Chemistry Terms
advertisement

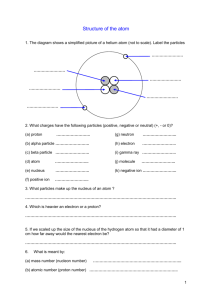
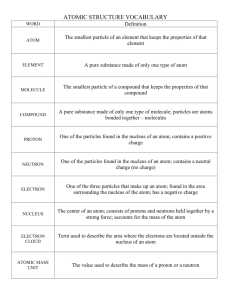
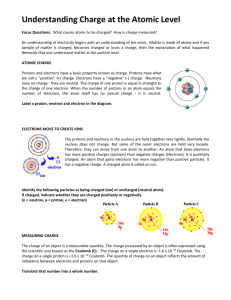
Chemistry Terms 63. chemical: a term used to descried a specific kind of atom or molecule 64. chemistry: the study of matter at the atomic level 65. atom: the smallest particle of an element that still has all the properties of that element 66. element: a pure substance made of only one kind of atom (approx. 92 natural elements) 67. molecule : molecules are made up of two or more atoms, the smallest amount of a compound that still has all the properties of the compound 68. nucleus: the central part of an atom made up of protons and neutrons 69. proton: positively charged particle of the atom found in the nucleus (each positively charged proton attracts 1 negatively charged electron) 70. neutron: particle of the atom with no charge found in the nucleus 71. electron: negatively charged particle of the atom found circling the nucleus (each negatively charged electron is attracted by 1 positively charged proton) 72. electron cloud: is the area around the atom’s nucleus where the electrons are found (also called: orbit, orbital, shell & energy level) 73. solid: the state of matter that has a definite shape and volume 74. liquid: the state of matter that does not have a definite shape but does have a definite volume 75. gas: the state of matter that does not have a definite shape or volume 76. interface: a boundary between two different substances 77. melting : when a solid changes into a liquid 78. freezing : when a liquid changes into a solid 79. evaporation: when a liquid changes into a gas 80. boiling: when a liquid quickly changes into a gas because it is heated 81. condensation: when a gas changes into a liquid due to a drop in temperature 82. solidification: when any other state of matter changes into a solid 83. liquefaction: when any other state of matter changes into a liquid 84. vaporization: when any other state of matter changes into a gas; (vapor is another word for gas) 85. sublimation: when a gas changes directly into a solid or when a solid changes directly into a gas (without going into a liquid state) 86. physical property: any characteristic of a substance that can be observed using the senses 87. physical change: a change in the size, shape or state of matter, (the original substance remains the same) 88. chemical property: a characteristic of a substance that describes how it behaves in a chemical reaction. 89. chemical reaction (change): a change that results in a new chemical or chemicals (the original substance(s) is changed into something new) 90. reactant: a chemical that is present when the chemical reaction begins 91. product: a new substance (chemical) present at the end of a chemical reaction 92. solution: formed when one substance is mixed completely with another 93. solute: the part of a solution that is dissolved (usually a solid) 94. solvent: the part of the solution that does the dissolving (larger amount/usually a liquid) 95. mixture: any solution that can be easily separated (by screen, filter, evaporation etc.) 96. compound: a substance made up of two or more different elements (water - H2O - is made of two different elements: hydrogen and oxygen) 97. periodic table: a chart of all the known elements: it gives information about the atoms of the different elements 98. chemical symbol: an abbreviation that represents each of the known elements on the periodic table and is used in chemical formulas (C - carbon, Fe - iron) 99. chemical formula: a description of a compound using chemical symbols and numbers (water’s chemical formula is H2O meaning 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen; glucose is C6H12O6) 100. atomic number: the number of protons in an atom 101. mass number (atomic mass) - total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom