Chapter 2
advertisement

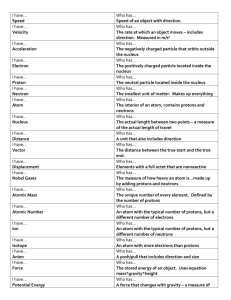
RAD 350 Chapter 2 I. The atom is the smallest part of an element that has ALL the properties of that element 112 elements have been identified 92 are natural 20 are artificially produced Particles SMALLER than an atom are called “sub-atomic particles” -1808 John Dalton classified elements according to atomic mass values - 50 years later, a Russian named Medeleev suggested the periodic table with the current 8 groupings -superscript is the atomic number (Z#) = NUMBER OF PROTONS -subscript is the ATOMIC MASS NUMBER (A#) = NUMBER OF PROTONS AND NUETRONS - in the late 1800’s, JJ Thomson was playing with a cathode ray tube and concluded that electrons are a vital part of atoms -1911 Ernest Rutherford introduced the nuclear model of the atom -1913 Niels Bohr improved the Rutherford model to that of a “mini solar system” with electrons in orbital shells about the nucleus in prescribed energy levels -the mass of an atom is small and called AMU -nucleons are found in the nucleus (protons and neutrons) II. Atoms of various elements may combine to form structures called molecules Sodium (Na) + Chlorine (CI) = sodium chloride -The number of PROTONS determines the CHEMICAL ELEMENT - Atoms with the SAME number of PROTONS, but different number of NEUTRONS are called ISOTOPES -The nucleons have about 2,000 times MORE MASS than ELECTRONS -Neutrons possess NO CHARGE -ELECTRONS possess one NEGATIVE CHARGE, but are only 1/2,000th the size of PROTONS/Neutrons NOTE: PROTONs are in the nucleus of the atom! Soon we will talk about PHOTONS (which are X-RAYS) and are discrete energy in space and have NO mass or charge!!! Please be sure to keep PHOTONS and PROTONS straight and separate! -For an atom to be neutral, the total positive charges in the nucleus (protons) MUST equal the total number of negative charges (ELECTRONS) in the orbital shells. -The shells begin next to the NUCLEUS and are letter starting with “K” and numbered starting at 1! Each shell only contain a MAXIMUM number of ELECTRONS based on it’s shell NUMBER 2n2 – thus 2 in the K shell, 8 in the L shell and so on. -The outer shell number does NOT always have the full number possible AND – the MAXIMUM number of electrons possible in the outer shell is EIGHT! -Atoms with only one electron in the outer shell are in GROUP ONE OF THE PERIODIC TABLE! Those with 8 are in GROUP 8 and so on. -The GROUP is numbered 1-8 and is HORIZONTAL in the TABLE SEE PAGE 29 – FIGURE 2-4!!! -The PEROIDS are numbered 1-8 and are VERTICAL with 1 at the TOP amd 7 at the BOTTOM -The CLOSER to the nucleus, the MORE binding energy the shell has, but the “on board” energy is less than that of an outer, more loosely bound electron -Electrons may be removed from ANY orbital shell by a process called IONIZATION. To remove and inner bound electron takes MORE energy to remove it than an outer because the inner shell electrons have MORE BINDING ENERGY than the outer shells -While BINDING energy varies with shell number, the force keeping the electrons from “spinning off into space” is called CENTRIPETAL FORCE Ionization produces an “ION PAIR” the atom, minus one electron “Pissed off Atom” as it now has one more positive charge than negative charges in the electrons – AND the ejected electron which has been liberated from the BINDING energy of the shell it used to occupy. A covalent bond occurs when two or more atoms SHARE an outer shell electron. III. Varied numbers of mass# and atomic # - ISOTOPE – Same number of protons, but different # of neutrons - ISOBAR – Different # of protons and neutrons, but same total # of nucleons - ISOTONES – Same # of neutrons, but different # of protons - ISOMER – Same atomic # and same atomic mass# - exist at differeing energy states due to different nuclear arrangement IV. Radioactivity Any nuclear arrangement is called a nuclide, but ONLY nuclei undergoing radioactive decay (radioactive disintegration or radioactive decay) are radionuclides. - BETA EMISSION : neutron conversion into a proton at the sametime an electron particle is emitted from the nucleus with a LOT of kinetic energy. The electron is just like a normal electron, but with more kinetic – “on board” energy. Since it came from an atom is called a Beta PARTICLE rather than an electron. - ALPHA EMISSION requires MUCH MORE energy and is VERY violent! The nucleus looses 2 units of positive charge (2 protons) and 4 total units of mass (4 amu’s lighter) – remember the nucleons of the atom are almost 2,000 times larger than an electron – therefore HEAVY particle emission – BUT since the mass is so LARGE, they do NOT travel or penetrate very far. -Most radioisotopes emit gamma rays simultaneously with the particulate emission - HALF LIFE is the period of time required for a quantity of radioactivity to be reduced to ½ it’s original value CARBON DATING uses this principle as the 14C isotope has a ½ life of 5,730 years. As a tree lives, it’s carbon14 is constant, at it’s death, it has less carbon 14 based upon it’s radioactive disintegration 1 HL = 50% f the orig = 50% ½ of the 50% or 25% of the original and so on – theoretically, there is always ½ of ½ of ½ remaining, so therefore istopes NEVER reach total stability VI. Types of Radiation – particulate and electromagnetic (also remember non-ionizing like infrared or microwave) A. Particulate radiation is any subatomic particle and can cause ionization (electrons, protons and neutron OR nuclear fragments) THEY MUST BE IN MOTION AND POSSES KINETIC ENERGY! b. An ALPHA PARTICLE is a “heavy helium atom” it has 2 protons and 2 neutrons, a mass of 4 amu, and 2 units of positive charge (from the 2 protons). Due to it’s LARGE mass, it is NOT very penetrating; only travels 5 cm in air; is rapidly absorbed on the skin’s surface inside the body – it is DEADLY! Think of a FAT skier or boarder skiing through trees – will NOT go very far due to his/her size before a tree stops him. C. BETA PARTICLES are electrons – amu=0, 1 negative charge; penetration is dependant upon it’s energy. 1 MEV will penetrate ½ cm of skin D. PHOTONS (not protons) – have NO mass; no charge and travel at the speed of light. If they are from an isotope they are GAMMA RAYS If they are electronically produced are called X-RAYS