File
advertisement

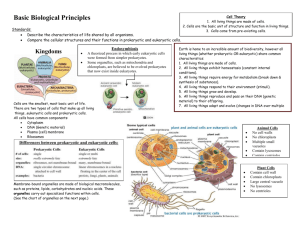
Name: _____________________________________________ Date: ____ Pd: ____ Review: Chapter 4 Test… complete by Friday, day of test. List of Topics on Test: Cell Organization: Cells -> Tissue -> Organ -> Organ System Significance of Microscope Robert Hooke Anton Van Leeuwenhoek Matthias Schleiden Theodor Schwann Rudolf Virchow The Cell Theory!!! (3 Parts) Surface Area to Volume Ratio (small cells vs. big cells) 3 Basic Parts of Cell (think egg) Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cell (IMPORTANT!!!) Plant Cell vs. Animal Cell Different Organelle Structure and Function 4.1 Cell Organization 1. Cells make tissues which make organs which make organ systems which finally make the organism. 2. Which of the following is an organ system and why: the stomach, a muscle cell within the stomach or the digestive system. (complete sentences) The digestive system is an organ system because it is composed of more than one organ (stomach, esophagus, small and large intestines, etc.). 3. Atoms and molecules make up cells. Are atoms and molecules LIVING? Explain. (complete sentences) Atoms and molecules are NOT living because they do not have the 7 characteristics for life. However, atoms and molecules compose cells which are the smallest basic unit for life. 4.1 History of the Cell Match the following scientists with their corresponding credit to the field of biology. 4. ___b__ Matthias Schleiden a. discovered live cells (sperm, blood) 5. ___e__ Theodor Schwann b. all plants are made of cells 6. ___c__ Rudolf Virchow c. all cells come from existing cells 7. ___d___ Robert Hooke d. discovered dead cells (cork, a plant) 8. ___a__ Anton Van Leewenhoek e. all animals are made of cells 9. Explain why the microscope was so essential to the discovery of the cell. (complete sentences) Cells are typically much too small to be able to observe with the naked eye. The microscope makes the image look much larger than it is in actuality, so you can see the cell when it’s magnified. 10. List the 3 parts of the cell theory. (1) All living things are made of cells (2) Cells are the basic structure and function of organisms (3) Cells come from existing cells 4.2 Cell Structure and Function 11. List 3 reasons why it’s better to have a smaller cell than a larger cell: (1) Nutrients, oxygen, waste, etc. can be transported in/out of the cell faster (more efficient, because of large surface area to volume ratio) (2) Molecules can more across the cell faster if it’s small (more efficient) (3) The nucleus has an easier time maintaining the functions of a smaller amount of cytoplasm 12. In our mini-experiment, we noticed that granulated sugar dissolves faster than the same mass of sugar, but in sugar cube form. Explain why this is, specifically talking about surface area and volume. (complete sentences) Although we used the same amount (volume as well as mass) of sugar, the granulated sugar dissolved faster because it had a much greater surface area than the compact cube of sugar. In other words, more of the surface of the sugar was exposed if it’s broken up for water to have access to the sugar molecules to pull them apart. This is like a cell because the smaller the cell, the greater surface area to volume ratio it has, and the more efficient the cell is at transporting material in and out of the cell. 4.3 Parts of the Cell 13. List the 3 basic parts of the cell: (*think of an egg!!!) (1) Cytoplasm (in all cells) (2) Plasma/Cell Membrane (in all cells) (3) Nucleus (only in eukaryotic animal and plant cells) 14. Put a check mark in each box representing what cell(s) each organelle/feature belongs to. Organelle/Feature Nucleus Cell/Plasma Membrane Cell Wall Cytoplasm Linear DNA Circular DNA Ribosomes Mitochondria Golgi Apparatus Vesicles (ex: lysosomes) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic x x (plant only) x X Prokaryotic x X X X X x X x X X X 15. What is the function of mitochondria? What important molecule does it make? It’s the powerhouse of the cell because it takes food energy and turns it into ATP. ATP can be used directly by the cell and stores energy—recall that you lose a phosphate group and energy is released. 16. What is the function of the Golgi apparatus? It’s the post office of the cell because it receives secretions and repackages it with a new membrane that has markers on it for a certain location in the cell. (Basically it receives, repackages, and ships stuff out into the cell.) 17. What is the function of ribosomes? The ribosome is the place of protein synthesis. 18. How do rough ER and smooth ER differ (both in structure and function)? RER has ribosomes and therefore synthesizes protein. SER has NO ribosomes and looks smooth and is the place where steroids are synthesized. 19. Which controls the cell, the nucleus or DNA? Explain your reasoning. (complete sentences) DNA controls the cell because all cells have DNA and need cellular control, but all cells do not have a nucleus. For example, bacteria is a prokaryotic cell and does not have a nucleus, but does have circular DNA floating around in the cytoplasm. It’s this DNA that controls cellular function. 4.4 Animal Cells vs. Plant Cells 20. Is a plant cell more similar to bacteria or an animal cell? Explain. (complete sentences) A plant is more similar to an animal cell because both are eukaryotic and hence have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. However, keep in mind that both plant cells and prokaryotic cells, like bacteria, do have cell walls that an animal cell does not have. 21. What are the 3 things that a plant cell has that an animal cell does not? (1) Cell Wall (2) Large, Central Vacuole (3) Plastid (ex: chloroplast) 22. Which will keep a plant from wilting, the cell wall or the vacuole? Explain. (complete sentences) A vacuole keeps a plant from wilting because it’s the place where most of the fluid is stored in a plant cell. The more fluid there is in the cell, the larger the cell is. However, if a plant lacks water and is wilting, then the vacuole also lacks fluid and the cell begins to shrink. When the cell shrinks, the plant withers and eventually dies. 23. What is the function of a chloroplast? Why is this important for a plant (hint: think back… a plant is an autotroph)? (complete sentences) A chloroplast is a plastid and makes its own food for the cell. This is essential for plant cells because they are autotrophs, meaning they make their own food from sources like sunlight (in the case of chloroplasts). We do not make our own food, so animal cells do not have plastids like chloroplasts. Instead, we eat plants and animals to get food which eventually is changed into energy. Read over chapter 4, your notes and check online for the answers to this study guide! Good luck studying!!!