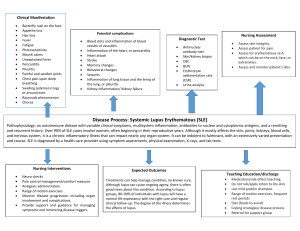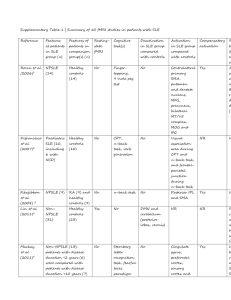
Systemic lupus erythematosus “Is it really lupus? Dreams have come true!” - House M. D. Disease Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic disease in which the immune system begins to perceive the cells of its own body as pathogens and attacks them. As a result, the work of internal organs is disrupted, the skin and the musculoskeletal system suffer. Medical history The doctor of the XIII century Rogerius believed that the facial injuries caused by the disease are similar to wolf bites, hence the name "lupus", which means "wolf" in Latin. Causes of lupus erythematosus Hereditary predisposition Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight. Occupational hazards. Smoking. Taking some medications. Stressful situations and excessive physical activity. Female gender. Symptoms Weakness, increased fatigue. Loss of body weight. Hyperthermia. Reduced performance. Headache, heaviness in the head. Main signs of SLE Pain. Joint deformity Myositis. "Lupus butterfly". Alopecia. Photosensitization. Treatment Glucocorticoids (GC) are first—line medication for SLE. Glucocorticoids are normally formed in the adrenal glands and prevent inflammatory processes. Synthetic forms in the form of tablets, skin cream or injections are used for treatment. Thanks for your attention!