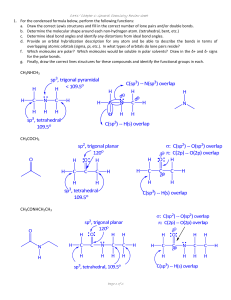
POST-LAB ASSIGNMENT
advertisement

CHML211 Exp. 1 Structure, Intermolecular Forces, and Solubility IN-LAB ASSIGNMENT: (EACH STUDENT will record the following data in his/her laboratory notebook in a well organized manner during lab period. Yellow carbon copies will be submitted for grading along with Post-Lab assignment.) …..max score = 20 pts. 1. Data/Calculations (The following information should be recorded directly into laboratory notebook.) NONE. All data will be entered directly into tables located in POST-LAB RESULTS section. 2. In-lab Questions (The following questions should be answered in laboratory notebook.) a. List the four factors that determine the relative polarity of a substance. b. Classify the following structures as hydrogen bond donors and acceptors (HDA), hydrogen bond acceptors only (HA), or neither. For the structures classified as HDA and HA, use an arrow to indicate where the hydrogen bonding can occur with another molecule. H H N O N OH O O isopropyl alcohol O propyl acetate O diethyl ether o-nitroaniline benzene CHML211 Exp. 1 Structure, Intermolecular Forces, and Solubility POST-LAB ASSIGNMENT: (EACH LAB GROUP will submit one copy of a typewritten, paragraph style report addressing all of the points listed below. Must be written using PAST TENSE, PASSIVE VOICE. ) …..max score = 50 pts. 3. Experimental (Write 1-2 paragraphs including all of the following. Do NOT present a bulleted outline.) Briefly describe the process used to determine the miscibility of organic liquids in water. Be sure to include names and volumes of any compounds used in this process. Briefly describe the process used to determine the miscibility of alcohols in hexane vs. water. Be sure to include names and volumes of any compounds used in this process. Briefly describe the process used to determine the solubility of organic solids. Be sure to include names and volume/mass of any compounds used in this process. 4. Results (Copy and paste the completed tables into your document.) Table 1.1 Miscibility of organic liquids and water Solvent IMF H2O Miscibility Structure (circle all (M or IM) that apply) Solvent Identity A methanol LDF HBA D-D HBD B ethyl acetate LDF HBA D-D HBD C dichloromethane LDF HBA D-D HBD D toluene LDF HBA D-D HBD E hexane LDF HBA D-D HBD Alcohol methanol F ethanol G 1-propanol H 1-butanol I Organic Layer (Top or Bottom) Table 1.2 Structure and miscibility of alcohols in hexane and water IMF Hexane Boiling Structure (circle all Miscibility Point (Co) that apply) (M or IM) LDF D-D HBA HBD LDF D-D HBA HBD LDF D-D HBA HBD LDF D-D HBA HBD H2O Miscibility (M or IM) Table 1.3 Structure and solubility of organic solids Organic Solid Structure IMF (circle all that apply) hexane J K L benzoic acid sodium benzoate naphthalene LDF HBA Solubility (Sol or Insol) water 10% NaHCO3 1M HCl D-D HBD I-D LDF HBA D-D HBD I-D LDF HBA D-D HBD I-D M p-nitroaniline LDF HBA D-D HBD I-D 5. Discussion (Write 1-2 paragraphs including the following.) Which solvents formed the top layer when mixed with water? Which solvents formed the bottom layer when mixed with water? Does this make sense based on the density of these solvents compared to that of water? Give actual numerical values to support your conclusion. Which alcohols were miscible with water, but not hexane? Which alcohols were miscible with hexane, but not water? How does the length of the carbon chain affect the molecular weight? Which intermolecular force increases with increasing molecular weight? How does the length of the carbon chain affect the boiling point of the alcohol? Does increasing the carbon chain length result in the alcohol becoming more polar or more nonpolar? Which organic solids were soluble in hexane? What intermolecular forces do the solid and hexane have in common? Which organic solids were soluble in water? What intermolecular forces do the solid and water have in common? Which organic solids were soluble in 10% NaHCO3? Some solids which were insoluble in water appear to be soluble in 10% NaHCO3. What effect does adding this aqueous basic solution have on this solid that accounts for this difference in solubility? Which organic solids were soluble in 1M HCl? Some solids which were soluble in water appear to be insoluble in 1M HCl. What effect does adding this aqueous acidic solution have on this solid that accounts for this difference in solubility? Include a short comment addressing what could be done differently to improve the experimental results, if repeated.