Low-specificity L-threonine aldolase
advertisement

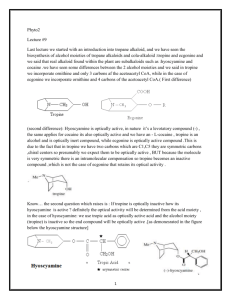
Tropine acyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.185, tropine:acyl-CoA transferase, acetyl-CoA:tropan-3ol acyltransferase, tropine acetyltransferase, tropine tigloyltransferase, TAT) is an enzyme with system name acyl-CoA:tropine O-acyltransferase.[1][2][3][4] This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction acyl-CoA + tropine CoA + O-acyltropine This enzyme exhibits absolute specificity for the endo/3alpha configuration found in tropine as pseudotropine. Glucokinase From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Jump to: navigation, search Glucokinase (hexokinase 4) Based on PDB entry 1GLK. Available structures Ortholog search: PDBe, RCSB PDB [show]List of PDB id codes Identifiers Symbols External IDs EC number GCK; FGQTL3; GK; GLK; HHF3; HK4; HKIV; HXKP; LGLK; MODY2 OMIM: 138079 MGI: 1270854 HomoloGene: 55440 ChEMBL: 3820 GeneCards: GCK Gene 2.7.1.2 [show]Gene Ontology RNA expression pattern More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 2645 103988 Ensembl ENSG00000106633 ENSMUSG00000041798 UniProt P35557 RefSeq (mRNA) RefSeq (protein) P52792 NM_000162 NM_010292 NP_000153 NP_034422 Location Chr 7: Chr 11: (UCSC) 44.18 – 44.24 Mb 5.9 – 5.95 Mb PubMed search [1] [2] This box: view talk edit Glucokinase EC number CAS number IntEnz BRENDA ExPASy KEGG MetaCyc Identifiers 2.7.1.2 9001-36-9 Databases IntEnz view BRENDA entry NiceZyme view KEGG entry metabolic pathway PRIAM PDB structures Gene Ontology profile RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum AmiGO / EGO [show]Search Glucokinase (EC 2.7.1.2) is an enzyme that facilitates phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate. Glucokinase occurs in cells in the liver, pancreas, gut, and brain of humans and most other vertebrates. In each of these organs it plays an important role in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism by acting as a glucose sensor, triggering shifts in metabolism or cell function in response to rising or falling levels of glucose, such as occur after a meal or when fasting. Mutations of the gene for this enzyme can cause unusual forms of diabetes or hypoglycemia. Glucokinase (GK) is a hexokinase isozyme, related homologously to at least three other hexokinases.[1] All of the hexokinases can mediate phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6phosphate (G6P), which is the first step of both glycogen synthesis and glycolysis. However, glucokinase is coded by a separate gene and its distinctive kinetic properties allow it to serve a different set of functions. Glucokinase has a lower affinity for glucose than the other hexokinases do, and its activity is localized to a few cell types, leaving the other three hexokinases as more important preparers of glucose for glycolysis and glycogen synthesis for most tissues and organs. Because of this reduced affinity, the activity of glucokinase, under usual physiological conditions, varies substantially according to the concentration of glucose.[2] Triglyceride lipases (EC 3.1.1.3) are a family of lipolytic enzymes that hydrolyse ester linkages of triglycerides.[1] Lipases are widely distributed in animals, plants and prokaryotes. At least three tissue-specific isozymes exist in higher vertebrates, pancreatic, hepatic and gastric/lingual. These lipases are closely related to each other and to lipoprotein lipase (EC 3.1.1.34), which hydrolyses triglycerides of chylomicrons and very low density lipoproteins (VLDL).[2] Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAP2K4 gene.[1] This gene encodes a dual specificity protein kinase that belongs to the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. This kinase is a direct activator of MAP kinases in response to various environmental stresses or mitogenic stimuli. It has been shown to activate MAPK8/JNK1, MAPK9/JNK2, and MAPK14/p38, but not MAPK1/ERK2 or MAPK3/ERK1. This kinase is phosphorylated, and thus activated by MAP3K1/MEKK. The knockout studies in mice suggested the roles of this kinase in mediating survival signal in T cell development, as well as in the organogenesis of liver.[2] Low-specificity L-threonine aldolase From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Jump to: navigation, search Low-specificity L-threonine aldolase EC number IntEnz BRENDA ExPASy KEGG MetaCyc PRIAM PDB structures Identifiers 4.1.2.48 Databases IntEnz view BRENDA entry NiceZyme view KEGG entry metabolic pathway profile RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum [show]Search Low-specificity L-threonine aldolase (EC 4.1.2.48, LtaE) is an enzyme with system name L-threonine/L-allo-threonine acetaldehyde-lyase (glycine-forming).[1][2][3][4][5] This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction (1) L-threonine glycine + acetaldehyde (2) L-allo-threonine glycine + acetaldehyde This enzyme requires pyridoxal phosphate.