CHEM 442 Lecture 23 Problems 23-1. Write down the Schrödinger
advertisement

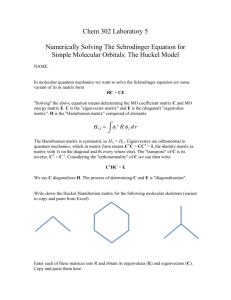
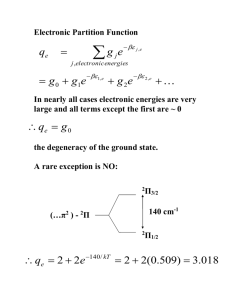
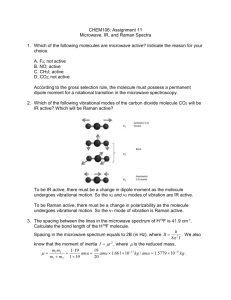
CHEM 442 Lecture 23 Problems 23-1. Write down the Schrödinger equation for the hydrogen molecule. Specify the range of summation indexes. 23-2. Write down the Schrödinger equation for the benzene molecule. Specify the range of summation indexes. 23-3. Write down the electronic Schrödinger equation in the Born–Oppenheimer approximation. Which coordinates are parameters and which are variables? 23-4. Write down the nuclear Schrödinger equation in the Born–Oppenheimer approximation. What is the potential energy surface? 23-5. Show mathematically that, in the limit that all nuclear masses tend to infinity, the molecular Hamiltonian reduces to an electronic Hamiltonian, which differs from the electronic Hamiltonian of 23-3 merely by a constant. 23-6. Explain how the concepts of equilibrium structure, dissociation energy, molecular vibrations, and molecular rotations derive from the Born–Oppenheimer approximation. 23-7. Draw the potential energy curves of the hydrogen molecule in the ground state (stable) and in the first excited state (unstable towards dissociation) as a function the atom-atom distance. Locate equilibrium bond lengths and draw vibrational energy levels. 23-8. Draw the potential energy curves of the water molecule in the ground state (stable) as a function of HOH bond angle. 23-9. What are the electronic, translational, vibrational, and rotational degrees of freedom in the hydrogen molecule? 23-10. What are the electronic, translational, vibrational, and rotational degrees of freedom in the benzene molecule?