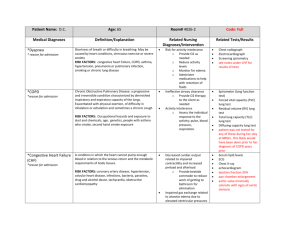
MEDICATIONS (a) Student: Erin Nowlin Client Information: MF 89 yr
advertisement
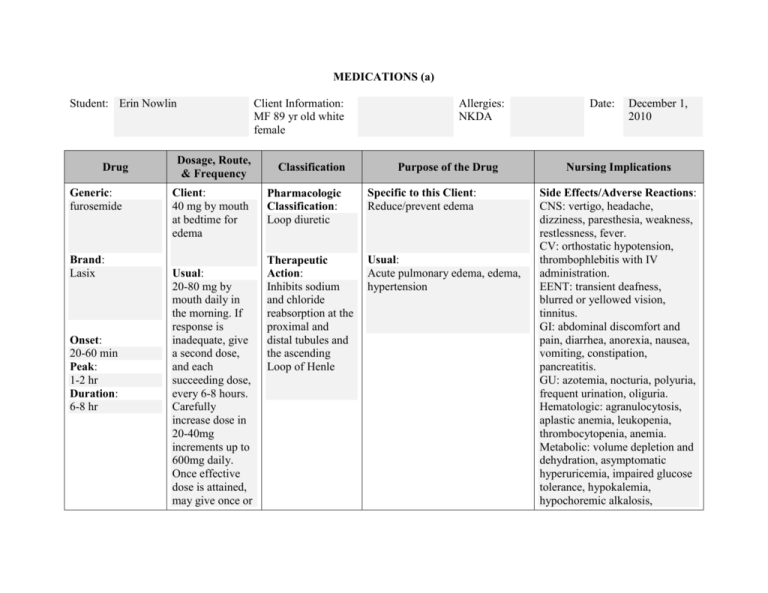
MEDICATIONS (a) Student: Erin Nowlin Drug Generic: furosemide Brand: Lasix Onset: 20-60 min Peak: 1-2 hr Duration: 6-8 hr Client Information: MF 89 yr old white female Dosage, Route, & Frequency Client: 40 mg by mouth at bedtime for edema Usual: 20-80 mg by mouth daily in the morning. If response is inadequate, give a second dose, and each succeeding dose, every 6-8 hours. Carefully increase dose in 20-40mg increments up to 600mg daily. Once effective dose is attained, may give once or Classification Allergies: NKDA Purpose of the Drug Pharmacologic Classification: Loop diuretic Specific to this Client: Reduce/prevent edema Therapeutic Action: Inhibits sodium and chloride reabsorption at the proximal and distal tubules and the ascending Loop of Henle Usual: Acute pulmonary edema, edema, hypertension Date: December 1, 2010 Nursing Implications Side Effects/Adverse Reactions: CNS: vertigo, headache, dizziness, paresthesia, weakness, restlessness, fever. CV: orthostatic hypotension, thrombophlebitis with IV administration. EENT: transient deafness, blurred or yellowed vision, tinnitus. GI: abdominal discomfort and pain, diarrhea, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, constipation, pancreatitis. GU: azotemia, nocturia, polyuria, frequent urination, oliguria. Hematologic: agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia. Metabolic: volume depletion and dehydration, asymptomatic hyperuricemia, impaired glucose tolerance, hypokalemia, hypochoremic alkalosis, Drug Dosage, Route, & Frequency twice daily. Classification Purpose of the Drug Nursing Implications hyperglycemia, dilutional hyponatremia, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia. Musculoskeletal: muscle spasm. Skin: dermatitis, purpura, photosensitivity reactions, transient pain at IM injection site. Other: gout. Interactions: Drug-drug. Aminoglycoside antibiotics, cisplatin: may increase ototoxicity. Use together cautiously. Drug-herb. Aloe: May increase drug effect. Discourage use together. Drug-lifestyle. Sun exposure: may increase risk for photosensitivity reactions. Advise patient to avoid excessive sunlight exposure. Effects on Labs: -May increase cholesterol, glucose, BUN, creatinine, and uric acid levels. May decrease calcium, hemoglobin, magnesium, potassium, and sodium levels. Drug Dosage, Route, & Frequency Classification Purpose of the Drug Nursing Implications -May decrease granulocyte, platelet, and WBC counts. Nursing Considerations: -Monitor weight, blood pressure, and pulse rate routinely with long-term use. -Drug is potent diuretic and can cause severe diuresis with water and electrolyte depletion. Monitor patient closely. -If oliguria or azotemia develops or increases, drug may need to be stopped. -Monitor fluid intake and output and electrolyte, BUN, and carbon dioxide levels frequently. -Watch for signs of hypokalemia, such as muscle weakness and cramps. -Consult prescriber and dietitian about a high-potassium diet or potassium supplements. Foods rich in potassium include citrus fruits, tomatoes, bananas, dates, and apricots. -Monitor blood glucose level in diabetic patients. -Drug may not be well absorbed orally in patient with severe heart Drug Dosage, Route, & Frequency Classification Purpose of the Drug Nursing Implications failure. Drug may need to be given IV even if patient is taking other oral drugs. -Monitor uric acid level, especially in patients with a history of gout. -Monitor elderly patients, who are especially susceptible to excessive diureses, because circulatory collapse and thromboembolic complications are possible. -Don’t confuse furosemide with torsemide or Lasix with Lonox, Lidex, or Luvox. Client Teaching: -Advise patient to take drug with food to prevent GI upset, and to take drug in morning to prevent need to urinate at night. If patient needs second dose, tell him to take it in early afternoon, 6-8 hours after morning dose. -Inform patient of possible need to potassium of magnesium supplements. -Instruct patient to stand slowly to prevent dizziness and to limit alcohol intake and strenuous Drug Dosage, Route, & Frequency Classification Purpose of the Drug Nursing Implications exercise in hot weather to avoid worsening dizziness upon standing up quickly. -Advise patient to immediately report ringing in ears, severe abdominal pain, or sore throat and fever; these symptoms may indicate toxicity. -Discourage patient from storing different types of drugs in the same container, increasing the risk of drug errors. The most popular strengths of this drug and digoxin are white tablets equal in size. -Tell patient to check with prescriber or pharmacist before taking OTC drugs. -Teach patient to avoid direct sunlight and to use protective clothing and a sunblock because of risk of photosensitivity reactions. Antidote: none References: Kluwer, W. (2011) Nursing 2011 drug handbook (31st ed.). Ambler, Pennsylvania: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins