Supplementary Table 1
advertisement
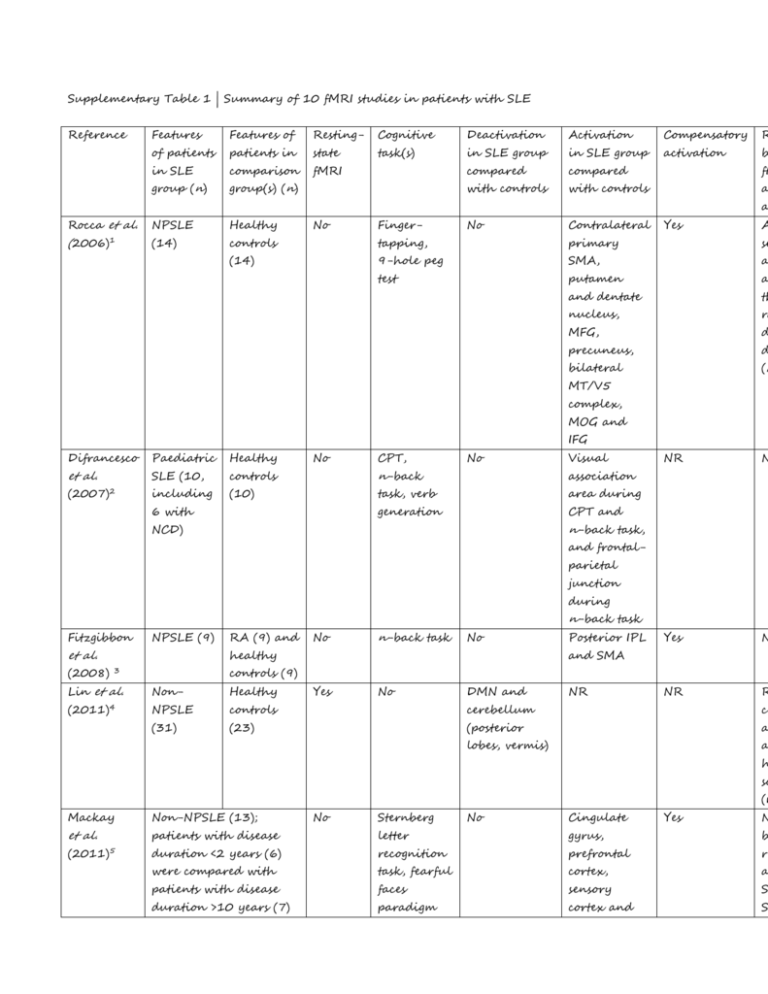
Supplementary Table 1 | Summary of 10 fMRI studies in patients with SLE Reference Features Features of Resting- Cognitive Deactivation Activation Compensatory R of patients patients in state task(s) in SLE group in SLE group activation b in SLE comparison fMRI compared compared fM group (n) group(s) (n) with controls with controls a a Rocca et al. NPSLE Healthy (2006)1 (14) controls tapping, primary se (14) 9-hole peg SMA, a test putamen a and dentate th nucleus, ra MFG, d precuneus, d bilateral (r No Finger- No Contralateral Yes A MT/V5 complex, MOG and IFG Difrancesco Paediatric Healthy et al. SLE (10, controls No n-back association (2007)2 including (10) task, verb area during generation CPT and 6 with CPT, No Visual NR N Yes N NR R n-back task, NCD) and frontalparietal junction during n-back task Fitzgibbon NPSLE (9) et al. (2008) RA (9) and No n-back task No healthy Posterior IPL and SMA controls (9) 3 Lin et al. Non- Healthy (2011)4 NPSLE controls cerebellum ce (31) (23) (posterior a lobes, vermis) a Yes No DMN and NR h sc (r Mackay Non-NPSLE (13); No Sternberg No Cingulate Yes N et al. patients with disease letter gyrus, b (2011)5 duration <2 years (6) recognition prefrontal re were compared with task, fearful cortex, a patients with disease faces sensory S duration >10 years (7) paradigm cortex and S Broca area in 40 Mak et al. Non- Healthy (2012)6 NPSLE (14) At diagnosis: controls Broca areas caudate, S (14) 3–7, 13, 24 Broca areas <4 and 32. 9–11, 34. n Post- Post- st treatment: treatment: p Broca areas Broca area C 5–9, 13, 17– 32 re Non- Healthy (2012)7 NPSLE (14) Shapira- Non- Healthy Lichter NPSLE et al. (12) No WCST w At diagnosis: Ren et al. No WCST Yes D 19, 23, 32, B 37, 40 is CBTC and Cerebellar- controls hippocampal- contralateral (14) amygdala frontal lobe Yes N NR N Yes In coupling No RAVLT DMN, TPN, controls particularly particularly (11) anterior left premotor medial cortex and prefrontal SMA (2013)8 cortex Hou et al. NPSLE Healthy (2013)9 (30) controls inferior fu (25) parietal co lobes, left st SMA, IFG p and MFG. a Frontal- S parietal (r Yes PVSAT No Superior and functional connectivity Difrancesco Paediatric Paediatric Continuous Precuneus, Left insular Yes, but et al. SLE with SLE No performance IFG, MFG, and left evident only (2013)10 NCD (7) without task, SFG, IPL, superior in patients NCD (14) n-back bilateral temporal with NCD task, VCA fusiform and gyri test occipital gyri N (relative deactivation) Abbreviations: amPFC, anterior medial prefrontal cortex; CBTC, cortico-basal ganglion-thalamic circuit; DMN, de network; fMRI, functional MRI; IFG, inferior frontal gyrus; IPL, inferior parietal lobule; MFG, middle frontal gyru middle occipital gyrus; NCD, neurocognitive dysfunction; NPSLE, neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus; reported; PVSAT, paced visual serial adding test; r, correlation coefficient; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; RAVLT, Rey verbal learning test; SFG, superior frontal gyrus; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; SLEDAI, SLE disease activity i Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics; SMA, supplementary motor area; STG, superior temporal gyrus positive network; VCA, visuoconstructional ability; WCST, Wisconsin card-sorting test. References: 1. Rocca, M. A., Agosta, F., Mezzapesa, D. M., Ciboddo, G., Falini, A., Comi, G. & Filippi M. An fMRI study of the motor system in patients with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Neuroimage. 