Examination #2 Bio 308-General Microbiology—Spring 2014
advertisement

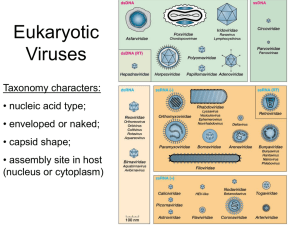
Examination #2 Bio 308-General Microbiology—Spring 2014 Steiner If there appears to be more than one answer, choose the best answer. Chapters 10, 13, 14, and 15 1. Common cold and flu are caused by which of the following pair of viruses? A) rhinovirus – orthomyxoviridae* B) enterovirus – retrovirus C) flavivirus – rhinovirus D) poxyvirus – papillomavirus 2. Polio and Rabies are caused by which of the following pair of viruses? A. Flavivirus- Morbillivirus B. Enterovirus- Hepatovirus C. Enterovirus- Lyssavirus* D. Filovirus- Flavivirus 3. Which of the following is NOT a negative sense RNA strand (-) virus? A. Morbillivirus B. Flavivirus* C. Lyssavirus D. Hepatovirus 4. Protease inhibitors are useful in blocking HIV replication because the HIV genome is ____________. A. regulated by proteins sensitive to protease B. polycistronic* C. has RNA that happens to be sensitive to proteases D. largely protein 5. The term viral specificity includes a number of different types of specificity. Which of the following is typically NOT considered to be associated with viral specificity? A. presence of specific attachment structures, e.g., spike glycoproteins B. whether or not the host can supply enzymes the virus needs for replication C. the fact that a particular virus must replicate within cells D. whether a virus has a capsid or an envelope* E. All of the above determine viral specificity (if you believe that all of the above are associated with viral specificity choose this answer). 6. Although Flu is seriously affecting young people this year only approximately _______ of individuals 18-64 have been vaccinated this year A. 10% B. 20% C. 30%* D. 50% 7. Which of the following is NOT a naked (non-enveloped) RNA virus? A. Lyssavirus* B. Enterovirus C. Rhinovirus D. Hepatovirus E. Rotavirus 1 8. Which of the above (question 7, A-E) is responsible for the common cold? A. B. C.* D. E. 9. Reactivation of chickenpox, long after the initial infection, leads to the disease A) cancer B) influenza C) shingles* D) varicella 10. Based largely on its shape and the fact that it includes an RNA polymerase, the figure below represents which of the following viruses? A. Hepatovirus B. Flavivirus* C. Rubella virus D. Lyssavirus* E. Hantavirus 11. Why is there concern about the recent outbreak of avian influenza of H10N8 type in China (choose the Best answer)? Because this A) avian influenza may destroy a large number of commercially important flocks of birds. B) strain of avian flu has some characteristics that may allow it to replicate efficiently in humans* C) avian influenza may readily spread to other countries. D) avian influenza is the first avian flu virus that lacks spike glycoproteins. 12. The new drugs to combat hepatitis C virus infections, Sovald and Olysio, function by: A. blocking viral attachment B. blocking RNA polymerase* C. blocking hepatitis C protease D. blocking RNA envelope formation 2 13. Prophages are responsible for production of the toxins found in: A) Staphylococcus aureus B) Micrococcus luteus C) Corynebacterium diphtheria* D) Streptococcus lactis 14. The figure below best depicts the replication of a: A. negative stranded RNA virus B. positive stranded RNA virus C. retrovirus D. DNA virus* 15. Which of the following teratogenic viruses is currently considered the worst (most cases and most damage done to the embryo)? A. herpes simplex virus type 1 B. herpes simplex virus type 2 C. cytomegalovirus* D. rubella 16. Which of the following is NOT a prion mediated disease? A. Fifth disease* B. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease C. Kuru D. Scrapie E. all of the above are prion mediated diseases (if you believe that all of the above are prion diseases, choose this answer). 3 17. A person may develop inflammatory bowl disease due to Clostridium difficile, after taking tetracycline for a long period of time. Which of the following hypotheses for what might be happening is the MOST reasonable? A. The antibiotic decreases the number of organisms that produce inhibitors of the growth of Clostridium difficile* B. Clostridium difficile uses the tetracycline as a nutritional source C. Tetracyclines irritate the intestinal wall thereby allowing Clostridium difficile to adhere and infect D. Tetracylcine induces mutations in Clostridium difficile which promotes growth of the organism. 