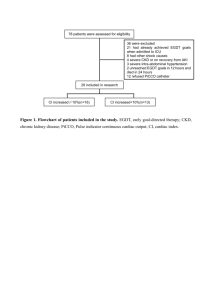
78 patients were assessed for eligibility 29 included in research CI
advertisement

78 patients were assessed for eligibility 36 were excluded 21 had already achieved EGDT goals when admitted to ICU 8 had other shock causes 4 severe CKD or on recovery from AKI 3 severe intra-abdominal hypertension 2 unreached EGDT goals in 12 hours and died in 24 hours 12 refused PiCCO catheter 29 included in research CI increased≥10%(n=16) CI increased<10%(n=13) Figure 1. Flowchart of patients included in the study. EGDT, early goal-directed therapy; CKD, chronic kidney disease; PiCCO, Pulse indicator continuous cardiac output; CI, cardiac index. Figure 2. The relationship between cardiac index percent change and creatinine clearance after resuscitation. Correlations were assessed by using Spearman regression model. Figure 3 shows a significant positive correlation between CI percent change and Ccr after resuscitation (ρ=0.548; P=0.002). Figure 3. The relationship between CI percent change(%) and probability of different renal outcomes A. Logistic regression model of relationship between cardiac index percent change (%) and the probability of no poor renal outcome. Note the plateau for the incidence of good renal prognosis when the lower limit of cardiac index percent change was 50%. B. ROC curve for CI percent change (%) to predict no poor renal outcome. The cardiac index percent change (%) after resuscitation had a moderate predictive value of non-poor renal outcome ( AUC 0.739, P=0.012). Using a cutoff value of 10% would have a sensitivity of 75% and specificity of 89%. Table 1.Patients’ characteristics CI un-increased group CI increased group P (n=13) (n=16) Age (years) 78(69-86) 75(65-83) 0.29 Males n (%) 7(54) 8(50) 1.00 Hypertension n (%) 9(69) 10(63) 1.00 Diabetes mellitus n (%) 5(38) 4(25) 0.69 Lungs n (%) 6(46) 10(63) 0.47 Abdomen n (%) 7(54) 4(25) 0.14 Soft tissue n (%) 0(0) 1(6) 1.00 Other n (%) 0(0) 1(6) 1.00 APACHE score II 24(24-30) 23(19-27) 0.13 SOFA score 11(10-12) 11(8-12) 0.19 Mechanical ventilation n (%) 10(77) 13(81) 0.70 Norepinephrine (ug/kg/rmin) 0.3(0.1-0.4) 0.2(0.2-0.4) 0.36 Hydroxyethyl starch n (%) 8(62) 7(44) 0.46 Colloid fluid n (%) 11(85) 13(81) 1.00 Hydroxyethyl starch amount (ml/kg) 11.7(7.1-18.6) 7.9(7.1-10.0) 0.20 Colloid fluid amount (ml/kg) 13.8(7.1-20.0) 8.2(5.0-10.6) 0.20 Crystalloid fluid amount (ml/kg) 26.8(15.7-34.7) 28.3(18.9-42.8) 0.51 Resuscitation fluid amount(ml/kg) 35.8(27.6-53.6) 36.1(25.8-52.4) 0.86 6.0(6.0 -7.0) 6.0(5.0-6.0) 0.27 8(62) 1(6) 0.003 AKI 2-3on admission n (%) 6(46) 4(25) 0.27 Persistent AKI n (%) 4(31) 1(6) 0.14 AKI 0-1on admission n (%) 7(54) 12(75) 0.27 New AKI n (%) 2(15) 0(0) 0.19 6(46) 3(19) 0.23 8(6-14) 8(7-19) 0.98 6(46) 5(31) 0.47 Source of infection Fluid Therapy EGDT period (hour) Poor renal outcome n (%) Use of renal-replacement therapy n (%) Days in ICU (days) 28-day mortality n (%) CI, cardiac index; APACHE, Acute physiology, age, chronic health evaluation; SOFA, sequential