learning plan - Melanie Dayle Lauren, RPN
advertisement
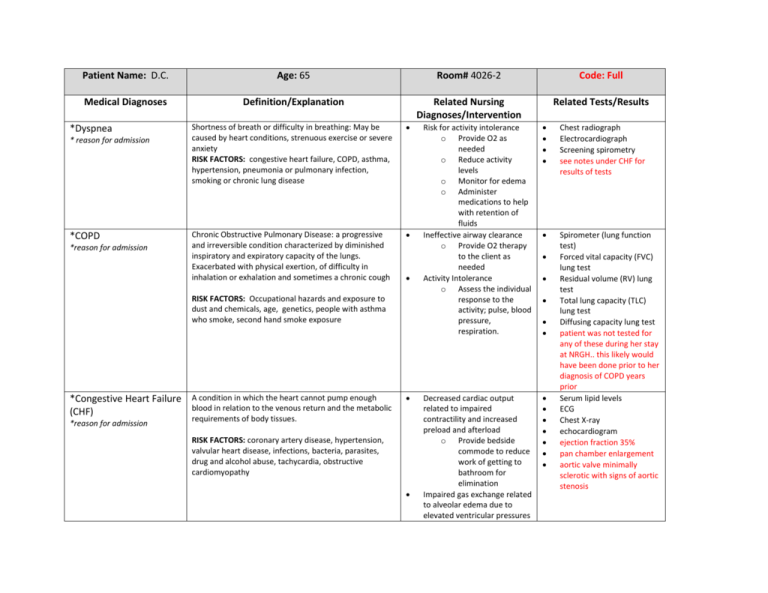
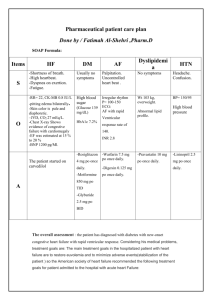
Patient Name: D.C. Age: 65 Room# 4026-2 Code: Full Medical Diagnoses Definition/Explanation Related Nursing Diagnoses/Intervention Related Tests/Results *Dyspnea * reason for admission *COPD *reason for admission Shortness of breath or difficulty in breathing: May be caused by heart conditions, strenuous exercise or severe anxiety RISK FACTORS: congestive heart failure, COPD, asthma, hypertension, pneumonia or pulmonary infection, smoking or chronic lung disease Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: a progressive and irreversible condition characterized by diminished inspiratory and expiratory capacity of the lungs. Exacerbated with physical exertion, of difficulty in inhalation or exhalation and sometimes a chronic cough RISK FACTORS: Occupational hazards and exposure to dust and chemicals, age, genetics, people with asthma who smoke, second hand smoke exposure *Congestive Heart Failure A condition in which the heart cannot pump enough blood in relation to the venous return and the metabolic (CHF) *reason for admission requirements of body tissues. RISK FACTORS: coronary artery disease, hypertension, valvular heart disease, infections, bacteria, parasites, drug and alcohol abuse, tachycardia, obstructive cardiomyopathy Risk for activity intolerance o Provide O2 as needed o Reduce activity levels o Monitor for edema o Administer medications to help with retention of fluids Ineffective airway clearance o Provide O2 therapy to the client as needed Activity Intolerance o Assess the individual response to the activity; pulse, blood pressure, respiration. Chest radiograph Electrocardiograph Screening spirometry see notes under CHF for results of tests Decreased cardiac output related to impaired contractility and increased preload and afterload o Provide bedside commode to reduce work of getting to bathroom for elimination Impaired gas exchange related to alveolar edema due to elevated ventricular pressures Spirometer (lung function test) Forced vital capacity (FVC) lung test Residual volume (RV) lung test Total lung capacity (TLC) lung test Diffusing capacity lung test patient was not tested for any of these during her stay at NRGH.. this likely would have been done prior to her diagnosis of COPD years prior Serum lipid levels ECG Chest X-ray echocardiogram ejection fraction 35% pan chamber enlargement aortic valve minimally sclerotic with signs of aortic stenosis o Hypertension Hypertension- a common, often asymptomatic disorder which is characterized by elevated BP persistently exceeding 140/90mm Hg. Essential HTN is the most common kind of HTN and has no identifiable cause RISK FACTORS: age; race; family history; weight; physical activity deficit; smoking; excessive sodium intake; stress; Potassium or Vitamin D deficiency; excessive alcohol intake; high cholesterol, sleep apnea; kidney disease Raise head of bed to reduce venous return to heart and lungs: alleviates pulmonary congestion o Administer O2 ad directed Excess fluid volume related to sodium and water retention o Administer diuretics as ordered o Keep track of input and output o Weigh patient daily to monitor edema Decreased cardiac output o Monitor blood pressure o Monitor peripheral and central pulse quality o Observe skin color, moisture, temp and cap refill o Observe for general edema Risk for ineffective tissue perfusion (cardiac, cerebral, periphery and visceral) o Maintain bed rest/elevate head of bed o Assess BP both lying and standing o Measure input and output o Monitor electrolytes, BUN and creatinine levels o Ambulate to ability; avoid exertion and Blood Pressure measurements patient’s postural BP averaged around 88/57 supine and 92/56 standing fatigue Microcytic Anemia Any time of anaemia characterized by small red blood cells. Blood cells are also hypochromic (paler) and therefore the concentration of hemoglobin is lower RISK FACTORS: iron deficiency, premenopausal women, older adults, alcoholism, chronic or critical injuries, iron poor diets, excessive