Anaphylaxis - Plymouth Hospitals
advertisement

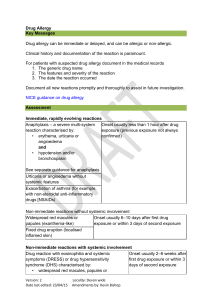
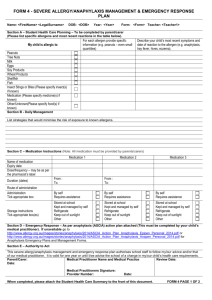
Anaphylaxis Key Messages Anaphylaxis is an acute severe systemic reaction which is most often allergic (but can be non-allergic, previously called anaphylactoid). It is commonly associated with urticaria and angioedema and occurs within minutes (typically less than 1 hour) of a trigger (eg food/drug/sting). Anaphylaxis is characterised by one or more of: i) ii) iii) iv) Airway – tongue/throat swelling, difficulty talking/hoarse voice Breathing – shortness of breath, wheeze, persistent cough Circulation – persistent dizziness or collapse, loss of consciousness Neurological – sense of impending doom, visual changes NICE guidance is that patients with a history of anaphylaxis should be referred to a specialist allergy clinic, and according to the specialist services national definition set 17 for allergy, “patients with anaphylaxis must be seen in a specialist allergy centre and not managed in the community”. For guidelines describing the management of urticaria and angioedema in the absence of systemic features see guidance for spontaneous urticaria and angioedema. Assessment and Management 1. Anaphylaxis should be treated immediately according to Resuscitation Council guidelines. Acute measurement of mast cell tryptase (immediately and 2 hours after the onset of symptoms) should be performed. 2. Identify any potential triggers (eg foods, drugs, stings, exercise) in the 4 hours before the reaction. 3. Advise patients to avoid potential triggers identified in the history pending further investigations. If a suspected trigger has been tolerated since the reaction it is excluded as a cause. 4. Prescribe self-injectable adrenaline (0.3mg x 2) with appropriate training to patients with: a. Anaphylaxis (see definition above) or a less severe allergic reaction in patients with asthma; And b. A potentially unavoidable suspected cause. All patients must have appropriate training in use of self-injectable adrenaline. Guidance is available at https://www.epipen.com/en/about-epipen/how-to-use-epipen Version: 3 Date last edited: 10/06/15 Locality; Devon wide Amendments by: Kevin Bishop Drug reactions are not an indication for self-injectable adrenaline, as drugs can usually be avoided unless there is altered consciousness. Investigations - Stings – check specific IgE to bee and wasp venom and mast cell tryptase. - Foods – check specific IgE to specific suspect foods 4 weeks after index reaction. There is no need to investigate foods which have been tolerated since the reaction as these are not the trigger. - Drugs – Ensure potential drug allergies are explained to the patient, and documented in the medical records with appropriate details. a. If there is a clear history consider identification jewellery. Referral Referral criteria Include details of index reaction with copy of appropriate correspondence (eg ED discharge summary) and suspected triggers. 1. Refer all patients with a history of anaphylaxis a. Patients with drug reactions should be referred if i. There is diagnostic uncertainty or multiple drugs were involved (especially where the reaction is systemic) ii. The suspected drug is essential for the patient’s ongoing management, and where alternatives clinically not suitable. Please document reasons for needing treatment with the drug. 2. Patients with a single obvious trigger for their anaphylaxis and no cofactors (eg asthma, cardiovascular disease) need not be referred routinely. Referral Instructions Refer to Peninsula Immunology and Allergy Service Refer via DRSS for NEW Devon CCG patients Choose and Book Selection Specialty: Allergy Clinic type: Allergy Service: DRSS- Western –Allergy & Immunology - CCG - 99p Referral forms DRSS Referral form Version: 3 Date last edited: 10/06/15 Locality; Devon wide Amendments by: Kevin Bishop Supporting Information http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/+/www.dh.gov.uk/en/Managingyourorganis ation/Commissioning/Commissioningspecialisedservices/Specialisedservicesdefinitio n/DH_4001689 http://www.siaip.it/upload/WAO_anaphylaxis_guidelines.pdf http://www.resus.org.uk/pages/reaction.pdf http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG134 Patient information http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/Anaphylaxis/Pages/Introduction.aspx http://www.anaphylaxis.org.uk/ https://www.allergyuk.org/severe-allergy-and-anaphylaxis/severe-allergy-andanaphylaxis http://www.medicalert.org.uk/ Evidence Pathway Group This guideline has been signed off by the Western Locality on behalf of NEW Devon CCG. Publication date: June 2015 Review date: May 2017 Version: 3 Date last edited: 10/06/15 Locality; Devon wide Amendments by: Kevin Bishop