Extra Genetics Practice Problems
advertisement

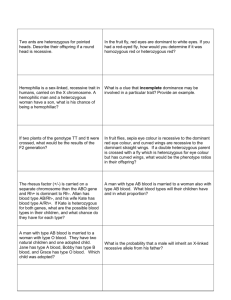
MORE GENETICS PRACTICE PROBLEMS Dihybrids/ Incomplete & Codominance/ Probability 1. A certain type of plant has red flowers (R) if they are dominant and white flowers (r) if they are recessive. Plant height also shows regular dominance – tall is dominant (T) and short is recessive (t). Cross a white tall flower that is heterozygous for height with a homozygous dominant flower. Show the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring 2. Dimples and freckles are both dominant: D = dimples F = freckles d = no dimples f = no freckles a. Cross a man that is heterozygous for both dimples and freckles with a woman who is homozygous dominant for dimples with no freckles. What is the probability that the offspring will be dominant for both features? b. Use the above cross. What is the probability that the offspring will be dominant for ONE trait and recessive for the OTHER? c. Cross a man that has no dimples but is heterozygous for freckles with a woman that has dimples but no freckles. The woman’s mom did not have dimples. What is the probability that the offspring will be dominant for both traits? d. Use the cross above (in part C). What is the probability that the offspring will be dominant for ONE trait and recessive for the OTHER? 3. In pea plants, the following traits are dominant/recessive: F – purple flowers R – round seeds f – white flowers r – wrinkled seeds This is your parental cross: T – tall plant t – short plant FfrrTt x ffRRTt a. What is the probability that you will have a dominant phenotype for AT LEAST 2 of the traits? b. What is the probability that you will have a dominant phenotype for all three traits? c. What is the probability that you will have a dominant phenotype for one trait and recessive phenotypes for the other two traits? d. What is the probability that you will have a recessive phenotype for all three traits? 4. In a certain type of dog, here are the following traits: (this is made up) B – brown fur b – white fur E – brown eyes e – blue eyes F – straight fur f – curly fur T – long tail t – short tail R – floppy ears r – pointy ears a. Write the genotype for the following individuals: i. White, homozygous dominant for eyes and fur type, long tail (heterozygous) with pointy ears ii. Heterozygous for fur color and eye color, pure straight fur, short tail and pointy ears iii. Heterozygous for all traits b. For the following crosses, here is your parental cross: BBeeFfTtrr x bbEeFfttrr i. What is the probability that the offspring will have a dominant phenotype for only two traits and recessive phenotypes for the other three traits? ii. What is the probability that the offspring will have a dominant phenotype for only one trait and will have the recessive phenotype for the other four traits? iii. What is the probability that the offspring will be heterozygous for all 5 traits? 5. Some birds are dark blue (B) and some birds are white (B’). A heterozygous bird has blue and white spots. Cross a dark blue bird with a white bird. What are the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring? Now cross two of those offspring to get the F2 generation. What are those genotypes and phenotypes? 6. Neck length in giraffe’s is incompletely dominant. When you cross a long neck giraffe (N) with a short neck giraffe (n), all the offspring have medium-length necks. Cross a long neck giraffe with a medium neck giraffe. Show the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. 7. Flower color is codominant (red and white), and plant height shows normal dominance. a. Cross a pure red short plant with a red/white spotted plant that is heterozygous for height. Show your punnett square and genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. b. Cross a white short plant with a plant totally heterozygous. Show your punnett square and genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. c. Consider that this is your parental cross: RRTt x RR’tt i. ii. iii. iv. What is the probability that you are going to get a spotted plant (can be tall or short)? What is the probability that you are going to get a red plant that is tall? What is the probability that you are going to get a white plant that is short? What is the probability that you are going to get a spotted plant that is short? 8. Fur color is incompletely dominant in a certain type of bears. A brown (B) bear crossed with a white bear (b) gives you a tan bear. Big ears are dominant (E) to small ears (e). a. Cross a tan bear with small ears with a brown bear heterozygous for ear size. b. Cross a white bear heterozygous for ear size with a brown bear with small ears. c. Cross a brown bear with pure big ears with a bear that is heterozygous for both traits. d. Consider that this is your parental cross: bbEe x Bbee i. ii. iii. iv. What is the probability that the bear will have big ears (can be any color)? What is the probability that the bear will be tan and have small ears? What is the probability that the bear will be white with big ears? What is the probability that the bear will be brown with big ears?