organ failure assessment. The data in the table are expressed as median (interquartile range) or number (%). Table 2. Hemodynamic parameters before and after EGDT HR (beats/min) MAP (mmHg) CVP (mmHg) CI (L/min/m2) SVI (ml/m2) SVRI (dyn.s.m2.cm-5) GEDI (ml/m2) GEF (%) CFI (L/min) ScvO2 (%) Lac (mmol/L) BeforeEGDT After EGDT P value BeforeEGDT After EGDT P value BeforeEGDT After EGDT P value BeforeEGDT After EGDT P value BeforeEGDT After EGDT P value BeforeEGDT After EGDT P value BeforeEGDT After EGDT P value BeforeEGDT After EGDT P value BeforeEGDT After EGDT P value BeforeEGDT After EGDT P value BeforeEGDT After EGDT P value CI un-increased group (n=13) CI increased group (n=16) P 113(90–134) 91(73–114) 0.002 65(58–73) 87(69–98) 0.002 10(5–12) 10(8–15) 0.045 3.2(2.7–4.3) 3.0(2.6–4.0) 0.022 34(28–37) 36(32–38) 0.11 1478(1231–2076) 1652(1273–2391) 0.06 793(670–936) 878(673–1056) 0.17 15(13–20) 16(13–20) 0.36 4.0(3.2–5.3) 3.8(2.9–4.5) 0.008 80(73–85) 80(75–83) 0.81 3.2(1.5–5.1) 1.7(1.2–2.8) 0.039 117(87–130) 95(78–107) 0.013 64(55–67) 86(76–93) <0.001 6(4–11) 11(8–15) 0.004 2.6(2.2–3.2) 3.8(3.1–5.2) <0.001 29(23–36) 43(40– 48) <0.001 1722(1497–2373) 1545(1185–1881) 0.163 651(634–771) 767(697–886) <0.001 17(16–22) 23(20–24) 0.013 4.2(3.7–4.9) 5.0(4.4–5.9) 0.003 79(76–81) 84(81–84) 0.005 2.4(1.3–3.3) 1.3(0.9–1.7) 0.03 0.69 0.76 0.60 0.96 0.56 0.89 0.06 0.028 0.14 0.003 0.34 0.43 0.035 0.50 0.19 0.012 0.96 0.003 0.66 0.026 0.44 0.25 MAP, mean arterial pressure; CVP, central venous pressure; HR, heart rate; CI, cardiac index; SVI, stroke volume index; SVRI, systemic vascular resistance index; GEDI, global enddiastolic volume index; GEF, global ejection fraction;ScvO2, central venous oxygen saturation ; Lac, arterial lactate acid. The data in the table are expressed as median(interquartile range) or number(%). Table 3. Renal function parameters before and after EGDT CI un-increased group CI increased group P (n=13) (n=16) BeforeEGDT 68(49-261) 83(56-133) 0.74 After EGDT 83(55-215) 76(63-127) 0.86 1.0 0.98 BeforeEGDT 8.4(4.9-14.4) 7.8(5.7-10.0) 0.61 After EGDT 8.5(4.5-14.8) 7.9(4.7-9.0) 0.65 0.27 0.27 BeforeEGDT 140(70-375) 74(28-148) 0.11 After EGDT 169(60-254) 125(60-179) 0.55 0.68 0.048 BeforeEGDT 4010 (2395-9143) 7894(3424-9910) 0.24 After EGDT 2766(2100-8817) 3642(2174-7375) 0.69 0.60 0.004 BeforeEGDT 85(40-128) 73(23-119) 0.35 After EGDT 67(43-128) 98(70-150) 0.11 0.31 0.013 BeforeEGDT 85(17-129) 59(45-101) 0.69 After EGDT 53(22-93) 82 (52-126) 0.08 0.034 0.12 BeforeEGDT 0.6(0.1-12.3) 0.7(0.3-1.5) 0.64 After EGDT 1.0(0.1-8.9) 1.0(0.5-1.8) 0.83 0.53 0.41 Serum Cr(umol/L) P value Serum Bun(mmol/L) P value Serum NGAL(ng/ml) P value Urinary Cr(umol/L) P value Urine output(ml/h) P value Ccr (ml/min) P value FeNa(%) P value Cr, creatinine ;Bun, urea nitrogen ; NGAL, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin ;Ccr, creatinine clearance; FeNa, fractional excretion of sodium. The data in the table are expressed as median(interquartile range) or number(%).