Animal and Plant viruses
advertisement

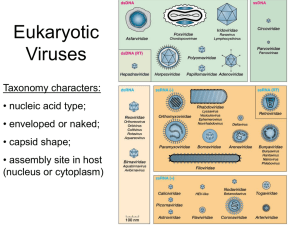
Animal and Plant viruses Plate Culture of Animal Viruses Figure 6.33 Figure 6.20 Papillomavirus (DNA) Life Cycle Figure 6.22 Picornavirus (RNA) Life Cycle Figure 6.23 Figure 11.15 Poliovirus Structure • The capsid is fundamentally icosahedral. • - Composed of three external proteins (VP1–3) • - VP4 protein subunits coat the interior and help package the (+) strand RNA genome. Figure 11.11B • The poliovirus binds to poliovirus receptor (PVR) through its VP2 and VP3 subunits. • -A conformational change in VP1 allows insertion of the genome into the cytoplasm. Figure 11.12 Poliovirus Replication • In the cytoplasm, the RNA is translated to make three large precursor peptides: P1–3. • - All three peptides are eventually cleaved by proteases to generate 11 proteins. Figure 11.13A Influenza Virus Structure • The flu virus has no geometric capsid. • RNA genome is loosely contained by a shell of matrix proteins. Figure 11.16 RNA segments are coated with nucleocapsid proteins (NPs). Two major envelope proteins: - Neuraminidase (NA) - Hemagglutinin (HA) Influenza virus: note envelope The Genome of Influenza A Virus Figure 11.17 • The key advantage of a segmented genome is that it facilitates recombination between two strains coinfecting the same cell. • - Instant new strain can evade the immune system. Figure 11.18B Influenza Virus Entry • Animation: Influenza Virus Entry into a Cell Click box to launch animation Figure 11.21 Influenza Virus Replication • Animation: Influenza Virus Replication Click box to launch animation Herpes Simplex Virus Structure • An icosahedral capsid houses the dsDNA genome. Capsid is surrounded by a protein tegument, which is contained within an envelope with spike proteins. Figure 11.31A Figure 11.32 Herpes Virus Replication • Animation: Herpes Virus Replication Click box to launch animation • Within a plant, the thick cell walls prevent a lytic burst or budding out of virions. • - Instead, plant viruses are transmitted to uninfected cells by plasmodesmata. Figure 6.26 Fig. 19-11 tRNA-like structure Stop codon Cap MTH RNP MP CP A viroid Figure 6-6 Viroids: infective RNA. Figure 6-7 Prion disease.