Scientists, Cell Theory and Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote
advertisement

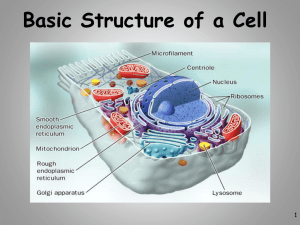
DO NOW 9/8/15 What is a cell and why do we have cells? Give one complete sentence. Cell Theory and Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote What is a Cell? Cell – Basic unit of living things. Organisms are either: Unicellular – made of one cell such as bacteria and amoebas. OR Multicellular – made of many cells such as plants and animals. Microscopes Light Microscope – magnifies tiny organisms up to 1,000 times. -Uses light and lenses. -We use these. Electron Microscope – magnifies up to a million times. -Uses electrons. The Discovery of Cells before nucleus true nucleus Eukaryotes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Has a nucleus with a nuclear membrane Bigger and more complex than prokaryotes Have membrane bound Organelles (golgi, ER, lysosomes…etc) DNA – double-stranded and forms chromosomes (highly organized) Can be uni- OR multicellular organisms Ex: animals, plants, fungi Prokaryotes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. NO nucleus NO membrane bound organelles (just ribosomes) ALL are unicellular Smaller than eukaryotic cells Existed before eukaryotic cells (smaller and more simple) DNA – single strand and circular Ex: ALL Bacteria WE DO: WHAT AND WHY Similarities vs Differences THEY DO: With your partner next to you, create a chart with similarities and differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes Eukaryote VS. Prokaryote Picture Food For Thought A scientist recently discovered a new organism. Upon looking at it under a microscope, you see an organism that possess ribosomes, a circular DNA strand and a cell membrane. You do not see visible evidence of mitochondria or other membrane bound organelles. Is this organism a prokaryote or eukaryote? Why? Do Now 9/9 The organism to the left is a Euglena. It has the ability to move like an animal cell because of its flagellum (tail) and can also undergo photosynthesis to make its own food. Would this organism be considered a prokaryotic or a eukaryotic organism? Why? Cell Size Surface area : Volume Cell Size Limits Are whale cells the same size as sea stars cells? Yes! THEY DO: TPS. Discuss this question with 1 partner Cell Size Limitations Getting things into cell at an efficient rate Removing things from the cell quickly Nutrients Water Oxygen wastes DNA limits cell size If cell is too big then DNA cannot make enough proteins to support the cell What limits the size of cells? Surface Area to Volume Ratio - How much space is on the outside (cell membrane) compared to the space on the inside of the cell. As the surface area of something increases, it’s volume increases faster Large Cell It takes more time for the nutrients to reach the center of this cell Smaller cell It takes less time for the same nutrients to reach the center of this cell THEY DO What are some advantages of having smaller cells Discuss with your partner: 3 minutes Conclusion As cell size increases, the surface area to volume ratio Decreases (small surface area to volume ratio), which can lead to death of a cell. Having a large surface area to volume ratio is important to the functioning of cells since it gets materials, nutrients, O2, & wastes into & out of it faster. Cells divide before they get too big! Food For Thought King Kong, a famous movie monster, was a large over sized gorilla with a bit of an anger problem. 1.Could an animal this size exist? 2.If this animal existed, would it possess few large cells or millions of small cells? Cell Theory and the Scientists Who Helped Shape It Scientists and the Cell Theory Anton van Leeuwenhoek http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anton_van_Leeuwenhoek Born: October 24, 1632 Died: August 30, 1723 He is known as the “Father of Microscopy.” Anton van Leeuwenhoek Discoveries: - 1673: He looked at pond scum under the microscope and discovered small organisms he called animalcules or little animals (Protists) - 1676: discovered bacteria http://www.kent.k12.wa.us/staff/TimLynch/sci_class/c hap09/lesson_protista/Protista_Lesson.html#Algae Robert Hooke http://www-groups.dcs.st-and.ac.uk/~history/PictDisplay/Hooke.html Born: July 18, 1635 Died: March 3, 1703 Wrote and published “Micrographia” Known as the “English Father of Microscopy” Robert Hooke Contributions: - He observed pieces of cork from the bark of a cork tree under the microscope. - His observations led him to coin the word “cell.” - “Cell”- means little rooms in Latin - He compared the small boxes to the small rooms that monks lived in. http://www.learner.org/channel/courses/essential/life/s ession1/closer1.html Matthias Schleiden Born: April 5, 1804 Died: June 23, 1881 German botanist http://www.britannica.com/eb/article9066147/Mathias-Jacob-Schleiden Discovered that all plants were made of cells Contributed to the creation of the cell theory Theodor Schwann Born: December 7, 1810 Died: January 11, 1882 German zoologist http://www.nndb.com/people/357/000096069/ Concluded that all animals are made of cells. Contributed to the creation of the cell theory Rudolph Virchow Born: October 13, 1821 Died: September 5, 1902 German pathologist http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Rudolf_Virchow.jpg He is known as the “Father of Pathology.” Discovered that all living cells come only from other living cells. The Cell Theory 1. 2. 3. All living things are made of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. Living cells come only from other living cells. Food For Thought Observation: Every year in the spring, the Nile River flooded areas of Egypt along the river, leaving behind nutrient-rich mud that enabled the people to grow that year’s crop of food. However, along with the muddy soil, large numbers of frogs appeared that weren ’ t around in drier times The above statement does not agree with which of the 3 parts of the cell theory? Why?