Section 3.4 Review Sheet: Passive Transport (Diffusion and
advertisement

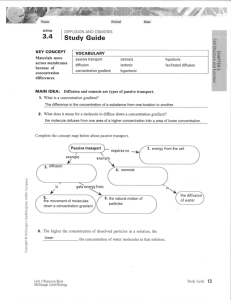
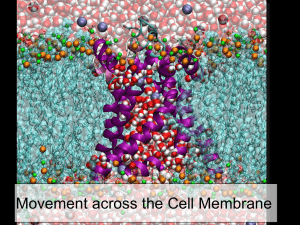
Section 3.4 Review Sheet: Passive Transport (Diffusion and Osmosis) Vocabulary for Section 3.4 • Osmosis • Diffusion • Passive transport • Concentration gradient • Isotonic – an isotonic solution has the same concentration of solutes as the cell, thus equal amounts of water enter and exit the cell. The cell’s size does not change. • Hypertonic – a hypertonic solution has more solutes than a cell, thus more water exits the cell in a hypertonic solution. The cell shrivels. • Hypotonic – a hypotonic solution has fewer solutes than a cell, thus more water enters a cell in hypotonic solution. The cell expands. • Solute – a substance dissolved in a solvent and is present at lower concentration than the solvent. For example, salt water is made up of a solvent, water, and a solute, sodium (sodium is dissolved in the water). Review Questions 1. What term describes the difference in concentration of a substance from one location to another? What does it mean for a molecule to diffuse down its concentration gradient? Concentration gradient. The molecule, say sodium, moves from a region of high sodium concentration to a region of low sodium concentration (thus the sodium has diffused down its gradient). 2. How does facilitated diffusion differ from diffusion? Explain why facilitated diffusion does not require energy from a cell? Molecules diffuse through protein channels. Energy is not needed because a molecule is still moving from a high concentration region to a low concentration region. 3. What term describes the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane down a concentration gradient? Osmosis 4. In which kind of solution would water move from the solution into the cell? Hypotonic 5. A cell is bathed in fluid. You notice that water is flowing out of the cell. In what kind of solution is this cell immersed? Hypertonic solution. 6. What would make a hypertonic solution isotonic? Add more water. Adding more water would change the solution’s concentration gradient. The added water would dilute the solution and change the concentration gradient. In an isotonic solution, the cell has an equal amount of water enter and exit cell (its size stays constant). Remember, a solution is isotonic to a cell if it has the same concentration of solutes as the cell. 7. When a person becomes dehydrated due to the loss of fluids and solutes, saline solution (water and salts) is infused into the bloodstream by medical personnel. Why is saline solution used instead of pure water? Pure water would be hypotonic relative to the contents of blood cells and could cause the cells to burst. The saline solution is isotonic relative to the cell contents.