Reproduction Study Guide
advertisement

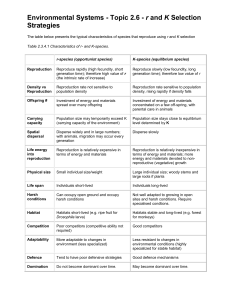
Reproduction Study Guide Name _______________________________ Test Date _______________ Parent Signature ______________________________________________ Reproduction What are sexual and asexual reproduction? 1. Survival of a _______________________________ depends on its ability to produce offspring. 2. Every organism comes from a parent through the process of ____________________________________. 3. The transfer of _____________________ ________________________ from parents to their offspring is known as reproduction. 4. Genetic material contains the information that controls an organism’s _____________________ and ___________________________. 5. The production of a new organism from two parents is called _______________________________ reproduction. 6. When an egg cell joins with a sperm cell, _________________________________ occurs. 7. Egg and sperm cells are examples of _________________________________. 8. A fertilized egg develops into an individual with traits from each _________________________________. 9. The production of a new organism from a single parent is called ______________________________ reproduction. Offspring are ___________________________ to parent because they share same genetic information. How do organisms reproduce asexually? 10. Most bacteria and unicellular protists reproduce by making a copy of their genetic material and _______________________________. 11. Cnidarians, sponges, and some fungi can reproduce through ____________________________. 12. The eggs of insects, fish, frogs, and lizards sometimes develop into new animals without being __________________________________. 13. New plants can grow from leaves, roots, or stems. This type of asexual reproduction is called _____________________________ ___________________________________. 14. Strawberry plants and ferns can reproduce asexually by forming __________________________________. This is a form of vegetative propagation. How do plants and animals reproduce? 15. When plant and animals reproduce sexually, a ______________________________ _______________ develops into an _________________________________. Seeds and Fruits 16. The ___________________________________ takes place in the ovary of a flower. 17. The ________________________________ in a flowering plant develops in a _______________________________. 18. As the seed develops, the ovary enlarges to become a ______________________________. 19. The development of a seed into a new plant is called ____________________________________________. Animal Eggs 20. Animals that reproduce sexually begin as fertilized _________________ ________________ that develop into embryos. 21. The egg’s ______________________________ provides food for a developing embryo. 22. Reptiles and birds have eggs filled with a liquid and surrounded by a tough _______________________________, so their eggs can be laid on land. 23. The embryos of most _________________________________ develop inside the mother. 24. ______________________________ are the only mammals that lay eggs. How do fungi reproduce? 25. ________________________ reproduce asexually through _____________________________. 26. Eventually the bud breaks off and lives as a new, _____________________________ ___________________________. 27. Multicellular fungi can also reproduce ________________________________. 28. These fungi are made of tiny filaments called __________________________________. Hyphae tangled together form ______________________________. 29. If you have ever walked through the forest and seen a mushroom growing from the mycelium, this structure is called a _______________________________ ___________________________. 30. Fruiting bodies produce _________________________________ which can grown into a new fungi. How do sexual and asexual reproduction compare? 30. An organism that reproduces asexually does not have to find a ____________________________. 31. Organisms that reproduce asexually tend to be well suited to their ____________________________________. 32. A major advantage of sexual reproduction is that it promotes _____________________________ in a species. 33. Why is sexual reproduction better than asexual reproduction for ensuring the survival of a species in a changing environment? ________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Reproduction Study Guide - Answers Name _______________________________ Test Date _______________ Parent Signature ______________________________________________ Reproduction What are sexual and asexual reproduction? 1. Survival of a species depends on its ability to produce offspring. 2. Every organism comes from a parent through the process of reproduction 3. The transfer of genetic material from parents to their offspring is known as reproduction. 4. Genetic material contains the information that controls an organism’s structure and function. 5. The production of a new organism from two parents is called sexual reproduction. 6. When an egg cell joins with a sperm cell, fertilization occurs. 7. Egg and sperm cells are examples of sex cells. 8. A fertilized egg develops into an individual with traits from each parent. 9. The production of a new organism from a single parent is called asexual reproduction. Offspring are identical to parent because they have same genetic information. How do organisms reproduce asexually? 10. Most bacteria and unicellular protists reproduce by making a copy of their genetic material and splitting. 11. Cnidarians, sponges, and some fungi can reproduce through budding. 12. The eggs of insects, fish, frogs, and lizards sometimes develop into new animals without being fertilized. 13. New plants can grow from leaves, roots, or stems. This type of asexual reproduction is called vegetative propagation. 14. Strawberry plants and ferns can reproduce asexually by forming runners. This is a form of vegetative propagation. How do plants and animals reproduce? 15. When plant and animals reproduce sexually, a fertilized egg develops into an embryo. Seeds and Fruits 16. The fertilization takes place in the ovary of a flower. 17. The embryo in a flowering plant develops in the seed. 18. As the seed develops, the ovary enlarges to become a fruit. 19. The development of a seed into a new plant is called germination. Animal Eggs 20. Animals that reproduce sexually begin as fertilized egg cells that develop into embryos. 21. The egg’s yolk provides food for a developing embryo. 22. Reptiles and birds have eggs filled with a liquid and surrounded by a tough shell so their eggs can be laid on land. 23. The embryos of most mammals develop inside the mother. 24. Monotremes are the only mammals that lay eggs. How do fungi reproduce? 24. Yeast reproduce asexually through budding. 25. Eventually the bud breaks off and lives as a new, individual organism. 26. Multicellular fungi can also reproduce asexually. 27. These fungi are made of tiny filaments called Hyphae. Hyphae tangled together form mycelium. 28. If you have ever walked through the forest and seen a mushroom growing from the mycelium, this structure is called a fruiting body. 29. Fruiting bodies produce spores which can grown into a new fungi. How do sexual and asexual reproduction compare? 30. An organism that reproduces asexually does not have to find a mate. 31. Organisms that reproduce asexually tend to be well suited to their environments. 32. A major advantage of sexual reproduction is that it promotes variety in a species. 33. Why is sexual reproduction better than asexual reproduction for ensuring the survival of a species in a changing environment? During sexual reproduction each offspring has a unique combination of traits from both parents. This gives a better chance that at least some of the offspring will be better adapted to a changing environment. During asexual reproduction the offspring is genetically identical to the parent. Without variation, offspring may not be as well adapted to a changing environment.