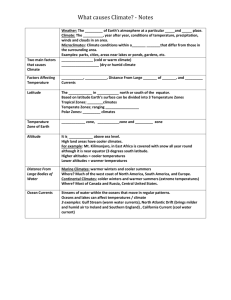
Notes- Cimate and Vegetation
advertisement

Climate Vegetation East Asia’s Climates Japan has similar extreme climates like the United States. Much of East Asia has a variety of climates. East Asia’s Climate Regions Eastern China has a humid subtropical climate – hot summers and cool winters with plenty of rain. To the north is an area where the summers are warm and winters are cold. South Korea and Japan are almost completely surrounded by water, summers are a bit cooler and winters are a bit warmer than in other places at the same latitude. The northern interior of China is very dry, here temperatures can range from very hot to very cold. To the south, the Plateau of Tibet has a cool, dry, highland climate. Storms in Asia Monsoons strongly affect the climates of East Asia. Monsoons are winds that blow across the region at certain times of the year Summer Monsoons Winter Monsoons the winds blow towards the east. * Pacific Ocean winds blow west toward The ones that begin in the interior the Asia continent of northern Asia are icy cold and Rain starts in June as a drizzle.(plum very dry rain) In parts of China , winds can The winds cause hot , humid rain in produce dust storms that can July sometimes last for days. Where they cross warm ocean waters, such as the South China Sea these monsoons pick up moisture an later drop it as rain or snow. Typhoons are violent storms. They develop over the Pacific Ocean. They can blow at a speed of 75 mph or more, which can cause major damage. Typhoons in eastern Asia are very similar to the hurricanes that sometimes strike the southern coastline of the United States during August and September. The Influences of Climate Climate influences many things in East Asia. It affects what people grow, how often they can plant, and how easily they can harvest their fields. Vegetation In eastern Asia much of the plant life, such as bamboo, which grows unbelievably fast during the wet season, is strong enough to tolerate seasonal differences in temperature and rainfall. Shrubs and many small flowering plants in the deserts of China spring up rapidly after summer rains and then disappears when dry weather returns. Deciduous trees are leaf-shedding trees that change with the weather and are found on the hillsides of Korea and Japan. The Life of the People Life in East Asia is greatly affected by climate. The region around the Huang He, or Yellow River, is a good example. The river is named for the brownish yellow loess that gets blown around by the desert winds and then picked up by the river and deposited to the east on the North China Plain. This plain is one of the best farming areas in China. The Huang He also floods. To get around that fact, a system of dams helps control the waters; but the river still floods over the banks because of monsoons, which has given it the name “China’s Sorrow”. It is considered both a blessing and a curse to farmers living near it.