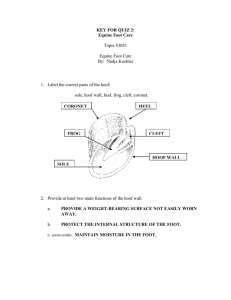
Foot Dissection (ch.15)
advertisement

Foot Dissection (ch.15) Diseases (ch.39) Correcting Faults of Confirmation and Gait (ch.45) 1. Why is it important to wear gloves when handling the specimen? To protect yourself from possible infections because specimens are frequently contaminated with Clostridium (Gas-forming bacteria) and other pathogens (disease causing bacteria). 2. Why must horseshoers know where the structures of the foot are in relation to each other? To properly remove horn from a normal or distorted foot, drive nails into it, or change weight distribution 3. The veterinarian is responsible for the medical treatment of a condition and the farrier is responsible for __________? The mechanical treatment. 4. What do D.A.C.C.T Stand for? Definition, Anatomy, Clinical signs, Cause, Treatment 5. What is the definition of Abscess? Common sepsis (infection) of the corium of the foot 6. When dealing with abscesses, you want to make sure the horse has had a current_________________? Tetanus shot 7. What is the definition of Avulsion of hoof? Loss of the hoof by tearing or sloughing. 8. What is the definition of Clubfoot? A deformed distal phalanx with a smaller hoof than the corresponding foot and a steeper angle of more then sixty-five degrees. May be inherited, acquired due to overnutrition during a growth period, or atrophied due to pain from trauma. 9. What is the definition of Coffin joint disease? Osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease of the coffin joint. 10. What is the treatment for contracted heels? Remove pain, frog pressure; pad to hold hoof moisture; thinning toe wall; hinged shoe with progressively larger inserts. 11. What is the treatment for Corns? Remove shoes; trim seat of corn below wall and bars. Bar shoe, or heart bar shoe, three-quarter bar shoe, or mushroom shoe to transfer weight and concussion to frog. Drain abscesses. 12. Fractures of the distal phalanx are classified into how many types? Seven (pg.530) 13. A hoof crack is referred to by location, what are the four locations? Toe, quarter, heel, bar 14. What is the definition of Keratoma? Rare horn tumor of the hoof wall that produces pressure on the distal phalanx. 15. How is Keratoma caused? Injury to the coronary band, hoof grooving, a hoof crack, a close nail, or a large hammered-in clip. 16. What is the definition of Laminitis/Founder? Serious systemic disease that affects the coria, causing a destruction of the hoof/bone bond resulting in the rotation and/or sinking of the distal phalanx, and leading to hoof distortion and lameness. 17. What is Low Ringbone? The exostosis and periostitis around the coffin bone. 18. What is Navicular Disease? Degeneration or accelerated remodeling of the navicular bone and related structures. 19. What are the three navicular disease forms? Articular (coffin joint and articular cartilage), Tendinous (navicular bursa and deep flexor tendon), and Ligamentar (Impar (distal) and collateral (Suspensory) navicular ligaments) 20. What is the treatment for Navicular disease? Raise hoof angle, dress toe back, move breakover back with rocker toe, support limb with egg bar shoe. 21. What is the definition of Osteromyelitis? Sepsis (infection) of the distal phalanx. Common sequel of founder. 22. What is the treatment for Pedal Osteitis? Relieve sole pressure; Heart bar shoe; cushioning pad. 23. What is the definition of Quittor? Sepsis of the lateral cartilage. 24. What can corrective shoeing do? Prevent wear and thus maintain balance or designed imbalance. Affect the placement and movement of the foot at the moment of landing or breaking by shoe configuration, shape, or projection. Increase the flight arc of the foot by addition of weight. 25. What defect can happen during a run or a gallop? Speedy cutting 26. What is Scalping? The interference between the toe of the front foot and the coronary region of the hind foot on the same side. By Justin t.