Fossil Fuels ch 19 note guide
advertisement

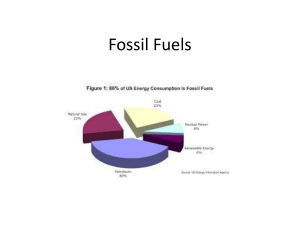
Fossil Fuels Chapter 19 – Note Guide 1. Energy Literacy 2. Energy Consumption A. Per Capita Energy Consumption Highly Developed nations represent ______________of the world’s population, but consume ___________ of commercial energy (energy sold in the market place) Each person uses _____-- as much energy as a person in a developing country B. Energy Requirement for Food Production Farmers in developing nations rely on ____________________________________ Farmers in developed countries require ___________________________________. C. Energy Consumption in the U.S. Industry ________, Buildings ______________. Transportation ______________ Most of the energy required in the North America is supplied by _____________. D. Fossil Fuels What are they? Grades of Coal Most abundant – known coal reserves could last for __________ Supplies ______________ of energy used worldwide Largest deposits found in E. Recovery Surface mining Subsurface mining Mountaintop removal F. How does a coal power facility create electricity? G. How does electricity get to homes and businesses? F. Safety Problems/Environmental Impact Mining dangerous Toxins Acid Mine drainage Climate change – global warming Acid Deposition (So2 and NOX) Coal Ash G. Solution o Surface Mining Control and Reclamation Act (1977) – o Scrubbers – Desulfurization systems installed to ___________________________ Sludge – Electrostatic Precipitators o Clean Coal Technologies o Fluidized-bed combustion o Coal gasification and liquefaction Oil and Natural Gas H. Refining o Crude oil – Fractionation tower o Petrochemicals – used in the production of fertilizers, plastics, paints, pesticides, medicines, and synthetic fibers o Natural Gas o Liquefied petroleum gas – Used as ______________________________ Examples: ____________________ and _________________ o Methane – Used for _________________, ________________________, and in the organic chemistry industry. Availability – supplies about ________________ of energy used worldwide. Oil o ________________ of the world’s known oil reserves are located in the _________. o Oil production is expected to ________________ sometime during the 21 st century and will then enter a decline. o Hubbert curve: Natural Gas o Almost half of the world’s known natural gas reserves are located in _________ and ________ o Reserves are more _______- than oil and could continue to rise even after oil production peaks. o Because it is a gas, it costs ______________ more to transport through pipelines and is therefore often not utilized. I. Recovery Geologic exploration searches for structural traps that may contain oil and natural gas deposits. Once oil or natural gas deposits have been located, wells are drilled and operated. J. Environmental Impact o Burning oil and natural gas emits _______________, contributing to _______________. o Burning oil releases ______________________, contributing to _______________ and the formation of photochemical _______________. o Transporting oil by _______________________________ carries the risk of a major spill. o Operating offshore oil wells contaminates water with relatively small amounts of oil, and also carries the risk of a major ____________________ o Oil exploration in environmentally sensitive areas poses permanent threats to ____________________ and _______________ in exchange for a very temporary supply of oil. K. Solutions o Natural gas is ____________________ and _________________ than oil. o _____________________- natural gas is used to produce both electricity and steam, providing electricity cleanly and efficiently (page 219) Synfuels – derivatives of _______________________. o _______________________ - underground sand deposits permeated with thick, asphalt-like oil called bitumen; once obtained, bitumen must be refined like crude oil. o ______________- rocks containing a mixture of hydrocarbons known as kerogen; rocks must be crushed and heated, then kerogen must be refined o ____________- reserves of ice-encrusted natural gas located deep underground in porous rock. o _______________- process of producing a liquid fuel out of coal, than can be cleaned before burning. o ________________ - production of methane gas from coal. L. An Energy Strategy for the U.S. o Reasons for a comprehensive energy policy o The supply of fossil fuels is _______________. o The production, transport, and use of fossil fuels __________________. o Our heavy dependence on foreign oil makes us ___________________ vulnerable. o Proposed Objectives: o Increase energy efficiency and conservation - ______________________ (support in the form of monetary payments, public financing, tax benefits, and tax exemptions) keep energy prices artificially low; when prices reflect the true costs of energy, including the environmental cost incurred in its production, transport, and use, energy will be used more efficiently by individuals, corporations, and industries. o Secure fossil fuel energy supplies - _________________ produced fossil fuels (especially natural gas) are a temporary strategy that will give us time to develop alternate energy strategies for the long term. o Develop alternative energy sources – a long-term goal to shift to ____________. o Accomplish the first three objectives without further damaging the environment – use _______________________ analysis when considering particular energy sources.