CHEMISTRY 110
advertisement

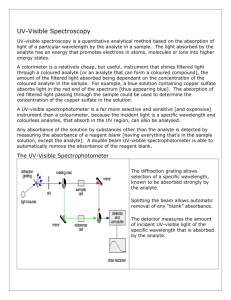
Chemistry 421/821 – First Exam Spring 2013 page 1 Name Answer Key 1) (15 points) You have just been hired as an analytical chemist working for a pharmaceutical company. Your first assignment involves a project to measure the concentration of a new drug (CPD-274) in plasma after patients have received a daily dose of 10 mg. You have a technician working for you. Please write a detailed step-by-step instruction explaining to your technician how to perform a calibration curve for CPD-274. Please include ALL important steps and relevant details. 1. Collect a full UV-vis spectrum to identify the wavelength at maximum absorption (max). a. Make sure to keep the highest observed absorbance at or below 1. b. If necessary, dilute the sample in half. 2. Prepare a blank sample just containing plasma. 3. Collect a full UV-vis spectrum of the plasma blank a. Make sure to keep the highest observed absorbance at or below 1. b. If necessary, dilute the sample in half. 4. If the plasma blank has a high absorbance at max, choose an alternate max where CPD274 has a high absorbance and plasma has a low absorbance 5. Determine the concentrations of CPD-274 in plasma that yields an absorbance of ~1 and 0.1 at max 6. Prepare ~10 standard samples of CPD-274 in plasma that are equally distributed between the minimum and maximal concentrations determined in part 3. 7. Measure the absorbance of the 10 CPD-274 standards versus the plasma blank. 8. Plot absorbance versus concentration 9. Determine the best-fit line. 2) (5 points) How can Black-body radiation be used to adjust the range of wavelengths produced by a tungsten lamp or similar light source? Blackbody radiation depends on temperature, so adjusting the temperature (amount of current flowing through the filament) will change the wavelengths of light produced by the light source. Chemistry 421/821 – First Exam Spring 2013 page 2 Name Answer Key 3) (8 points) Please identify the property of light that is employed by the specified monochromator or filter: a. (2 points) Prism refraction b. (2 points) Transmission Grating diffraction, constructive and deconstructive interference a. (2 points) Reflection Grating reflection, constructive and deconstructive interference b. (2 points) Interference filter reflection, constructive and deconstructive interference 4) (6 points) If an absorption filter with a bandwidth of 150 nm and a maximum transmission at 320 nm is used in a UV/vis spectrometer, what is the approximate range of wavelengths available for measuring an analytes absorption spectrum? 320 +/- 150 nm Bandwidth is peak-width (range of wavelengths) at half-height, so the majority of the wavelengths that reach the sample or detector is approximately twice the bandwidth 5) (6 points) Please answer the following questions related to the general operation of a UV-vis spectrometer: a. (3 points) Identify a potential source of systematic error in the calibration of a Spectronic 20. Incorrect setting of the occlude or V-shaped slot during the 0%T or 100%T calibration. In other words, letting some light instead of 0%T or not letting enough or too much light in for 100%T. Use of cylinder or soiled cuvette, path-length is not constant. Incorrect setting of b. (3 points) Why does the error associated with a photomultiplier tube increase with increasing percent transmission? Increasing %T means more light is hitting the detector that provides more energy and increases shot noise, random transfer of e- across the cathode/anode junction. Saturation of detector is also acceptable. Chemistry 421/821 – First Exam Spring 2013 page 3 Name Answer Key 6) (20 points) Given the following calibration curves and best-fit lines for analytes A, B, and C: 0.8 A: y =0.0987x + 4E-05 B: y = 0.0514x + 0.0011 C: y = 0.0263x + 0.0002 0.7 Absorbance 0.6 A 0.5 B 0.4 C 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 Concentration (uM) a. (4 points) Which analyte has the lowest sensitivity? Explain. C, smallest slope b. (4 points) What is the selectivity coefficient between analytes A and B? kc,a = mc/ma = 0.0514/0.0987 = 0.521 c. (4 points) Which analyte has the highest limit of detection? Explain. C, smallest slope: cm = (Sm-Sbl)/slope d. (4 points) Which analyte has the smallest dynamic range? Explain. A, smallest linear region of calibration curve e. (4 points) Estimate the absorbance for a mixture containing 4 M of analyte C, 6 M of analyte B, and 2 M of analyte A. AT = AA +AB +AC = 0.105 + 0.31 + 0.2 = 0.615 Chemistry 421/821 – First Exam Spring 2013 page 4 Name Answer Key 7) (12 points) Please identify one advantage and one disadvantage for each of the following detectors: a. (4 points) Photovoltaic Cell (Barrier-Layer Cell) Advantage: cheap, rugged, no external power source Disadvantage: not very sensitive, shows fatigue, difficult to amplify signal. b. (4 points) Photomultiplier Tube (PMT) Advantages: very sensitive, very fast response Disadvantages: need high voltage power supply, intense light damages c. (4 points) Silicon Diode or Photodiode detectors Advantages: spatial detector Disadvantages: not very sensitive 8) (10 points) You are designing a UV-vis spectrometer and are expecting the red region of the spectrum (650 nm) to have a 60o reflective angle given a 30o incident angle of the light source. What property/feature of an (a) echellete grating and (b) prisim monochromator would you need to achieve this goal? [hint: refractive index of air is 1.0003] (a) n = d(sin i + sin r) d=n (sin i + sin r) = (1)(650 nm)/(sin 30o + sin 60o) d= 475 nm/blaze (1/475 nm/blaze) x 106 nm/mm = 2105 blazes/mm therefore, need an echellete grating with 2105 blazes/mm (b) sinsin= sinsin=(1.0003) sin 30o/ sin 60o = 0.578 Therefore, need a prism with a refractive index of 0.578. Of course, a refractive index has to be > 1, so such a prism cannot exist. Chemistry 421/821 – First Exam Spring 2013 page 5 Name Answer Key 9) (12 points) Please answer the following general questions about fluorescence and phosphorescence: a. (4 points) What fundamental components are found in both instruments used to measure UV-vis and fluorescence? Light source, monochromator, detector, sample holder, mirrors, slits; basically the equipment is the same. b. (4 points) Why are molecular vibrations important to fluorescence? Fluorescence depends on the lifetime of the excited electronic state. Transitions between excited and ground electronic states can be facilitated by overlapping vibrational states. Thus, molecular vibrations provide an efficient relaxation pathway and the elimination of fluorescence. c. (2 points) A sketch a molecule that would be UV active, but not fluorescent. Fluorescent compounds tend to be rigid and aromatic, where a UV active compound only requires a double bond. So, any non-rigid compound with at least a double bond is acceptable. d. (2 points) Identify one approach to prevent quenching of fluorescence. Decrease temperature, increase viscosity, degas (remove oxygen) Chemistry 421/821 – First Exam Spring 2013 page 6 Name Answer Key 10) (6 points) The following calibration curve was based on the relative fluorescence of a compound (L) a complex (P:C). 6 M of this compound was added to 3 M of a protein and the observed fluorescence was 26. Please determine the KD for the compound bound to a protein (P) to form a complex (P:C). The ligand complex and the protein are not fluorescent. P:C KD P+L [Changes announced during the exam] The P:C concentration comes from the observed fluorescence and calibration curve. Thus, a fluorescence of 26 corresponds to a concentration of 2 M for P:C. Correspondingly, the concentration of the ligand and peptide is simply their original concentration reduced by the P:C concentration. Therefore: [L] = 6 M – 2 M = 4 M [P] = 3 M – 2 M = 1 M KD [ compound ][ P ] [P :C ] [ 4 M ][ 1 M ] 2 M [ 2 M ]