Label the next clean front in your notebook “BRAINPOP
advertisement

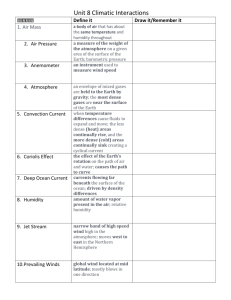
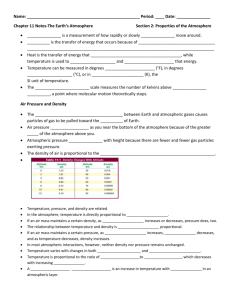
Label the next clean front in your notebook “BRAINPOP KNOWLEDGE” (like it’s a new notebook) Each new topic/ movie has its own page (or pages, depending on whether you use the back or not)!!! Your new “Table of Contents” should look like this: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Climate Types Weather Water Cycle Natural Disasters …and so on pg. 1 pg. 3 pg. 5 pg. 7 Facts for Notebook: Climate Types: Climate is an area’s pattern of weather over time. There are 5 major climate types worldwide. Tropical climates are hot because they receive more direct sunlight than other areas. (equator) Temperate climates often have very warm summers and cool winters. Oceans tend to make temperatures in coastal areas more extreme (makes warmer climate feel warmer; makes cooler climate feel cooler) Arid climates are very dry and receive very little rainfall. All deserts are not hot. For example: The Sahara desert is very hot, but the Gobi desert can sometimes have a temperature that drops below freezing. NEW PAGE Weather: Weather is the state of the atmosphere at any particular time. (Ask yourself: What is the atmosphere like RIGHT NOW? That’s the WEATHER!) Temperatures are lower at night because temperature depends on energy from the sun. (There is no sun at night, so there is less energy to heat the air) A thermometer measures temperature. “H” on a weather map stands for HIGH PRESSURE High pressure brings clear skies and sunny weather. “L” on a weather map stands for LOW PRESSURE Low pressure brings rain and stormy weather. A barometer measures air pressure. Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. The hotter the air outside, the more moisture the air can hold. You cannot see the water vapor in the air because it exists as a colorless gas. The difference between absolute humidity and relative humidity is absolute humidity refers to how much water the air CAN hold while relative humidity refers to how much water the air ACTUALLY holds. A hygrometer measures humidity. The earth’s poles tend to be cold because they do not get direct sunlight. Instead, sunlight strikes these points at different angles. NEW PAGE Water Cycle: The sum total of all the water on earth and its atmosphere is called the hydrosphere. Oceans, the atmosphere, and groundwater are all reservoirs (or storage places) in the water cycle. Water constantly cycles from the earth to the atmosphere and back. Draw this cycle in your notbook below this statement. Water Cycle Diagram Draw this cycle in your notebook here. The sun causes surface water to evaporate. When rainwater contributes to the flow of rivers and streams it is called runoff. Precipitation looks like this: Draw precipitation here. 2 examples of condensation would be 1. water vapor turning back to liquid in the air (clouds) 2. steam from a teapot turning back into liquid water The amount of water on Earth is constant. The amount we have now is the same amount we had 1000 years ago, and will be the same amount 1000 years from now. The oceans contain the most water on Earth. NEW PAGE Natural Disasters: Hurricanes, Thunderstorms, and blizzards are all meteorological disasters. (related to weather) The most common cause of tsunamis is underwater earthquakes. If a natural disaster happened in our area we would have to evacuate (or move to another area.) Items that should be in my “ready kit” List these items here. Tornadoes and hurricanes are similar because they both have strong winds. A blizzard (winter storm) is different from a hurricane in that winter storms are associated with extreme cold, and hurricanes are tropical storms that happen in warm water. Examples of natural disasters are: Tornado Draw a picture of a tornado here. Hurricane Draw a picture of a hurricane here. Tsunami Draw a picture of a tsunami here. Flood Draw a picture of a flood here. Blizzard Draw a picture of a blizzard here. Wildfire Draw a picture of a wildfire here. Earthquake Draw a picture of an earthquake here.