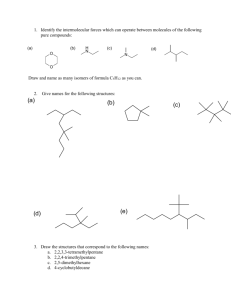
Physics
advertisement
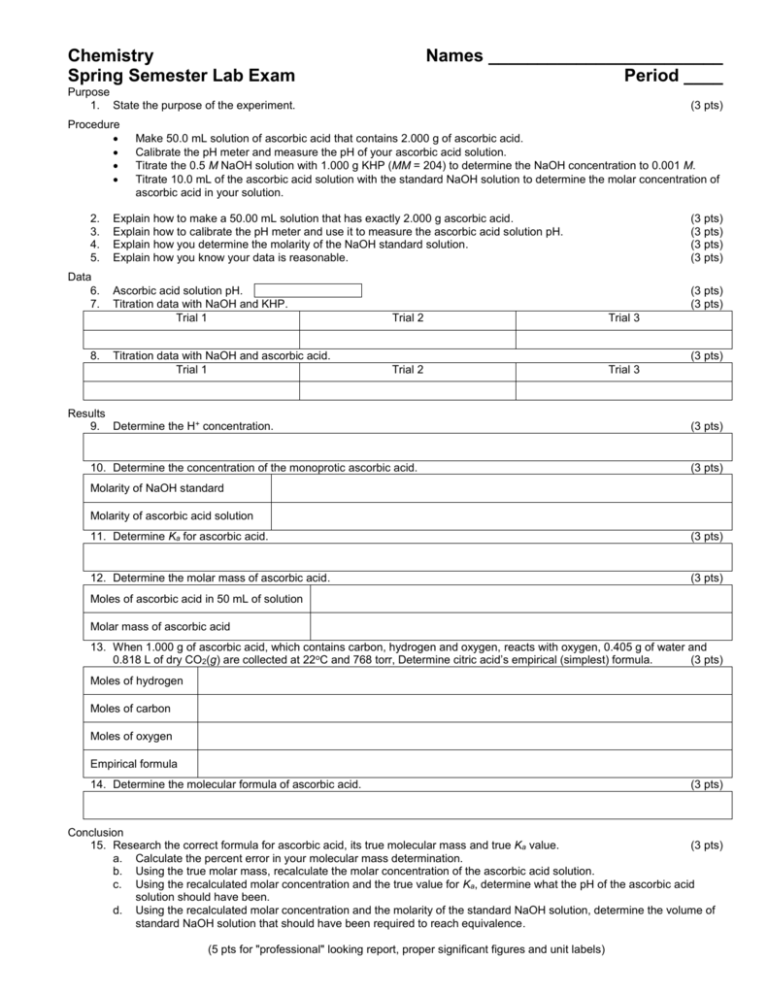
Chemistry Spring Semester Lab Exam Names ________________________ Period ____ Purpose 1. State the purpose of the experiment. (3 pts) Procedure 2. 3. 4. 5. Data 6. 7. 8. Make 50.0 mL solution of ascorbic acid that contains 2.000 g of ascorbic acid. Calibrate the pH meter and measure the pH of your ascorbic acid solution. Titrate the 0.5 M NaOH solution with 1.000 g KHP (MM = 204) to determine the NaOH concentration to 0.001 M. Titrate 10.0 mL of the ascorbic acid solution with the standard NaOH solution to determine the molar concentration of ascorbic acid in your solution. Explain how to make a 50.00 mL solution that has exactly 2.000 g ascorbic acid. Explain how to calibrate the pH meter and use it to measure the ascorbic acid solution pH. Explain how you determine the molarity of the NaOH standard solution. Explain how you know your data is reasonable. (3 pts) (3 pts) (3 pts) (3 pts) Ascorbic acid solution pH. Titration data with NaOH and KHP. Trial 1 (3 pts) (3 pts) Trial 2 Trial 3 Titration data with NaOH and ascorbic acid. Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 (3 pts) Results 9. Determine the H+ concentration. 10. Determine the concentration of the monoprotic ascorbic acid. (3 pts) (3 pts) Molarity of NaOH standard Molarity of ascorbic acid solution 11. Determine Ka for ascorbic acid. (3 pts) 12. Determine the molar mass of ascorbic acid. (3 pts) Moles of ascorbic acid in 50 mL of solution Molar mass of ascorbic acid 13. When 1.000 g of ascorbic acid, which contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, reacts with oxygen, 0.405 g of water and 0.818 L of dry CO2(g) are collected at 22oC and 768 torr, Determine citric acid’s empirical (simplest) formula. (3 pts) Moles of hydrogen Moles of carbon Moles of oxygen Empirical formula 14. Determine the molecular formula of ascorbic acid. (3 pts) Conclusion 15. Research the correct formula for ascorbic acid, its true molecular mass and true Ka value. (3 pts) a. Calculate the percent error in your molecular mass determination. b. Using the true molar mass, recalculate the molar concentration of the ascorbic acid solution. c. Using the recalculated molar concentration and the true value for Ka, determine what the pH of the ascorbic acid solution should have been. d. Using the recalculated molar concentration and the molarity of the standard NaOH solution, determine the volume of standard NaOH solution that should have been required to reach equivalence. (5 pts for "professional" looking report, proper significant figures and unit labels)