Evidence of Evolution LAB
advertisement

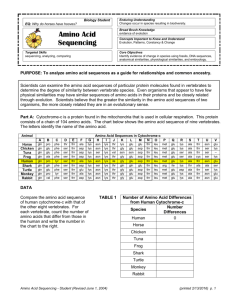
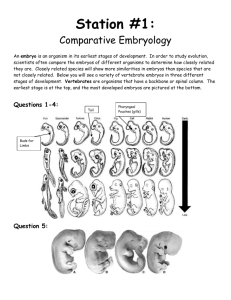
Name: Evidence of Evolution Period: Date: DNA Evidence Cytochrome-c is a protein found in the mitochondria that is used in cellular respiration. This protein consists of a chain of 104 amino acids. The chart below shows the amino acid sequence for cytochrome-c of five vertebrates. Animal Horse Shark Human Turtle Monkey Amino Acid Sequences in Cytochrome-C gln gln gln gln gln pro gln pro glu pro phe phe tyr phe tyr thr ser ser ser ser thr thr thr thr thr ala asp ala glu ala lys lys lys lys lys asn ser asn asn asn lys lys lys lys lys thr thr ile thr thr lys gln gly gly gly glu gln glu glu glu glu glu asp asp asp thr thr thr thr thr leu leu leu leu leu met arg met met met glu ile glu glu glu lys lys lys asp lys ala thr ala ala ala thr ala thr thr thr asn ala asn ser asn glu ser glu lys glu 1. Compare the amino acid sequence of human cytochrome-c with that of the other four vertebrates. For each vertebrate, count the number of amino acids that differ from those in the human. Write the number in the data table. Using the amino acid differences, which organism is most closely related to humans? Using the amino acid differences, which organism is least closely related to humans? 2. Based on the data, list the order in which these vertebrates are related to humans using the data table. Place the vertebrates more similar to humans in sequence from the top. RISD Curriculum & Instruction 2012-2013 Name: Evidence of Evolution Period: Homologous Structures Procedure: 1. Color the homologous bones below according to the color scheme below: Green = humerus Red = radius Blue = ulna Yellow = metacarpals Purple = phalanges 1. Do homologous structures have the same function in different organisms? 2. What do homologous structures have in common? 3. How does the existence of homologous structures support the theory of evolution? RISD Curriculum & Instruction 2012-2013 Date: Name: Evidence of Evolution Period: Date: Phylogenetic Trees A phylogenetic tree is a diagram that depicts the lines of evolutionary descent of different species, organisms, or genes from a common ancestor. The trees have branches, the length of which is proportional to the hypothesized time between the divergence of the organisms. Each node at the fork represents a common ancestor. 1. Look at organisms B, C, and D. These are organisms that can be found in present time. Sequence the common ancestors shown from oldest to most current. 2. Look at organisms B and C. They share three common ancestors, X, A, and Z. How many common ancestors do organisms D and B share? 3. Which of the present day organisms are the most closely related? RISD Curriculum & Instruction 2012-2013 Name: Evidence of Evolution Period: Date: Cladograms What is a cladogram? It is a diagram that depicts evolutionary relationships among groups. It is based on phylogeny, which is the study of evolutionary relationships. Cladistics form of analysis that looks at features of organisms that are considered "innovations", or newer features that serve some kind of purpose. (Think about what the word "innovation" means in regular language.) These characteristics appear in later organisms but not earlier ones and are called derived characters. 1. Examine the sample cladogram, each letter on the diagram points to a derived character, or something different (or newer) than what was seen in previous groups. Match the letter to its character on your student data sheet. Note: This cladogram was created for simplicity and understanding, it does not represent the established phylogeny for insects and their relatives. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Wings 6 Legs Segmented Body Double set of wings Jumping Legs Crushing Mouthparts Legs Curly Antennae 2. To make a cladogram, you must first look at the animals you are studying and establish characteristics that they share and ones that are unique to each group. For the animals on the table, indicate whether the characteristic is present or not. Cells Backbone Legs Hair Slug (snail) Catfish Frog Tiger Human RISD Curriculum & Instruction 2012-2013 Opposable Thumbs Name: Evidence of Evolution Period: Date: Biogeography Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species across the globe. Scientists refer to biogeography as evidence of evolution. Species that developed from a common ancestor are usually found geographically near each other. Procedure: 1. Compare the appearance of the six penguins. Record your observations in the data table on your student handout. 2. Write the letter for each penguin on the map according to their given latitude and longitude. 3. Answer the questions that follow on your student data sheet. Penguin Distinguishing Characteristics African penguin Galapagos penguin Humboldt penguin Chinstrap penguin Adelie penguin Gentoo penguin RISD Curriculum & Instruction 2012-2013 Most similar to: Name: Evidence of Evolution Period: Date: A. African penguin (35°S, 25°E) D. Chinstrap Penguin (180°W, 80°S) B. Galapagos penguin (10°S, 90°W) E. Adelie Penguin (120°E, 65°S) C. Humboldt penguin (75°W, 15°S) F. Gentoo Penguin (30°E, 70°S) RISD Curriculum & Instruction 2012-2013