18. Which of the following antibiotics functions by blocking the movement of the basic building block of the cell wall from the cytoplasm to the growing peptidoglycan? A. penicillin B. vancomycin C. cephalosporin D. bacitracin* 19. If an organism is resistant to penicillin it is most likely to also become resistant (cross-resistant) to: A. vancomycin B cephalosporin* C. bacitracin D. tetracycline 20. Rifamicin A) inhibits RNA synthesis* B) inhibits nucleic acid synthesis C) disrupts cell membrane function D) acts as an antimetabolite 21. The development of second-line and third-line antimicrobial agents demonstrates A) cross-resistance B) the effectiveness of first-line drugs C) an effective method to limit drug resistance D) the increasing difficulty of treating drug resistant bacteria* 22. The compound below: A) inhibits RNA synthesis B) inhibits nucleic acid synthesis C) disrupts cell membrane function D) acts as an antimetabolite* 4 23. _________ disrupts membrane function of Gram negative organisms. A. erythromycin B. chloramphenicol C. quinolones D. polymyxin* E. isoniazid 24. Vidarabine and idoxuridine are drugs that __________. A) inhibit RNA synthesis B) inhibit nucleic acid synthesis* C) disrupt cell membrane function D) act as an antimetabolite 25. Which of the following is NOT a good method to limit drug resistance? A. maintain antibiotics at high levels for a long enough time to kill all pathogens B. limit antibiotics to essential uses only C. administer two antibiotics simultaneously at lower concentrations, than when used singly D. use antibiotics in animal feed to remove harmful bacteria from the food chain* E. All of the above methods are useful for limiting drug resistance (if you believe that all of the above methods are useful for limiting drug resistance choose this answer). 26. The best description of the test below is: A. minimal inhibitory concentration test B. Agar diffusion test C epsilometer test* D. antibiotic sensitivity test 5 27. The figure below demonstrates the mode of action of: A. amphotericin B* B. polymyxin C. Griseofulvin D. imidazoles 28. Recently, there was a warning in Manchester England about a hospital superbug that is resistant to carbapenemase (KPC) and is linked to 16 deaths, The organism is ___________. A) B) C) D) E) Staphylococcus aureus Micrococcus luteus Corynebacterium diphtheria Streptococcus lactis Klebsiella pneumonia* 29. Legionnaires' disease and tetanus can best be described as a: A. communicable diseases B. contagious diseases C. noncommunicable infectious diseases* D. noninfectious diseases 30. Which of the following is NOT a virulence factor for some organisms? A. pili B. hyaluronidase C. adhesins D. lipopolysaccharide E. All of the above are virulence factors for some organisms (if you believe that all of the above are virulence factors for some organisms choose this answer)* 31. which of the following statements about endotoxins is the MOST accurate (choose the best answer). A) B) C) D) are more powerful than exotoxins per unit weight are unstable have nonspecific effects such as fever* are actively secreted into medium 6 2. __________ is produced by macrophages that have degraded a Gram negative bacterium. This substance triggers the hypothalamus to produce __________ which in turn increases body temperature (fever). A. endotoxin, prostaglandins B. exotoxin, interleukin C. interleukin, prostaglandin* D. endotoxin, interleukin 33. I am a toxin that causes a marked increase in cellular cyclic AMP, by ADP-ribosylation of adenyl cyclase, which in turn results in an upset in the osmotic balance leading to massive diarrhea. I am A. botulinum toxin B tetanus toxin C. cholera toxin* D. diphtheria toxin 34. Which of the above (question 33, A-D) stops neurons from releasing the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma aminobutyric acid and glycine and thereby blocks nerve transmission inhibition. A. B.* C. D. 35. Viruses used for gene therapy are typically engineered to have a(an) ______________. A. productive infection B. abortive infection* C. latent infection D. persistant infection 36. The relative number of individuals affected by a particular disease, during a set period of time, within a given population, is called A) epidemic B) nosocomial infections C) notifiable disease D) morbidity* 37. An infectious disease, that occurs in a random and unpredictable manner, e.g., eastern equine encephalitis, is termed: A) sporadic* B) pandemic C) epidemic D) propagated epidemic 38. The total number of people infected within a population at a given time is the A) incidence B) etiology 7 C) prevalence* D) morbidity 39. Which of the following microorganisms are found in soil, a nonliving reservoir? A) B) C) D) Yersinia pestis Pseudomonas aeruginosa Klebsiella pneumoniae Clostridium tetani* 40. A recent study revealed that ___________ can rid HIV infected babies of the virus. A. earlier treatment of the babies with anti-HIV drugs* B. new formulations of HIV drugs designed for babies C. replacing the babies blood supply D. increasing the incubation temperature of the newborns 41. A recent article points out that a group of parents in Queens, NY, have started a campaign to fight against __________ which takes more lives than the best-known cancers or heart attacks. A. measles B. sepsis* C. urinary tract infections D. upper respiratory infections 42. A recent report indicated, for the first time, that ______________ can be used to repel HIV. A. nutrition B. gene editing* C. continuous infusion of drugs for 48 hours D. decreasing the body temperature for extending periods of time 43. A new treatment for hepatitis C virus infections, that uses a(an) _____________ provides hope for a “cure” of the disease. A. endocytosis inhibitor B. a protease inhibitor C. RNA polymerase inhibitor* D. DNA polymerase inhibitor 8