The Cell ppt..
advertisement
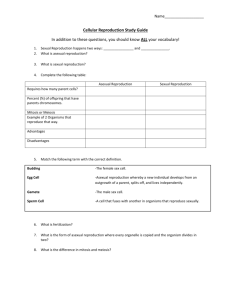
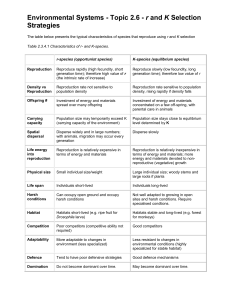
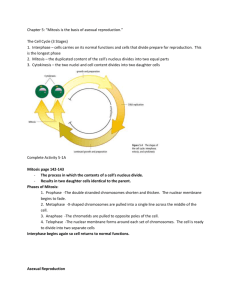
The Cell Theory Science 8: Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Organ Systems Curriculum Outcomes Addressed: - Illustrate and explain that the cell is a living system that exhibits the following characteristics of life (304-4) - Explain that growth and reproduction depend on cell division (304-6) http://us.123rf.com/400wm/400/400/eraxion/eraxion1006/eraxion100600408/7149016-human-cells.jpg The Cell Theory • The cell theory is a theory or method used to classify things as either living or non-living. • The two main points of the cell theory state that – All living things are composed of cells – All cells come from pre-existing cells Characteristics of Living Things The cell theory consist of six characteristics of living things. Anything that has all six of these characteristics is classified as a living thing. 1. Living things are composed of cells 2. Living things reproduce, grow, and repair themselves 3. Living things require energy 4. Living things respond to the environment 5. Living things have a life span 6. Living things produce wastes Characteristics of Living Things 1. Living things are composed of cells All living things (plants and animals) are made up of cells. Non-living things are not made up of cells Characteristics of Living Things 2. Living things reproduce, grow, and repair themselves Living things are able to reproduce (make more versions of themselves) either by sexual reproduction (meiosis) or asexual reproduction (mitosis). Living things grow by continuously making more copies of their cells via mitosis (cell division). Living things are able to repair themselves (for example, to heal a scar) by making more copies of their cells via mitosis (cell division). Characteristics of Living Things 2. Living things reproduce, grow, and repair themselves There are two ways (methods of cell division) by which cells can make copies or versions of themselves. MEIOSIS: A type of cell division that results in two daughter cells, each with half the chromosome number of the parent cell. This is referred to as sexual reproduction. An example of this is the reproduction of a baby cow by two parents. MITOSIS: A type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each the same as the parent cell. This is referred to as asexual reproduction. An example of this is tissue growth (healing a scar). Characteristics of Living Things 3. Living things require energy All cells (and therefore, living things) need energy in order to carry out their everyday functions, ranging from the smallest tasks such as breathing or healing a scar, to larger tasks such as hunting or reproducing (producing offspring). Plants get their energy from the sun (in order to carry out photosynthesis, for example), and animals get their energy from eating nutrients or from eating other animals that get their energy from plants. What happens to a plant that is cut off from the sun for a long period of time? What happens to a person whose food is taken away for a long period of time? Their cells stop working, and they eventually die. Characteristics of Living Things 4. Living things respond to the environment Living things and their environments are interconnected. A person’s skin may burn or turn brown in response to being exposed to the sun; a species of prey animals might evolve its colour over time in order to blend into the environment so that they are less easily spotted by their predators; wolves may adapt to hunt in a different location if their current environment runs out of their prey species; a plant may change its direction of growth over a short period of time, leaning closer to where the sunlight comes from on a daily basis. All of these are examples of ways in which living things respond to their environment. Characteristics of Living Things 5. Living things have a life span Living things exist only for a limited period of time. The natural course for any living thing is that it eventually dies; plants eventually wilt, people grow old and pass away, and every species of animal has its own range of life span. The most common theory as to why living things die is that is that cells fail to copy themselves accurately as the organism ages Characteristics of Living Things 6. Living things produce wastes All living things need to remove waste from their bodies because they can be poisonous if kept inside. All living things produce some type(s) of wastes; Humans and animals excrete liquid waste as urine, unused or superfluous food and nutrients as feces, and other wastes when they breathe out (carbon dioxide); Plants excrete oxygen via photosynthesis during respiration. The Size of Cells • The majority of cells are microscopic and cannot be seen with the unaided eye (without a microscope) Interactive Cell Size and Scale: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/cells/scale/ Alive or Not? • http://www.thinkcans.net/gamescentre/alive-or-not-alive