Amino Acid Graphing Activity
advertisement

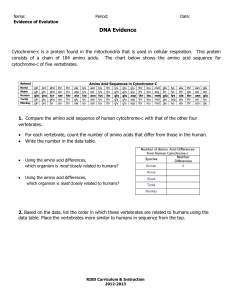
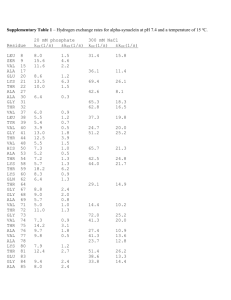
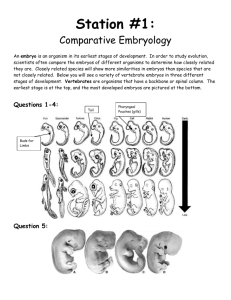
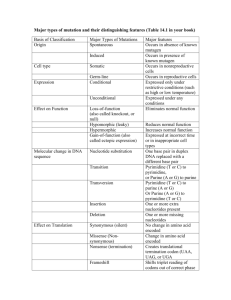
Enduring Understanding Changes occur in species resulting in biodiversity. Biology Student EQ: Why do horses have hooves? Broad Brush Knowledge evidence of evolution Amino Acid Sequencing Concepts Important to Know and Understand Evolution, Patterns, Constancy & Change Targeted Skills sequencing, analyzing, comparing Core Objectives Identify evidence of change in species using fossils, DNA sequences, anatomical similarities, physiological similarities, and embryology. PURPOSE: To analyze amino acid sequences as a guide for relationships and common ancestry. Scientists can examine the amino acid sequences of particular protein molecules found in vertebrates to determine the degree of similarity between vertebrate species. Even organisms that appear to have few physical similarities may have similar sequences of amino acids in their proteins and be closely related through evolution. Scientists believe that the greater the similarity in the amino acid sequences of two organisms, the more closely related they are in an evolutionary sense. Part A: Cytochrome-c is a protein found in the mitochondria that is used in cellular respiration. This protein consists of a chain of 104 amino acids. The chart below shows the amino acid sequence of nine vertebrates. The letters identify the name of the amino acid. Animal Horse Chicken Tuna Frog Human Shark Turtle Monkey Rabbit A B C D E F G Amino Acid Sequences in Cytochrome-c H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V gln gln gln gln gln gln gln gln gln pro glu glu ala pro gln glu pro val phe phe phe phe tyr phe phe tyr phe thr ser ser ser ser ser ser ser ser thr thr thr thr thr thr thr thr thr ala asp asp asp ala asp glu ala asp lys lys lys lys lys lys lys lys lys asn asn ser asn asn ser asn asn asn glu glu glu glu glu ile glu glu glu lys lys ser ser lys lys asp lys lys ala ala ala ala ala thr ala ala ala thr thr thr cys thr ala thr thr thr asn ser ser ser asn ala ser asn asn glu lys -lys glu ser lys glu glu lys lys lys lys lys lys lys lys lys thr thr val thr ile thr thr thr thr lys gly asn gly gly gln gly gly gly glu glu asn glu glu gln glu glu glu glu asp asp asp asp glu asp asp asp thr thr thr thr thr thr thr thr thr leu leu leu leu leu leu leu leu leu met met met met met arg met met met DATA Compare the amino acid sequence of human cytochrome-c with that of the other eight vertebrates. For each vertebrate, count the number of amino acids that differ from those in the human and write the number in the chart to the right. TABLE 1 Number of Amino Acid Differences from Human Cytochrome-c Number Species Differences Human 0 Horse Chicken Tuna Frog Shark Turtle Monkey Rabbit Amino Acid Sequencing - Student (Revised June 1, 2004) (printed 2/13/2016) p. 1 DATA ANALYSIS 1. Based on the data, list the order in which these vertebrates are related to humans. Place the vertebrates more similar to humans in sequence at from the top. TABLE 2 Similarity Ranking Animal AA Difference Human 0 2. Using the amino acid differences, which organism is most closely related to humans? ____________ 3. Using the amino acid differences, which organism is least closely related to humans? ____________ 4. A cladogram is a tree-like diagram showing evolutionary relationships. Use the data from Table 2 and fill in the cladogram to show the relationship of these animals compared to the human. Label the location on the cladogram where you would place the common ancestor to all of these animals. 0 5 10 15 Number of Amino Acid Differences 5. In the table you completed above, the number listed for the chicken and horse as compared to the human differs by only one. Compare the differences in amino acid sequences between the horse and the chicken. The difference is ____ . Considering both sets of data, can you conclude from this that the horse and the chicken are closely related? _______ Why or why not? _____________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ CONCLUSION: Summarize the concept of amino acid comparisons as they would indicate the possibility/closeness of a common ancestor. ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ Amino Acid Sequencing - Student (Revised June 1, 2004) (printed 2/13/2016) p. 2