removed Hcond surroundings system heat Heat of condensation Vaporization Point (the temperature a liquid turns into a gas) = Condensation Point (the temperature a gas turns into a liquid) Melting/Fusion is.. the vibrations in a solid are strong enough to… overcome attractions that keep solid atoms together Solid liquid: Fusion To cause this change…. heat/energy needs to be added Hfus surroundings system heat Heat of fusion Liquid Solid: Solidification To cause this change…. heat/energy needs to be removed Hsolid surroundings system heat Heat of solidification Melting (Fusion) Point (the temperature a solid turns into a liquid) = Solidification Point (the temperature a liquid turns into a solid) Relationships Endothermic Exothermic +Hvap = - Hcond - +Hfus= Hsolid Energy in Physical Changes Heat of Physical Changes Table On your note sheet: types of thermochem problems Substance Melting point °C Heat of fusion (kJ/kg) Helium -269.65 5.23 Hydrogen -259.31 58.6 Nitrogen -209.97 25.5 Oxygen -218.79 Ethyl alcohol Heat of solidification (kJ/kg) Heat of condensation (kJ/kg) Boiling point °C Heat of vaporization (kJ/kg) -268.93 20.9 -252.89 452 -195.81 201 13.8 -5.23 -58.6 -25.5 -13.8 -182.97 213 -20.9 -452 -201 -213 -114 104.2 -104.2 78 854 -854 Mercury -39 11.8 357 272 Water 0.00 334 100.00 2256 Sulfur 119 38.1 444.60 326 Lead 327.3 24.5 1750 871 Antimony 630.50 165 1440 561 Silver 960.80 88.3 2193 2336 Gold 1063.00 64.5 2660 1578 1083 134 -11.8 -334 -38.1 -24.5 -165 -88.3 -64.5 -134 2567 5069 -272 -2256 -326 -871 -561 -2336 -1578 -5069 Copper When doing word problems…. 1. Find the question word: determine what you are looking for. WANT 2. What #s did the problem give you GIVEN 3. If only one # always start grid with that # 4. If Multiple #’s you NEED a formula Ex.1 How much heat is absorbed when 24.8 g water is evaporated? Ex 2 How much heat is transferred when 400 grams of mercury (Hg) is vaporized? Ex 3 If 300 kJ of heat is available, how much copper can be melted? Ex 4 How much heat is transferred when 100 grams of ethyl alcohol condenses? Sublimation SOLID skips liquid stage goes straight into GAS stage Demo 1: Sublimation You forgot your glass of water outside. The next time you are outside, you realize your glass is empty. What happened? Evaporation Vs Boiling • Both are Vaporization • Both allow liquid turn into a gas BUT…. • Evaporation is NOT Boiling Evaporation In an open container Δ occurs @ the surface Evaporation It’s a cooling process Evaporation Explain how the following description is an analogy for evaporative cooling: If the fastest runner is removed from a race, the resulting average speed of the runners that remain will be lower. Boiling Liquid has enough HEAT/ENERGY to overcome the External Pressure Vapor Pressure = External Pressure to make something boil Energy/Heat is added Or the EXTERNAL pressure is changed Boiling Affect of Temp on Contained Liquid KE of particles particle collisions VP This why a tea kettle whistles Vacuum no gas particles = no collisions = NO PRESSURE Demo 2: Boiling Atmospheric Pressure Gas particles in Air colliding in earth’s atmosphere More gas particles = More collisions= More pressure Elevation and Atmospheric Pressure ↑ Elevation = ↓ Atmospheric Pressure b/c less gas particles =less collisions = P Sea Level more gas particles = more P Elevation and BP Pressure Cooker Creates a High External Pressure a bubble of vapor can’t form unless KE= T BP is = hotter liquid= shorter cooking time