Osmosis and Diffusion Practice Worksheet
advertisement

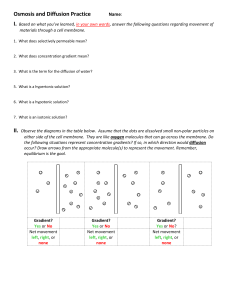
Osmosis and Diffusion Practice I. Name: Based on what you’ve learned, in your own words, answer the following questions regarding movement of materials through a cell membrane. 1. What does semi-permeable mean? 2. What is the net movement of molecules from high to low concentrations? 3. What is the term for the diffusion of water? 4. What does dynamic equilibrium mean? 5. What is a hypertonic solution? 6. What is a hypotonic solution? 7. What is an isotonic solution? II. Observe the diagrams in the table below. Assume that the dots are dissolved small non-polar particles on either side of the cell membrane. They are like oxygen molecules that can go across the membrane. Do the following situations represent concentration gradients? If so, in which direction would diffusion occur? Draw arrows from the appropriate molecule to represent the movement. Gradient? Yes or No Net movement left, right, or none Yes Right Gradient? Yes or No Net movement left, right, or none Yes Left Gradient? Yes or No? Net movement left, right, or none No None III. Observe the diagrams in the table below. Assume that the dots are dissolved particles (like protein or carbohydrate molecules) on either side of the cell membrane. Do the following situations represent concentration gradients? If so, in which direction would osmosis occur? = water, = dissolved particle. Again, use arrows to show the movement of the appropriate molecules. Gradient? Yes or No Yes 1free water molecule:5fwm Gradient? Yes or No Yes 7:1 Gradient? Yes or No? No. 3:3 Net movement left, right, or none Left (2 water) Net movement left, right, or none Right (3 water) Net movement left, right, or none None IV. Observe the table below. Are the following hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic solutions? Which way will water mostly move? (some situations may have water moving equally) intracellular fluid (inside the cell) 5% salt 10% salt 3% glucose 2% protein 9% salt 13% water 59% water 90% water 74% glucose extracellular fluid (outside of the cell) 10% salt 10% salt 1% glucose 1% protein 9% salt 25% water 45% water 92% water 87% glucose Hypotonic, Hypertonic, Isotonic Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic Hypotonic Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic Hypotonic Hypotonic water moves mostly inside or outside the cell outside inside inside inside outside inside inside 50% Salt Solution V. Observe the diagram and answer the questions. The boxes represent different solutions the same cell is placed in. Hypertonic 1. Label the boxes hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic. 1 0% salt 2. What will happen to the cell if it is placed in a 50% salt solution? (draw arrows showing water’s net movement) Cell will shrink as water moves out to equalize the free water molecule concentration on both sides of the membrane. 3. What will happen if the cell is placed in pure water? (draw arrows showing water’s net movement) Cell will swell as water moves out to equalize the free water molecule concentration on both sides of the membrane. Pure Water Hypotonic