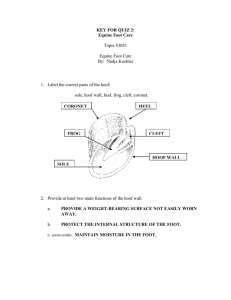
Understanding the Equine Hoof A. Parts of the Hoof

KEY
Note Taking Guide
Topic# 3051
Understanding the Equine Hoof
By: Nadja Koehler
A.
Parts of the Hoof
a.
Hoof Wall i.
Made up of keratinized epithelial cells ii.
Cells are arranged in tubules and run from
. coronary band to ground surface iii.
Hoof wall is thicker
. becomes thinner at the quarters at the toe and
. iv.
To give color the hoof wall contains pigment.
v.
Functions
1.
Helps retain moisture .
2.
Provides weight bearing surface for hoof .
3.
Protects internal structures of foot . b.
Laminae i.
Two layers
1.
_ Insensitive ________--forms of hoof wall. inner layer
2.
__ Sensitive _________--covers surface of coffin bone c.
Bars ii.
White Line
1.
Yellowish colored area where the two layers intermesh. i.
Area of hoof wall that is reflected back
toward the toe. ii.
Location: heel area of hoof iii.
Function: prevent over-expansion of hoof wall
.
.
d.
Sole i.
Covers bottom of coffin bone. ii.
Sensitive iii.
Self-limiting growth-- sloughs off when thickness becomes geater than thickness of hoof wall . iv.
Concave at ground surface
1.
This prevents sole from bearing weight directly v.
Easily bruised e.
Frog i.
Location: occupies area between bars ii.
1.
Occurs when bearing excessive weight such as heavy riders (for size of horse) or when a horse has “flat feet”.
Shaped like a
1.
Apex—point wedge .
2.
Cleft—ridge iii.
Sensitive iv.
Produced by papillae v.
Elastic—flexible
1.
Kept this way by greasy secretions from fat glands between digital cushion and frog
2.
Moisture content of frog is
50%. f.
__ Digital________ Cushion i.
Also called plantar cushion. ii.
Fleshy “heel”. iii.
Functions: shock absorber for foot pumps blood from foot back to heart g.
Bones i.
____ Three ________ bones:
1.
___ Short Pastern ___________--Partly in and above hoof.
2.
___ Navicular _______________--Smallest, increases articulation and movement of coffin bone.
3.
___ Coffin ________________--Largest bone. Located to front and outer side of hoof. Provides shape and rigidity needed for weight bearing.
Resembles a miniature hoof in shape.
B.
The Hoof as a Heart
a.
Blood is pumped to the hoof arteries. from the heart through b.
When your horse steps on the ground pressure is put on the veins in the plantar cushion which forces the blood back to the heart. c.
As your horse lifts up its foot the pressure is and the blood flows back to the hoof due to heart pulses . released gravity and
C.
Healthy Hooves
a.
Most lameness can be prevented by management . b.
The horses frog c.
Good foot care includes: proper foot care and is a good indicator of foot health. i.
Regularity-- routine cleaning ii.
Frequency-- periodic trimming
.
. iii.
____ Cleanliness _____________ iv.
Use of proper corrective measures-- and treatment d.
Always clean from heel to toe.
. corrections e.
Applying too much pressure during cleaning can cause damage and/or disturb moisture balance . f.
The goal or trimming is: to maintain proper shape and length of hoof g.
Your horse’s hooves should be trimmed every
4-6 weeks depending on usage.
D.
Causes of Lameness
a.
Stone in the Foot i.
Stones lodge between shoe and frog . b.
Bruised Sole i.
Direct injury of flat of foot by stones or irregular ground. c.
Corns i.
Bruising of sole between bar and hoof wall. ii.
Caused by: poor fitted shoes or irregular reshoding d.
Pricked Foot or PUNCTURE WOUNDS i.
Foreign objects directly entering e.
Hoof Cracks sole . i.
Occur mostly from dry or untrimmed hooves but can also occur by injury of hoof-forming tissue. f.
___THRUSH___________ i.
Bacterial infection of frog and sole due to irregular cleaning and dirty conditions . g.
__LAMINITIS__________ i.
Inflammation of the laminae. ii.
Caused by:
1.
overeating of grain
2.
3.
ingestion of cold water by a hot horse retained afterbirth
4.
an over fat horse
5.
h.
Navicular Disease idle horse on lush pasture i.
Injury to the navicular bone ii.
Common in breeds with genetic conformation defects.
. iii.
Heavy use on hard ground increases probability of occurrence.