exercise Diabetes Mellitus 2 A complex disorder of carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism that is primarily a result of a relative or complete lack of insulin secretion by the beta cells of the pancreas or of defects of the insulin receptors. Patients with Type II are also further classified into further categories of either Obese or Non Obese Imbalanced Nutrition: less than body requirements o Explain the importance of adequate nutrition o Weigh the body daily; monitor results of lab tests o Monitor blood glucose levels before every meal o Administer insulin as required Risk for injury related to GI bleeding o Examine stools and emesis for gross and occult blood RISK FACTORS: metabolic syndrome, race, age, diet, family history Acute Kidney Failure the rapid loss of the kidneys’ ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in the body RISK FACTORS: hospitalization, advanced age, diabetes, blockages, high blood pressure, kidney disease, liver Activity Intolerance/ o monitor vital signs o encourage alternate rest/activity to provide exercise without tiring patient Altered Nutrition: less than body requirements o Monitor and record intake of protein, iron and Vit C to provide nutrients needed for hematopoiesis o Suggest eating smaller more frequent meals to increase dietary intake Anemia tests Iron level 4 (low) Iron binding 88 (high) Iron Sat’s 0.05 (low) and full hematology profile WBC 11.5 (high) Hemoglobin 109 (low) MCV 80 (low) Red Cell Distribution 19.2 (high) Neutrophils 9.58 (high) Monocytes 1.15 (high) Liver profile: AST 1668 (high) ALT 934 (high) GGTP 198 (high) Troponin 0.49 (high) Blood glucose monitoring patient’s blood glucose sitting at 4.9, dropped from 6.3 steadily over the two days I had her Occult blood stool test o Patient was constipated and was not able to supply stool o disease, heart failure CVA Cerebrovascular accident (Stroke): an abnormal condition of the brain characterized by occlusion by an embolus, thrombus, or cerebrovascular hemorrhage or vasospasm, resulting in ischemia of the brain tissues normally perfused by the damaged vessels RISK FACTORS: age, race, gender, family history, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes GERD Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease: chronic disease characterized by the reflux (backwards movement) of stomach acid or sometimes bile into the esophagus. When the signs and symptoms of acid reflux occur more than twice a week or interfere with daily life, doctors then diagnose GERD. RISK FACTORS: Obesity; smoking; dry mouth; asthma; diabetes; delayed stomach emptying Administer H2 receptor antagonists (TUMS or other nonaluminum or magnesium antacids) as a prophylaxis for gastric stress ulcers Risk for ineffective renal perfusion o Assess for signs of decreased tissue perfusion o Assess for causative factors related to temporarily impaired arterial blood flow o Monitor INR and PT o Administer O2 as needed Infective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion o Maintain usual/improved level of consciousness, cognition, and motor/sensory function. Risk for discomfort o offer antacid relief as needed o eliminate acidic foods from diet Risk for electrolyte imbalance o ensure proper nutrition and fluid intake samples as required during my time with her Computed tomography MRI cerebral angiography patient did not have these tests during her stay at NRGH, but would have had these done when her CVA occurred sometime prior to her admittance Barium X ray Upper Endoscopy pH test tests indicated high levels of erosion in upper GI tract, and pH levels indicative of excessive gastric secretions Osteoarthritis (OA or Degenerative Arthritis) a joint inflammation that results from cartilage degeneration. RISK FACTORS: gender, age, bone deformities, joint injuries, obesity, certain diseases, certain occupations Impaired physical mobility o assist in movements that involve major joints and large muscle movements such as standing, sitting and reaching Self-Care deficit o Assist in personal care when required. o Provide cleaning supplies and items on bedside table and close