chapter_16_relay_race
advertisement

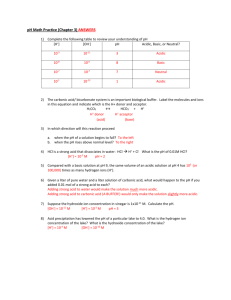
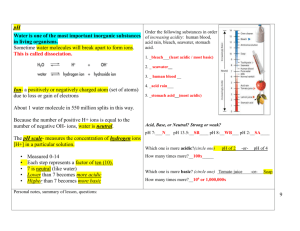
Chapter 16 Relay Race #1 Match the following terms to the correct definition: ____1. Arrhenius acid A. can act as an acid or base ____ 2. Arrhenius base B. [H+] = [OH-] ____ 3. Brosted-Lowry acid C. produces OH- ions in aqueous solutions ____ 4. Bronsted-Lowry base D. completely dissociates in water ____5. Strong Acid E. [OH-] > [H+] ____6. Weak Acid F. proton donor ____ 7. Amphoteric G. changes color in acidic and basic solutions ____ 8. Neutral solution H. [H+] > [OH-] ____ 9. Acidic solution I. moles of H+ added equal the moles of OH- in analyte ____ 10. Basic solution J. partially dissociates in water ____ 11. Indicator K. a solution that resists a change in pH when an acid ____ 12. Equivalence point or base is added ____ 13. Buffered solution L. proton acceptor M. produces H+ ions in aqueous solutions Chapter 16 Relay Race #1 Match the following terms to the correct definition: ____1. Arrhenius acid A. can act as an acid or base ____ 2. Arrhenius base B. [H+] = [OH-] ____ 3. Brosted-Lowry acid C. produces OH- ions in aqueous solutions ____ 4. Bronsted-Lowry base D. completely dissociates in water ____5. Strong Acid E. [OH-] > [H+] ____6. Weak Acid F. proton donor ____ 7. Amphoteric G. changes color in acidic and basic solutions ____ 8. Neutral solution H. [H+] > [OH-] ____ 9. Acidic solution I. moles of H+ added equal the moles of OH- in analyte ____ 10. Basic solution J. partially dissociates in water ____ 11. Indicator K. a solution that resists a change in pH when an acid ____ 12. Equivalence point or base is added ____ 13. Buffered solution L. proton acceptor M. produces H+ ions in aqueous solutions Chapter 16 Relay Races #2 1. Write a chemical equation to show how each of the following react with water: a. HCN b. NH4+ c. H2PO4- 2. Which of the following solutions would have a pH of 14? a. NaOH c. HF b. HCl d. H2O 3. What are two limitations to using liquid indicators? 4. When the pH of a solution decreases, the [H+] to [OH-] ratio a. Decreases c. stays the same b. Increases d. can increase or decrease Chapter 16 Relay Races #2 1. Write a chemical equation to show how each of the following react with water: a. HCN b. NH4+ c. H2PO4- 2. Which of the following solutions would have a pH of 14? a. NaOH c. HF b. HCl d. H2O 3. What are two limitations to using liquid indicators? 4. When the pH of a solution decreases, the [H+] to [OH-] ratio a. Decreases c. stays the same b. Increases d. can increase or decrease Chapter 16 Relay Race #2 1. Which of the following are conjugate acid-base pairs? (Mark all that apply) c. HCl/Clc. HC2H3O2/C2H3O2d. H2O/O2d. NH4+/NH3 2. What is the pH of a solution if [OH-] is 1.0x10-4 M? Is the solution acidic, basic or neutral? SHOW WORK!! 3. Calculate the [H+] for each of the following solutions and state whether the solution is acidic, basic or neutral: a. pH = 6.99 b. pOH = 10.50 4. pH is a measure of a. the hydrogen ion concentration b. the hydrogen gas concentration c. hydroxide ion concentration d. hydrolysis Chapter 16 Relay Race #2 1. Which of the following are conjugate acid-base pairs? (Mark all that apply) e. HCl/Clc. HC2H3O2/C2H3O22f. H2O/O d. NH4+/NH3 2. What is the pH of a solution if [OH-] is 1.0x10-4 M? Is the solution acidic, basic or neutral? SHOW WORK!! 3. Calculate the [H+] for each of the following solutions and state whether the solution is acidic, basic or neutral: a. pH = 6.99 b. pOH = 10.50 4. pH is a measure of a. the hydrogen ion concentration b. the hydrogen gas concentration c. hydroxide ion concentration d. hydrolysis Chapter 16 Relay Race #3 1. Draw what the HNO2/KNO2 buffer solution looks like in the beaker below: 2. Write the chemical equation to show how the above buffer would react with any HCl and NaOH added. (HINT this requires TWO different chemical equations) 3. Why are buffers able to resist a pH change when an acid is added, but pure water cannot? Chapter 16 Relay Race #3 1. Draw what the HNO2/KNO2 buffer solution looks like in the beaker below: 2. Write the chemical equation to show how the above buffer would react with any HCl and NaOH added. (HINT this requires TWO different chemical equations) 3. Why are buffers able to resist a pH change when an acid is added, but pure water cannot? Chapter 16 Relay Race #4 1. Calculate the [H+] in a solution if [OH-] = 4.20x10-8 M and tell if the solution is acidic, basic or neutral. a. [H+] = 2.38x10-7 M, basic c. [H+] = 2.38x10-7 M, acidic -7 M b. [H+] = 7.27x10 , basic d. [H+] = 4.20x10-7 M, neutral 2. A _________ acid always has a ______________ conjugate base. a. Strong, strong c. weak, weak b. Weak, strong d. Homer, Simpson 3. ALL neutralization reactions between an acid and a base ALWAYS make what two things? 4. If 50,0 mL of H2SO4 solution requires 20,0 mL of Al(OH)3 to titrate it to the equivalence point, what is the concentration of the H2SO4 solution? Chapter 16 Relay Race #4 1. Calculate the [H+] in a solution if [OH-] = 4.20x10-8 M and tell if the solution is acidic, basic or neutral. a. [H+] = 2.38x10-7 M, basic c. [H+] = 2.38x10-7 M, acidic b. [H+] = 7.27x10-7 M, basic d. [H+] = 4.20x10-7 M, neutral 2. A _________ acid always has a ______________ conjugate base. a. Strong, strong c. weak, weak b. Weak, strong d. Homer, Simpson 3. ALL neutralization reactions between an acid and a base ALWAYS make what two things? 4. If 50,0 mL of H2SO4 solution requires 20,0 mL of Al(OH)3 to titrate it to the equivalence point, what is the concentration of the H2SO4 solution?







![[OH - ] < 1.0 x 10](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007110510_1-bfa16e7ddc01a3c98cff3c549f0ddc6b-300x300.png)

