Solubility graph and solutions CW 1 What is the solubility of
advertisement

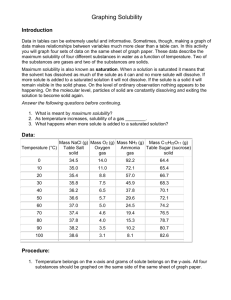
Solubility graph and solutions CW 1 1. What is the solubility of potassium nitrate (KNO3) in 100.0 g of water at 60.0°C? 2. What is the minimum temperature needed to dissolve 100 g of NaNO3 in 100.0 g of water? 3. What is the solubility of NaNO3 in 100 g of water at 60.0°C? 4. How much more KClO3 can be dissolved at 80°C than at 30°C? 5. How much more NaCl will dissolve at 100°C than at 50°C? 6. How much more NaNO3 will dissolve in 100 g of water at 30°C than KNO3? 7. A solution contains 50.0 g of NH4Cl in 100.0 g of water at 50°C. Is this solution saturated or unsaturated? 8. If 140 g of KNO3 is mixed with 100.0 g of water at 40°C, how much will not dissolve? 9. 70.0 g of solute is added to 100 g of water at 30°C. All 70.0 g of solute dissolves. According to your solubility chart, what possible compounds are capable of dissolving 70.0 g at 30°C? (Hint: there are only two) 10. A saturated solution of NH4Cl at 50°C is cooled to 30°C. What will happen? 11. If a saturated solution of KNO3 at 40°C is heated to 70°C, how much more could be dissolved? 12. A solution contains 30 g of KCl in 100.0 g of water at 80°C. Is this solution saturated or unsaturated? The following do not require info from the graph above: 13. What is the molarity of a solution that contains 275 g of NaCl in 955 mL solution? (molar mass of NaCl = 58.44 g/mol) 275 / 58.44 = 4.71 mol NaCl 14. How would you take a saturated solution and make it unsaturated? 15. How many moles of HCl are present in 1.30 L of a 0.63 M HCl solution? (molar mass of HCl = 36.46 g/mol) 16. If 220 mL of solvent is added to a 1.2 L 3.0 M solution, determine the concentration of the final solution. 17. A NaOH solution contains 0.70 mol of NaOH, and its concentration is 0.345 M. What is the volume? 18. Describe how to dilute 250 ml of a 3.0 M solution to a 1.0 M solution 19. How would you find out if a solution at 50°C was saturated? 20. How many milliliters of a 0.251 M solution contain 2.50 g of NaCl? (molar mass of NaCl = 58.44 g/mol) Solubility graph and solutions CW 1 Answers 1. What is the solubility of potassium nitrate (KNO3) in 100.0 g of water at 60.0°C? 100 g (start at 60°C, trace up to KNO3 line, then over to mass scale on Y-axis) 2. What is the minimum temperature needed to dissolve 100 g of NaNO3 in 100.0 g of water? 35°C 3. What is the solubility of NaNO3 in 100 g of water at 60.0°C? 124 g ( ± 2) 4. How much more KClO3 can be dissolved at 80°C than at 30°C? 30 g (difference in solubility at each temperature, 40 – 10, ± 2 on each) 5. How much more NaCl will dissolve at 100°C than at 50°C? (40 – 38, ± 1 on each) 2g 6. How much more NaNO3 will dissolve in 100 g of water at 30°C than KNO3? 96 – 46 = 50 g (solubility of NaNO3 – KNO3 at that temperature) 7. A solution contains 50.0 g of NH4Cl in 100.0 g of water at 50°C. Is this solution saturated or unsaturated? Saturated (The solubility is 50 g, so if you put in 50 g then it’s full) 8. If 140 g of KNO3 is mixed with 100.0 g of water at 40°C, how much will not dissolve? 140 – 60 = 80 g will not dissolve 9. 70.0 g of solute is added to 100 g of water at 30°C. All 70.0 g of solute dissolves. According to your solubility chart, what possible compounds are capable of dissolving 70.0 g at 30°C? (Hint: there are only two) KI and NaNO3 (only ones with solubility higher than 70 g at that temp) 10. A saturated solution of NH4Cl at 50°C is cooled to 30°C. What will happen? 50 – 41 = 9 grams will precipitate out of solution. (that’s how much the solubility drops, answer must be worded this way) 11. If a saturated solution of KNO3 at 40°C is heated to 70°C, how much more could be dissolved? 130 – 60 = 70 g more (or close to it) 12. A solution contains 30 g of KCl in 100.0 g of water at 80°C. Is this solution saturated or unsaturated? Unsaturated The following do not require info from the graph above: 13. What is the molarity of a solution that contains 275 g of NaCl in 955 mL solution? (molar mass of NaCl = 58.44 g/mol) 275 / 58.44 = 4.71 mol NaCl 4.71 / 0.955 = 4.93 M (round at the end) 14. How would you take a saturated solution and make it unsaturated? Heat it up or add more solvent 15. How many moles of HCl are present in 1.30 L of a 0.63 M HCl solution? (molar mass of HCl = 36.46 g/mol) 0.63 = n / 1.30 n = 0.82 moles 16. If 220 mL of solvent is added to a 1.2 L 3.0 M solution, determine the concentration of the final solution. (3.0) (1.2) = C2 (1.44) C2 = 2.5 M 17. A NaOH solution contains 0.70 mol of NaOH, and its concentration is 0.345 M. What is the volume? 0.345 = 0.70 / V (cross multiply) V = 2.0 L 18. Describe how to dilute 250 ml of a 3.0 M solution to a 1.0 M solution M1V1 = M2V2 (3.0) (250) = (1.0) V2 V2 = 750 mL Add 500 mL of solvent to the solution 19. How would you find out if a solution at 50°C was saturated? Cool it down to see if any precipitate forms or Add more solute and see if a precipitate forms 20. How many milliliters of a 0.251 M solution contain 2.50 g of NaCl? (molar mass of NaCl = 58.44 g/mol) 2.50 / 58.44 = 0.0428 moles 0.251 = 0.0428 / V V = 0.170 L 170 mL