to patient for ease of access. o provide call bell for patient to seek help when required Anti CCP test X-Rays These tests were not performed during the client’s stay in the hospital Medications Prednisone Class: therapeutic antiasthmatic Dose/Route: 25 mg PO Drug Interactions: thiazide and loop diuretics, digoxin Indications Used systemically in inflammatory, allergic, hematologic, neoplastic and autoimmune disorders (Used for COPD for this patient) Contraindications/Side Effects Use cautiously in chronic treatment. Avoid in known alcohol, bisulfite and tartrazine hypersensitivity Depression, euphoria, headache, increased intracranial pressure, hypertension, anorexia, nausea, acne, muscle wasting, osteoporosis, Domperidone Class: antidopaminergic/ antiemetic Dose/Route: 10 mg PO QID Drug Interactions: For management of dyspepsia, heartburn, epigastric pain, nausea, and vomiting. Side effects include galactorrhea, gynecomastia, or menstrual irregularities. Fluticasone-Salmeterol Class: corticosteroid Dose/Route: 250-500 mcg BID nebulizer Drug Interactions: Ketoconazole, Ritonavir, clarithromycin, erythromycin used in the management of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Candidiasis Headache, dysphonia, hoarseness, bronchospasms, cough, wheezing, adrenal suppression Clopidogrel Class: antiplatelet agent Dose/Route: 75 mg PO Drug Interactions: aspirin, NSAIDs, heparin, warfarin, thrombolytic agents, phenytoin, fluvostatin Reduction of atherosclerotic events (MI, stroke, vascular death) Depression, dizziness, fatigue, headache, cough, dyspnea, bleeding, neutropenia Paroxetine Class: anti-anxiety Dose/Route: 20mg PO Drug Interactions: MAOIs, cimetidine, digoxin, NSAIDs, tramadol Major depressive or panic disorders Anxiety, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, weakness, respiratory disorders, constipation, diarrhea, dry mouth, nausea, sweating Levothyroxine Class: hormones Dose/Route: 150 mcg PO daily Drug Interactions: Bile acid sequestrants. May increase effects of Warfarin, May increase insulin requirements in diabetes, Increased CV effects with adrenergics. Prescribed to help increase thyroid activity. Should not be used with calcium, iron, magnesium or zinc supplements Pantoprazole Magnesium Class: proton pump inhibitor Dose/Route: 40 mg PO BID Drug Interactions: warfarin and drugs requiring acid pH Reduces acid secretions in stomach. Used to treat erosive esophagitis associated with GERD Hypersensitivity, headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence, eructation Insulin lispro Class: insulin Dose/Route: supplemental SubQ QID and AM/Supper Drug Interactions: Diabetes- fast acting insulin Insulin isophane NPH Class: insulin Dose/Route: SubQ AM/Supper QID Drug Interactions: Diabetes- regular insulin Metoprolol Class: anti-anginal Dose/Route: PO Drug Interactions: general anaesthesia, IV phenytoin, verapamil, concurrent use with ephedrine, cocaine, amphetamines, epinephrine, MAOIs Ipatropium nebulizer (Atrovent) Class: bronchodilator Dose/Route: nebulizer Drug Interactions: Hypertension, angina pectoris, prevention of MI, management of class II or III heart failure. Iron Gluconate Class: iron Dose/Route: 300 mg PO Drug Interactions: dimercaprol Hypochromic anaemia Uncompensated CHF, pulmonary edema, cardiogenic shock, bradycardia, heart block Fatigue, weakness, constipation, blurred vision, wheezing, bradycardia, CHF, pulmonary edema COPD, asthma Dehydration, low BP, fast and weak pulse, shock, nausea, vomiting blood, dizziness, coma, convulsions, skin flushing Dalteparin Class: blood thinner Dose/Route: 5000 IU SubQ Q24hr Drug Interactions: Drugs that affect platelet function and coagulation incl. warfarin, aspirin, NSAIDs, clopidogrel, and thrombolytics PRNs Ipatropium Hypertension, CHF: prevention of venous thromboembolisms Ventolin Diarol bronchodilator Anti-hyperglycemic Indications bronchodilator Dizziness, headache, insomnia, edema, constipation, nausea, vomiting, urinary retention, anemia Contraindications/Side Effects Dizziness, headache, nervousness, blurred vision, sore throat, bronchospasm, cough, hypotension, palpitations