Unit B Chemistry Unit study guide
advertisement

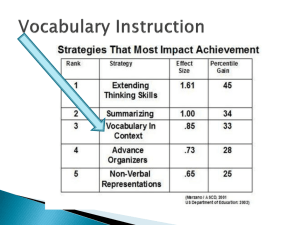
Unit B Chemistry Unit study guide Unit Test on Thursday, 12-20-12 Activity 12-29, p. B-3 to B-85 Be able to identify Atomic number and mass with protons, electrons and neutrons Rows of periodic table are called_____________ Columns of periodic table are called___________________ What is reactivity? Names, placement and characteristics of Families- Alkali metals, alkali earth metals, transition metals, halogens, noble gases as well as metals vs nonmetals Why are lanthanides and actinides on bottom? What are the only two liquids? Where are the gasses? Which element is in a group of its own? Which element is needed for substances to burn? Mendeleev did such a great job creating his periodic table because: Number of atoms in a molecule Be able to label an atom- proton, neutron, electron, nucleus, electron cloud and understand what they are Know difference between the Reactant and the product of a chemical equation What is the law of conservation of mass Why should chemical equations be balanced? What is a subscript? A coefficient? What is the difference between a mixture, compound and element How to determine chemical symbol and chemical formula (element vs compound) (atom vs molecule) What is chemical change and evidence of chemical change What to consider when choosing materials Product life cycle What happens with an Exothermic reaction Identify Number of elements and number of atoms Chemical property vs physical property Is size and shape a physical property? Most common phase of the elements Relative density. Float vs sink and be able to place on chart Density of water Poly vs mono? Natural vs synthetic polymers? Examples of each Draw difference between monomer, polymer and cross linked polymer What does crosslinking do to a polymer? How does its properties change? What does ppm mean? Good and bad of dilution, incineration and reclaiming What is waste? Green Chemistry guidelines and how use in own household Choice of materials based on its properties Activity 12 Evaluating Materials Vocab: Material, Material Scientist, Materials engineer, Property ◦ Also Evidence and tradeoffs Properties of Materials ◦ How properties and other factors are used to choose a product ◦ ie- cost, environmental impact of production and of waste, recyclability, reliability during use, ease of use Advantages and disadvantages to glass, plastic, aluminum Activity 13- Product Life Cycle Vocab: Life cycle, Life cycle diagram, raw materials, manufacturing, useful life, end of life Product Life Cycle Diagram and Parts of life cycle- compare Raw materials- (for aluminum, plastic, glass) Manufacturing Useful life End of life Activity 14 Physical and Chemical Properties of Materials Vocab: chemical property, physical property, density, material Physical vs Chemical Properties ◦ Physical: density, electrical conductivity, flexibility, color, texture, hardness, luster (brilliant, glassy, dull- light reflection), light transmission (opaque, translucent, transparent) ◦ Chemical: Reaction with other substances, pH, flammability How we use properties to select best materials Activity 15 Families of Elements Vocab: atom, atomic mass, element, family, metal, periodic table of elements Periodic Table Families Properties of elements Organization Activity 16 Elements and the Periodic Table p. B-22 Vocab: chemical formula, compound, molecule Also mixture Mendeleev Elements vs Compounds vs Mixtures Atoms vs Molecules Chemical Names and Formulas Activity 16A- Atomic Structure and Chemical Interactions Vocab: electron, neutron, proton, nucleus, electron cloud Atomic Structure- see notes Atom Atomic number Mass Valence Electrons Activity 17 Modeling Molecules Vocab: chemical bond Chemical bonds Using models Activity 18 Properties of Plastic Vocab: plastic How physical and chemical properties affect use and identify different plastics Density Relative density Activity 19 Creating New Materials Vocab: cross-link, monomer, polymer, product, reactant, chemical reaction Reactants vs Products Chemical reactions Evidence of chemical reaction Color change Temperature change Formation of new substance with different properties Gas production Precipitation Production of light or sound Activity 20 Modeling Polymers Monomers vs polymers Cross linked polymers Properties of monomers, polymers, cross linked polymers Use of Models Activity 21- Polymer Parts Vocab: polymerization Synthetic vs Natural Polymers Plastics are Polymers but not all Polymers are plastics What does cross linking do to properties of polymer? Activity 22 Environmental Impact of Computers Vocab: recycling Material make-up of a computer % recyclable Hazardous waste produced DURING production Use of circle and bar graphs Activity 23 Producing Circuit Boards Vocab: circuit board, etch Also: toxic Raw materials How obtain Copper Copper waste Copper health effects Good Bad Proper and acceptable disposal Activity 24 Diluting the Problem Vocab: concentration, control, dilution, indicator, parts per million, serial dilution Dilution/concentration ◦ Acceptable amounts for disposal Pros and Cons of Dilution Use of Indicators Parts of experiment notes ◦ Independent vs Dependant variable ◦ Control ◦ Constant ◦ Trials Activity 25 Conservation of Mass Vocab: closed system, open system, conservation of mass, exothermic reaction, mass THE LAW Law of Conservation of Mass- “Matter is neither created nor destroyed” Counting atoms- is it Balanced? Chemical equation- At the end of a reaction, the same atoms exist, but they are grouped together in as different molecules. Reactants vs Products Coefficient vs subscript Activity 26 Incinerating the Waste Vocab: combustion, incineration Pros and cons of Incineration Can you “destroy” copper? Incineration vs landfills Activity 27 Reclaiming the Metal Vocab: reclaim Also: evidence, trade-off Pros and cons Health affects of other metals used Is it worth it? Precipitation Cost involved Activity 28 Another approach to Metal Reclamation Vocab: precipitate, filtrate, filtration Pros and Cons Using liquids to reclaim copper Filter precipitates Effectiveness of capturing all of copper Can copper compound be used? Cost involved Activity 29 The Green Computer Decision Computer life cycle Evaluate and compare options Trade-offs Green Guidelines Life Cycle of a Computer Green Chemistry Guidelines