Chapters 11-13
advertisement

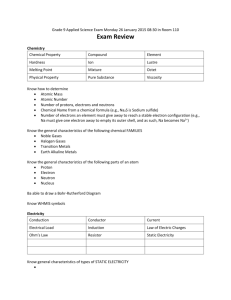
Grade 9 Academic – Physics Unit 3 Outline: Characteristics of Electricity 2012-2013 Block Overall expectations: assess some of the costs and benefits associated with the production of electrical energy from renewable and non‑renewable sources, and analyse how electrical efficiencies and savings can be achieved, through both the design of technological devices and practices in the home; investigate, through inquiry, various aspects of electricity, including the properties of static and current electricity, and the quantitative relationships between potential difference, current, and resistance in electrical circuits; demonstrate an understanding of the principles of static and current electricity. Key Topics & Key Terms (Chapters 11-13) Homework - Textbook - additional worksheets CHAPTER 11 – Static Electricity 1 Introductory Activities Diagnostic Quiz – Electricity Basics/Math Info. What do you already know? 2 11.1 & 11.4 Static Electricity (PPT #1) Lab activity – static electricity exploration stations Video: Bill Nye – static electricity Electric charge (+, –, Ø) The law of electric charges (attraction & repulsion) LAB: Testing for Conductors and Insulators (Inv 11.5 pg. 484-485) Introduction to using an electroscope 3 Key terms: electric charge, neutral, positive charge, negative charge, static electricity, electric force, induced charge separation, electroscope, conductor, insulator 11.2 Charging by contact (PPT#1&2) The electrostatic series (Table 1 p 473) Charging by conduction using the electroscope Grounding LAB ACTIVITY: Predicting Charges (”Charge Detective”) Title page, glossary Math Worksheets Pg 459 Q1-6 Bill Nye worksheet Make a list in a 3-column table with the headings: “good conductors, fair conductors and good insulators” 11.1 Pg. 471 #4-7 11.4 Pg. 482 #1,3,4,6,7 11.2 Pg. 477 #1,3, 5, 6, 8 Key terms: friction, electrostatic series, conduction, grounding, electric discharge 4 5 6 11.6 Charging by induction (PPT#1&2) Charging objects temporarily & permanently by induction LAB ACTIVITY: charging objects by induction (pg. 490-491) 11.6 Pg. 489 #2, 5, 6 Key terms: induction Practical Quiz #1: charging an electroscope (TI; wt-3) positively by conduction negatively by conduction positively by induction negatively by induction Applications of Static Electricity (PPT#1) Electric discharge & Lightning Electrostatic paint sprayers, electrostatic dusters, electrostatic precipitators, fabric softener sheets, laser printers, electrostatic lifting apparatus, electrostatic speakers, lightning rods, grounding cars Chapter 11 Review p 498, Self Quiz p 500 (ref. Ch.11, old 9 text Pg 462) 11.8 p 495 Q1,5 Check: Block Key Topics & Key Terms Homework - Textbook - additional worksheets CHAPTER 12/13 – Current Electricity 7 8 9 10 Electrical Energy Sources & Generating Electricity (Smartboard) Video: Bill Nye – Current Electricity (12.1) 12.3 & 12.4: Electric Cells, Current electricity (AC & DC) 12.5: Social, economic, and environmental implications of the production of electrical energy in Canada (wind, solar, hydro, coal, oil, natural gas, nuclear) Key terms: current electricity, electrical energy, electric cells, AC, DC 12.7 Power (PPT#3) P = E/t (symbols & SI units), P= IxV % Efficiency = (useful E output/total E input) x 100 Cost of electricity Chapter 12 review p 542, self quiz p 544 Key terms: power, kilowatt hour, efficiency UNIT TASK: Personal Energy Audit (TI, CM, AP; wt-3, PPT #3, Smartboard) Part 1: conducting an individual electrical energy audit Part 2: analyzing data Part 3: solutions Bill Nye worksheet 12.1 Pg. 508 Q3,5,6 12.3 Pg. 514 #3,4,6 12.4 Pg. 517 #2, 4 12.5 p528 Q3,5 Worksheet (generating E) Worksheets (power, electrical efficiency) 12.7 Pg. 535 #2-7 See handouts Electrical Circuits (PPT#4, Smartboard) 12.2: electric circuits, series vs. parallel circuits 13.1: Circuit diagram symbols 12.2 Pg. 510 #2, 4-6 13.1 Pg. 554 #1-6 (worksheets) Key terms: electric circuit, load, switch, ammeter, voltmeter, fuse, connecting wires, series, parallel, current, potential difference QUIZ #2: circuit diagrams (KU,CM; wt-1) 11 13.3 Current (PPT#5) current & electric shocks I = Q/t (symbols & SI units) Review: metric conversion & GRASP method of calculations LAB ACTIVITY: building circuits & measuring current with an ammeter Worksheet (current & charge) 13.3 Pg. 557 #1-4 12 13.5 Potential Difference (“Voltage”) PPT #5 V = E/Q (symbols & SI units) LAB ACTIVITY: building circuits & measuring voltage with a voltmeter LAB ACTIVITY: measuring voltage & current in series & parallel circuits (13.6 pg.562-563) Worksheet (Energized & de-energized charges) 13.5 Pg. 561 #2-4 13 13.7 & 13.9 Resistance & Ohm’s Law (PPT#6) R = V/I (symbols & SI units), graphing skills Factors that affect resistance: wire length, wire material, and cross-sectional area of a wire Key terms: resistance QUIZ #3: P, I, V calculations (TI; wt-3) Worksheet (resistance) 13.7 Pg. 566 #2, 3, 5-7 13.9 Pg. 570 #2-9 QUIZ #4: Ohm’s Law (TI; wt-3) LAB: Ohm’s Law (see rubric: TI, CM, ; wt-3) 14 15 16 13.10 Comparing Series & Parallel Circuits GIZMO: Circuit builder (opt) Chapter 13 review p 580, self quiz p 582 Unit Review (see website review handout posted) FINAL EVALUTION: Unit 3 Test (KU/TI/CM/AP; wt-5) 13.10 Pg. 575 #3-7 GIZMO questions Check: