Math 10 Test Outline:
advertisement

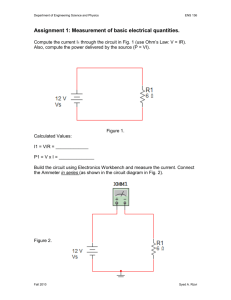
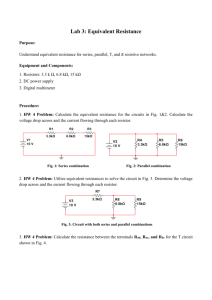
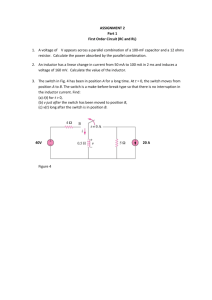
Science 9 Test Outline: Characteristics of Electricity (7.1 – 9.2) Prescribed Learning Outcomes: These are the outcomes covered by this test as defined in the Science 9 Curriculum. C5 explain the production, transfer, and interaction of static electrical charges in various materials C6 explain how electric current results from separation of charge and the movement of electrons C7 compare series and parallel circuits involving varying resistances, voltages, and currents C8 relate electrical energy to power consumption Chapter 7 Breakdown: 7.1 Static Charge [p. 248] Write the definition of static charge [p. 248]: _________________________________________ What was Benjamin Franklin’s theory of electricity? [p. 249] Understand what is happening in fig. 7.3 [p. 250] where electrons are being transferred from one material to another. Count the number of negative charges in both materials before and after (A B). What changed? Define and give an example of an insulator [p. 252]:___________________________________ Define and give an example of a conductor [p. 252]:___________________________________ What is the unit of electric charge? What is grounding and why is it important to know how it works? [p. 254] DO #4 – 10, 12, 13, 15 [p. 257] 7.2 Electric Force [p. 258] Why is electric force an action-at-a-distance force and not a contact force? [p. 258] List the laws of static charge [p. 259]: Explain the difference between charging by conduction and charging by induction [p. 259]. Explain why a charged balloon will stick to a neutral wall. Draw a diagram to illustrate this: DO #1-6, 9, 10 [p. 265] DO #5-7, 12 [p. 266] Page 1 of 3 Chapter 8 Breakdown: 8.1 Electric Potential Energy and Voltage [p. 270] What’s another name for voltage? [p. 272] Fill in the following chart: Name Voltage Symbol I Unit Device Ohmmeter Draw a diagram of a dry cell battery and label all parts. [p. 273] 8.2 Electric Current [p. 280] Look at fig. 8.9 on p. 281 and read the descriptions (A – E). Think about how this is similar to electrons in a circuit. Draw circuit diagrams of the three circuits at the top of p. 283 using the symbols from fig. 8.10: Name Circuit A Circuit B Circuit C Diagram Conventional current flows from the ________ terminal to the ________ terminal of a battery. Explain why electrons actually flow in the opposite direction to current using the keywords attract and repel. DO #3 – 5, 9, 13 [p. 289] 8.3 Resistance and Ohm’s Law [p. 290] Define resistance [p. 290]: ________________________________________________________ Write the formula for Ohm’s Law [p. 292]: ________________ Read over and remember the conversions at the bottom of p. 293. What do the colour bands on a resistor tell you? [p. 297] DO #1, 3 – 5, 7 – 10, 12, 13 [p. 301] DO #2, 4, 21, 23, 25 – 29, 31 [p. 303] Page 2 of 3 Chapter 9 Breakdown: 9.1 Series and Parallel Circuits [p. 306] Review all BLM circuit diagram worksheets –make calculations and solve for missing values Copy out the indicated figures on pages 309 and 312 as well as their captions: Fig. 9.5, pg. 309 Fig. 9.6, pg. 309 Caption: Caption Fig. 9.9, pg. 312 Fig. 9.10, pg. 312 Caption: Caption: To increase the total resistance of the circuit, should we add resistors in parallel or in series? DO #1 – 4, 6 – 10 [p. 319] 9.2 The Power of Electricity [p. 320] Fill in the following table: Name Power Energy Energy in the Home Unit watt kilowatt-hour Unit Symbol J Define electrical power [p. 322]: ___________________________________________________ Write the formula to calculate power [p. 323]: ________________ What does it mean if a hair dryer shows a power rating of 2000 W? Write the formula for energy consumption [p. 324]: ________________ Why do we use kilowatt-hours when measuring energy used in the home? What does a surge protector do? [p. 326] Review all Workbook Questions and Answers DO #3, 9 – 11 [p. 329] Review all Notes DO #2 – 7, 9 – 11, 14 – 22 [p. 330, 331] Page 3 of 3 Bring a Calculator to the test