Eukaryotic Viruses
advertisement

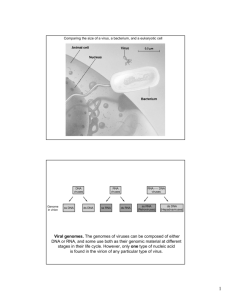
Eukaryotic Viruses Taxonomy characters: • nucleic acid type; • enveloped or naked; • capsid shape; • assembly site in host (nucleus or cytoplasm) Attachment and Penetration: Attachment phase is conceptually similar to phage. Penetration can be very different (capsid may enter). NOTE: in both mechanisms the nucleic acid is “uncoated”, i.e. capsid disassembles. Enveloped virus fusing with endosome membrane for release of capsid. Release by exocytosis DNA virus Papovavirus (warts) Transcription & replication in nucleus; capsid assembly in nucleus. RNA Virus Types Polio; common cold In the cytoplasm. (RdRp) In the cytoplasm; except influenza Orthomyxoviruses (Influenza Virus): • Attachment and penetration by endocytosis, then -ssRNA is uncoated. • Unique for RNA viruses to replicate in the nucleus; Uses RdRp to make +ssRNA then to –ssRNA. • Needs a capped primer (C) for mRNA synthesis and ribosome recognition; steals C from host mRNA at 5’end. • Viral envelope proteins transported from RER to GA to plasma membrane; others associate with –ssRNA to form nucleocapsid. Budding release (below): RNA viruses = respiratory enteric orphan viruses In the cytoplasm. In the cytoplasm. Retrovirus (+RNA) Infection Types and Outcomes • Acute versus Persistent Infections: – Chronic (replicates at low levels & constant yet mild symptoms) – Latent (stops reproduction after initial infection; goes dormant until induced to activate replication again) – Slow (vary slow replication and spread; years before symptoms) • Cytocidal effects (death) and cell damage: – – – – – – Inhibit host macromolecule synthesis Lysosome malfunction (host cell self digests) Plasma membrane abnormalities Direct viral protein toxicity Protein aggregation (inclusion bodies) Host cell changes to a malignant cell (cancer) • • • • Tumors form by neoplasia and anaplasa; may spread by metastasis. Virus may carry oncogenes (genes for various cancer causing protein). Viral promotors may insert and turn on expression of host oncogenes. 8 cancers involving viruses: Burkitt’s lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma (Epstein-Barr virus); cervical cancer (papillomavirus); Kaposi’s sarcoma (herpes 8), Hepatitis B & C, T-cell and hairy-cell leukemias, Rous sarcoma.