M&L Chapter 2.2 – PROPERTIES OF WATER Pages 40 – 44
advertisement

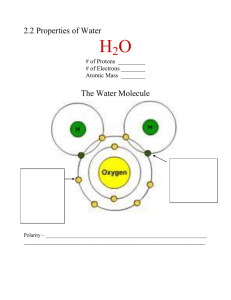
M&L Chapter 2.2 – PROPERTIES OF WATER Pages 40 – 44 2.2 THE PROPERTIES OF WATER 1. Why is Earth called the “Blue Planet? Name__________________________________ Pr ____ The Water Molecule 2. True or False. Water is one of the few compounds that is found in its liquid state on Earth. 3. Why is water a neutral molecule? A. Polarity 4. When oxygen shares a pair of electrons with hydrogen, why are the electrons more likely to be found near the oxygen nucleus than the hydrogen nucleus? 5. Oxygen is at one end of a water molecule. The two hydrogens are at the other. Which end has a partial positive charge? _______________________________ Which end has a partial negative charge _______________________________ B. Hydrogen Bonding 6. Where do hydrogen bonds form? 7. What three atoms does hydrogen form a hydrogen bond?_______________________________ 8. Which of the following is the weakest bond? Covalent, ionic, or hydrogen. (circle one) 9. “Because water is a polar molecule, it is able to form ______________________ hydrogen bonds, which account for many of water’s special properties.” 10. Why is ice less dense than liquid water? Cohesion 11. Define cohesion: 12. When water molecules are drawn together by hydrogen bonds, they can cause water to bead up on a smooth surface. Their hydrogen bonds also allow them to form a network that small insects can walk on, a property called ______________________________________. Adhesion 13. Define adhesion. 14. What causes water to creep up the side of a graduated cylinder? 15. The ability of water to rise up into a narrow tube (without sucking on it!) is called _________________________________.) Where do you see this in living organisms? ___________________________________________. 16. On the diagram to the right, label where cohesion is occurring. Label where adhesion is occurring. Heat Capacity 17. Define heat capacity: 18. Why is water’s heat capacity so large? 19. Name one advantage to living things of water having such a high heat capacity. Solutions and Suspensions 20. Define a mixture. 21. Give an example of a mixture. A. Solutions 22. Describe what water molecules do when small amounts of ionic (or polar) substances are added to them. See Figure 2-9 and the text. 23. Define solute. _______________________________________________________________ 24. Define solvent _______________________________________________________________ 25. What do we call a solution in which water has dissolved all the solute it can and can dissolve no more? __________________________ B. Suspensions 26. Why is blood a suspension? Acids, Bases, and pH 27. Write the chemical reaction for a water molecule splitting apart to form ions (we say that the water molecule is “disassociating”). 28. What ratio of water molecules are dissociated at any one time? __________________________ 29. Why is water neutral, even if it splits into charged ions? 30. What is the range of the pH scale? ______________________ 31. What pH is neutral? ______ What is the pH range of acids (acidic solutions)? ______ of bases (basic solutions)? ___________ 32. Acids have more _____ ions than ____ions. Bases have more ____ ions than _____ ions. A. Acids 33. Define an acid. 34. Where on the pH range would you find a strong acid? __________ B. Bases 35. Define a base. 36. Where on the pH range would you find strong bases? _________ C. Buffers 37. What is the pH range of most of the cells of the human body? ___________________ 38. “Controlling pH is necessary for maintaining ___________________.” 39. Define “buffer.” 40. Name two blood buffers. Read the “Chapter Mystery” on Page 33. What is the question you are trying to answer? Read the first clue on Page 37. Where does the oxygen fish need come from? _______________________________________________ How are the two atoms of oxygen gas joined together? (what kind of bond?) ______________________ Read the second clue on page 42. How does the temperature of Antarctic waters affect the amount of dissolved O2 available to ice fish?