30, 478–484 (2006). 2. DiFrancesco, M. W., Holland, S. K., Ris, M. D., Adler, C. M., Nelson, S., DelBello, M. P., Altaye, M. & Brunner, H. I. Functional magnetic resonance imaging assessment of cognitive function in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus: a pilot study. Arthritis Rheum. 56, 4151–4163 (2007). 3. Fitzgibbon, B. M., Fairhall, S. L., Kirk, I. J., Kalev-Zylinska, M., Pui, K., Dalbeth, N., Keelan, S., Robinson, E., During, M. & McQueen, F. M. Functional MRI in NPSLE patients reveals increased parietal and frontal brain activation during a working memory task compared with controls. Rheumatology (Oxford). 47, 50–53 (2008). 4. Lin, Y., Zou, Q. H., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Zhou, D. Q., Zhang, R. H., Zhang, Y. W., Lii, H. T. & Fang, Y. F. Localization of cerebral functional deficits in patients with non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum. Brain Mapp. 32, 1847–1855 (2011). 5. Mackay, M., Bussa, M. P., Aranow, C., Uluğ, A. M., Volpe, B. T., Huerta, P. T., Argyelan, M., Mandel, A., Hirsch, J., Diamond, B. & Eidelberg, D. Differences in regional brain activation patterns assessed by functional magnetic resonance imaging in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus stratified by disease duration. Mol. Med. 17, 1349–1356 (2011). 6. Mak, A., Ren, T., Fu, E. H., Cheak, A. A., Ho, R. C. A prospective functional MRI study for executive function in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus without neuropsychiatric symptoms. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 41, 849–858 (2012). 7. Ren, T., Ho, R. C. & Mak, A. Dysfunctional cortico-basal ganglia-thalamic circuit and altered hippocampal-amygdala activity on cognitive set-shifting in non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 64, 4048–4059 (2012). 8. Shapira-Lichter, I., Vakil, E., Litinsky, I., Oren, N., Glikmann-Johnston, Y., Caspi, D., Hendler, T. & Paran, D. Learning and memory-related brain activity dynamics are altered in systemic lupus erythematosus: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Lupus 22, 562–573 (2013). 9. Hou, J., Lin, Y., Zhang, W., Song, L., Wu, W., Wang, J., Zhou, D., Zou, Q., Fang, Y., He, M. & Li, H. Abnormalities of frontal-parietal resting-state functional connectivity are related to disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS ONE 8, e74530 (2013). 10. DiFrancesco, M. W., Gitelman, D. R., Klein-Gitelman, M. S., Sagcal-Gironella, A. C., Zelko, F., Beebe, D., Parrish, T., Hummel, J., Ying, J. & Brunner, H. I. Functional neuronal network activity differs with cognitive dysfunction in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 15, R40 (2013).