Click Here To
advertisement
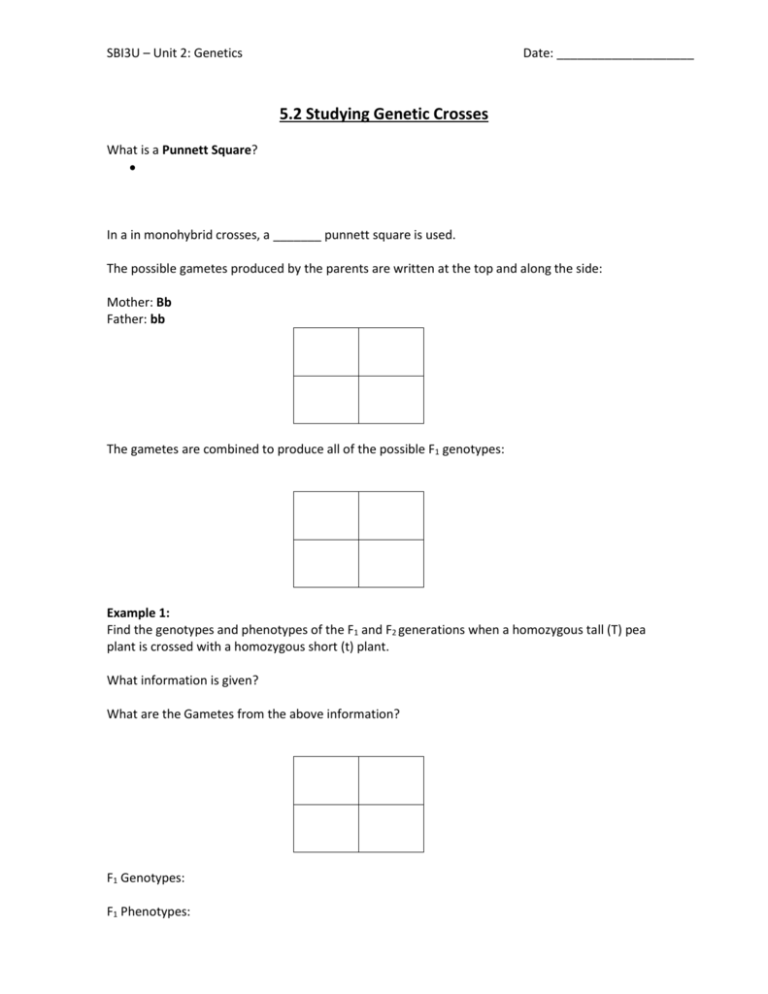
SBI3U – Unit 2: Genetics Date: ____________________ 5.2 Studying Genetic Crosses What is a Punnett Square? In a in monohybrid crosses, a _______ punnett square is used. The possible gametes produced by the parents are written at the top and along the side: Mother: Bb Father: bb The gametes are combined to produce all of the possible F1 genotypes: Example 1: Find the genotypes and phenotypes of the F1 and F2 generations when a homozygous tall (T) pea plant is crossed with a homozygous short (t) plant. What information is given? What are the Gametes from the above information? F1 Genotypes: F1 Phenotypes: SBI3U – Unit 2: Genetics Date: ____________________ Example 1 Continued….. To find the F2 generation, you cross the offspring produced in the F1 generation. Given: Gametes: F2 Genotypes: F2 Phenotypes: Homozygous Parents Cross: - in the case of a cross that involves parents that are homozygous for a particular trait. F1 will always have: • Genotypes that are ______________________________________ • Phenotypes that resemble the ______________________________________________ F2 will always have: • Genotypic ratio of ________________ (1 homozygous dominant: 2 heterozygous: 1 homozygous recessive) • Phenotypic ratio of ____________ (3 dominant 1 recessive) Test Cross Cross an unknown parent (BB or Bb) with a known parent (bb) Case #1 – unknown parent = BB • If all F1 show the dominant trait, then the unknown parent was BB SBI3U – Unit 2: Genetics Date: ____________________ Case #2 – unknown parent = Bb If even one F1 shows the recessive trait, then the unknown parent was Bb TO DO: Section 5.2 (Part 1) Practice Problems p. 212 #1-10 (practice problems) Learning Check p. 212 #7-12