Atmospheric Winds: Trade Winds, Jet Streams, Land & Sea Breezes
advertisement

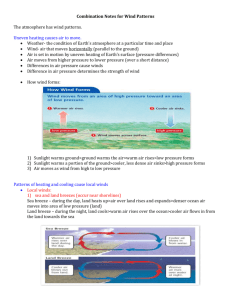
1)What are trade winds, easterlies, and westerlies? What is the latitude for each of them. Include a diagram 2)What are jet streams? What speeds do they travel? Where are they the fastest? How far above the surface are they? 3)What are land and sea breezes? Use a diagram. 1) Trade winds are winds that blow from east to west between 0 and 30 degrees latitude. Easterlies are winds that blow from east to west between 60 and 90 degrees latitude, storms occur when easterlies and westerlies meet. Westerlies are winds that blow from west to east from 30 to 60 degrees latitude. 2) Jet streams are a type of wind in the upper atmosphere that blow from west to east for thousands of kilometers, they separate warm and cool air. Jet streams can go up to 200 mph. The larger the temperature difference the faster the jet stream will go. These winds occur 6-9 miles above earth. 3) Land and Sea breezes occur near shorelines. The land heats up faster during the day, you have high pressure over the water blowing toward the land. The land cools down faster during 4)How are land and sea breezes different at night? 5)What causes monsoons? How are the monsoons in the summer different than the monsoons in the winter? night, so you have high pressure over the land going toward the sea. 4) During the day the high pressure is over the water. During the night high pressure is over the land. 5) Monsoons are caused by the changing of the winds’ direction. The winter monsoons occur when the land is cooler. The summer monsoons occur when the land is warmer. Monsoons last for a much longer period than land and sea breezes. Sea and land breezes switch daily, monsoons switch seasonally.